Abstract
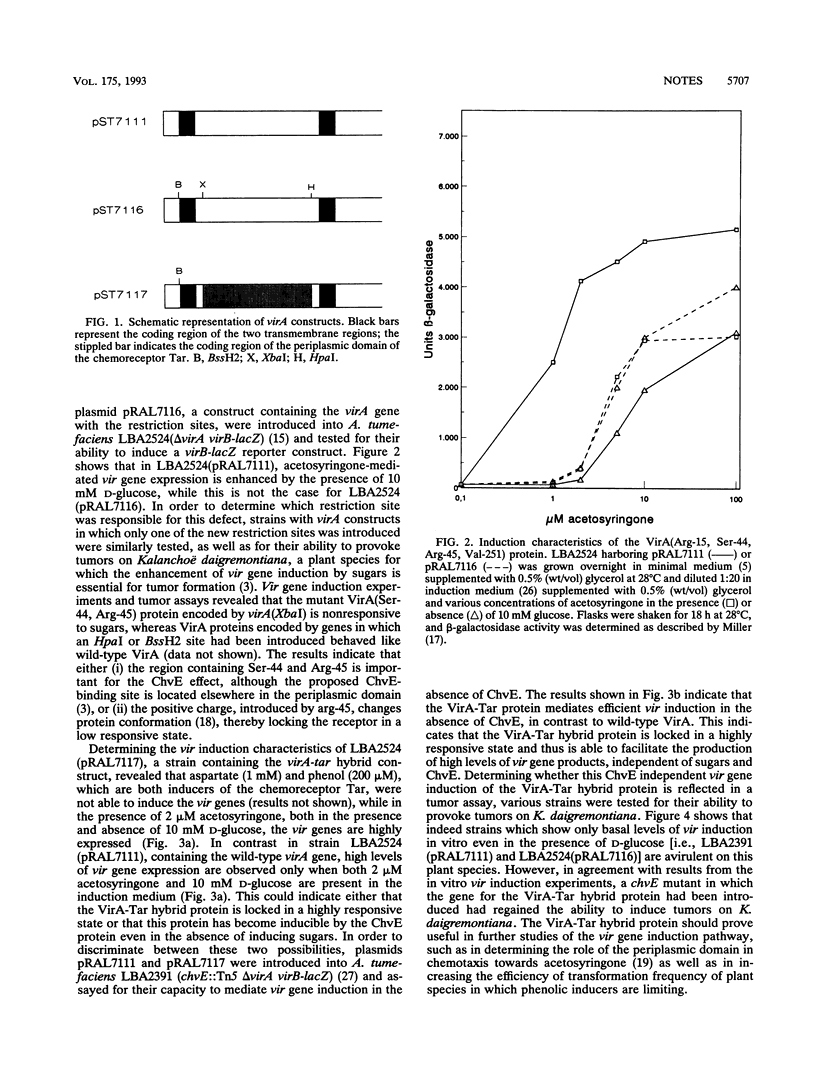
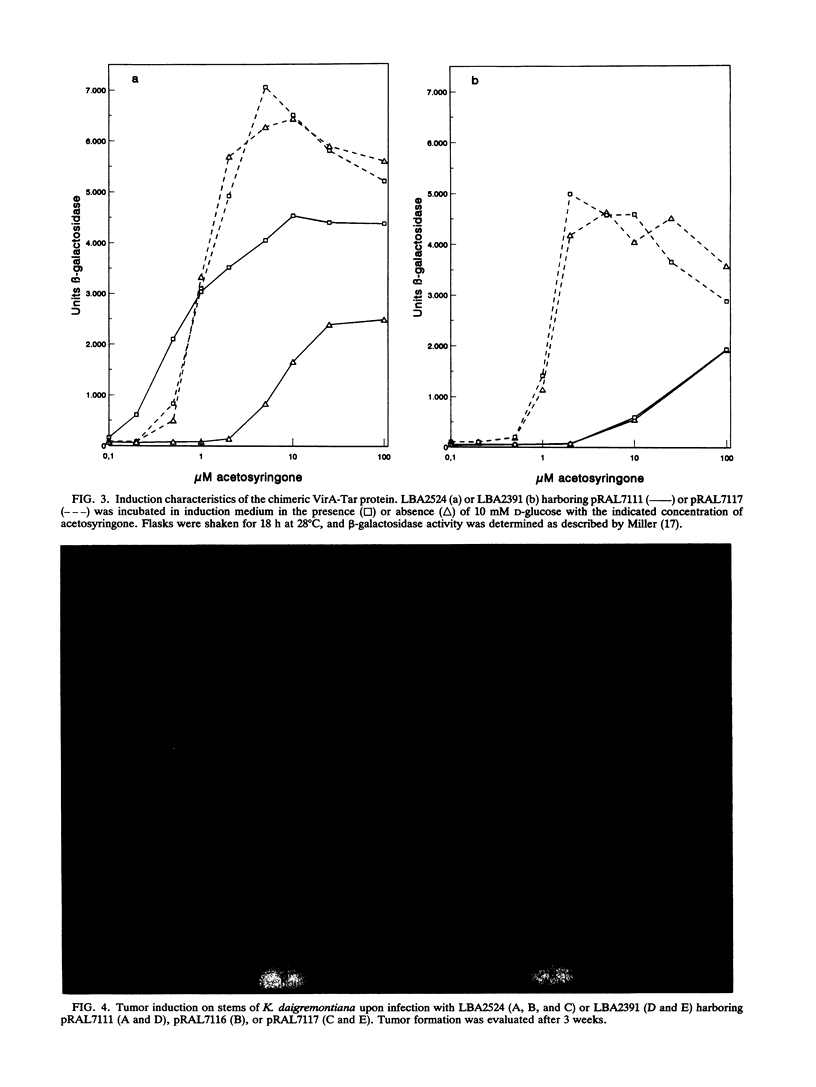
The wild-type VirA protein is known to be responsive not only to phenolic compounds but also to sugars via the ChvE protein (G. A. Cangelosi, R. G. Ankenbauer, and E. W. Nester, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:6708-6712, 1990, and N. Shimoda, A. Toyoda-Yamamoto, J. Nagamine, S. Usami, M. Katayama, Y. Sakagami, and Y. Machida, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:6684-6688, 1990). It is shown here that the mutant VirA(Ser-44, Arg-45) protein and the chimeric VirA-Tar protein are no longer responsive to sugars and the ChvE protein. However, whereas the chimeric VirA-Tar protein was found to be locked in a highly responsive state, the VirA(Ser-44, Arg-45) mutant protein appeared to be locked in a low responsive state. This difference turned out to be important for tumorigenicity of the host strains in virulence assays on Kalanchoë daigremontiana.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama T., Takanami M., Oka A. Signal structure for transcriptional activation in the upstream regions of virulence genes on the hairy-root-inducing plasmid A4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8711–8725. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Sugars induce the Agrobacterium virulence genes through a periplasmic binding protein and a transmembrane signal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6708–6712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardina P., Conway C., Kossman M., Manson M. Aspartate and maltose-binding protein interact with adjacent sites in the Tar chemotactic signal transducer of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1528–1536. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1528-1536.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., Schilperoort R. A. Agrobacterium and plant genetic engineering. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):15–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00015604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y., Morel P., Powell B., Kado C. I. VirA, a coregulator of Ti-specified virulence genes, is phosphorylated in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1142–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1142-1144.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imae Y., Oosawa K., Mizuno T., Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Phenol: a complex chemoeffector in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):371–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.371-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Roitsch T., Christie P. J., Nester E. W. The regulatory VirG protein specifically binds to a cis-acting regulatory sequence involved in transcriptional activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):531–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.531-537.