Abstract
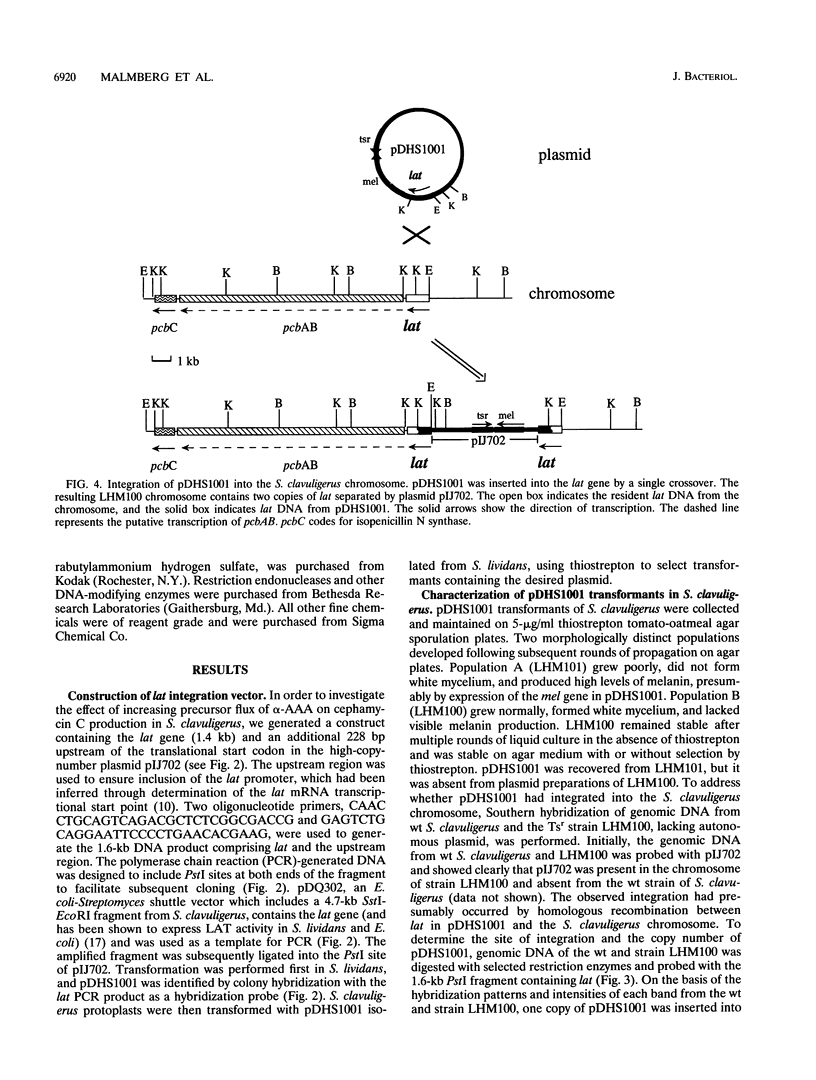
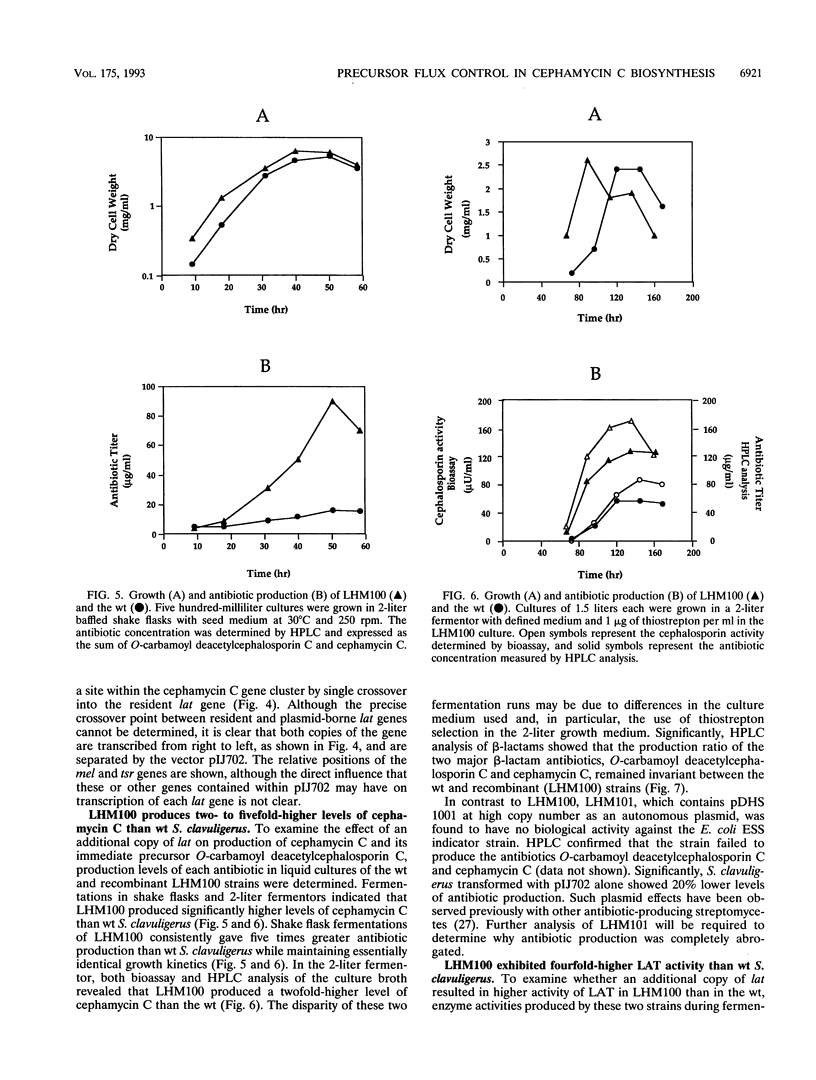
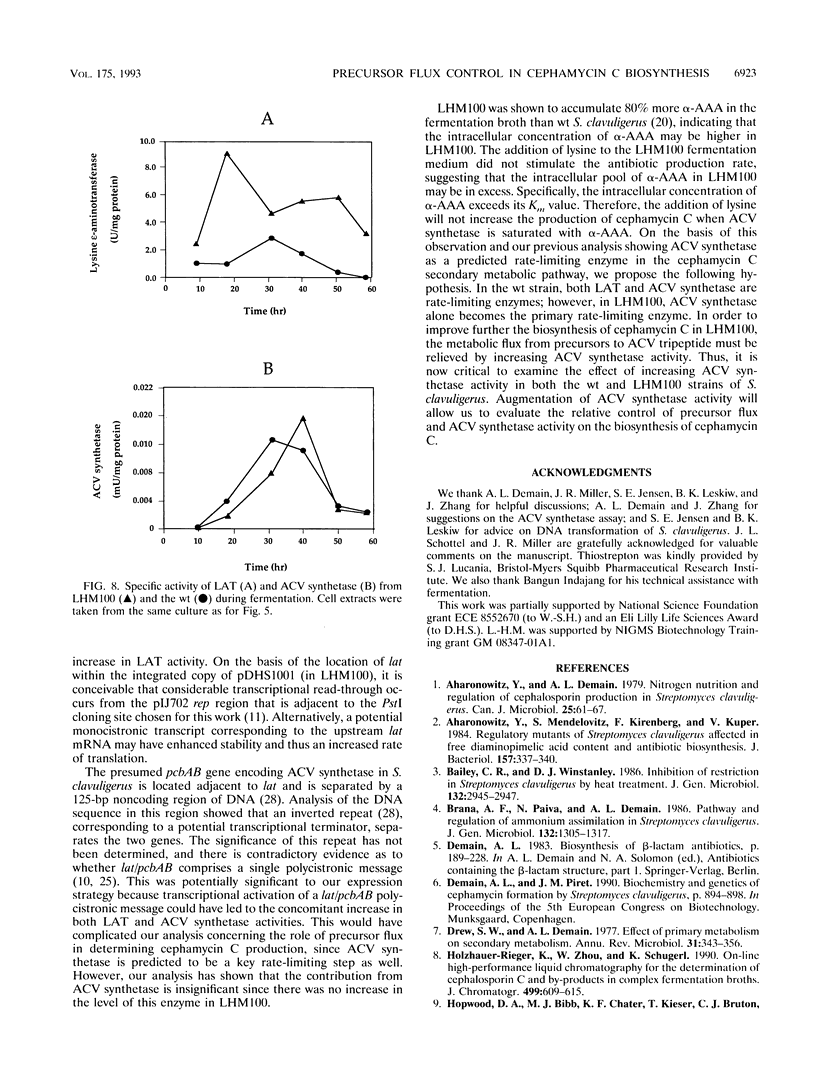
Targeted gene insertion methodology was used to study the effect of perturbing alpha-aminoadipic acid precursor flux on the overall production rate of beta-lactam biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. A high-copy-number plasmid containing the lysine epsilon-aminotransferase gene (lat) was constructed and used to transform S. clavuligerus. The resulting recombinant strain (LHM100) contained an additional complete copy of lat located adjacent to the corresponding wild-type gene in the chromosome. Biological activity and production levels of beta-lactam antibiotics were two to five times greater than in wild-type S. clavuligerus. Although levels of lysine epsilon-aminotransferase were elevated fourfold in LHM100, the level of ACV synthetase, whose gene is located just downstream of lat, remained unchanged. These data strongly support the notion that direct perturbation of alpha-aminoadipic acid precursor flux resulted in increased antibiotic production. This strategy represents a successful application of metabolic engineering based on theoretical predictions of precursor flux in a secondary metabolic pathway.
Full text
PDF