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The VirA protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is autophosphorylated and is essential for vir gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.525-530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K., Dudley M. W., Hess K. M., Lynn D. G., Joerger R. D., Binns A. N. Mechanism of activation of Agrobacterium virulence genes: identification of phenol-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8666–8670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattanovich D., Rüker F., Machado A. C., Laimer M., Regner F., Steinkellner H., Himmler G., Katinger H. Efficient transformation of Agrobacterium spp. by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6747–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers L. S., Regensburg-Tuïnk T. J., Bourret R. B., Sedee N. J., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Membrane topology and functional analysis of the sensory protein VirA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1919–1925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I., von Heijne G. Fine-tuning the topology of a polytopic membrane protein: role of positively and negatively charged amino acids. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1135–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90390-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazour G. J., Das A. Characterization of the VirG binding site of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6909–6913. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Conserved domains in bacterial regulatory proteins that respond to environmental stimuli. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):579–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. H., Ashby A. M., Brown A., Royal C., Loake G. J., Shaw C. H. virA and virG are the Ti-plasmid functions required for chemotaxis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens towards acetosyringone. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):413–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda N., Toyoda-Yamamoto A., Nagamine J., Usami S., Katayama M., Sakagami Y., Machida Y. Control of expression of Agrobacterium vir genes by synergistic actions of phenolic signal molecules and monosaccharides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6684–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. virA and virG control the plant-induced activation of the T-DNA transfer process of A. tumefaciens. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M. Signal transduction in bacteria. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):395–400. doi: 10.1038/344395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk S. C., Nester E. W., Hooykaas P. J. The virA promoter is a host-range determinant in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):719–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Kerstetter R. A., Ward J. E., Nester E. W. A protein required for transcriptional regulation of Agrobacterium virulence genes spans the cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1616–1622. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1616-1622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C. Two-way chemical signaling in Agrobacterium-plant interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):12–31. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.12-31.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



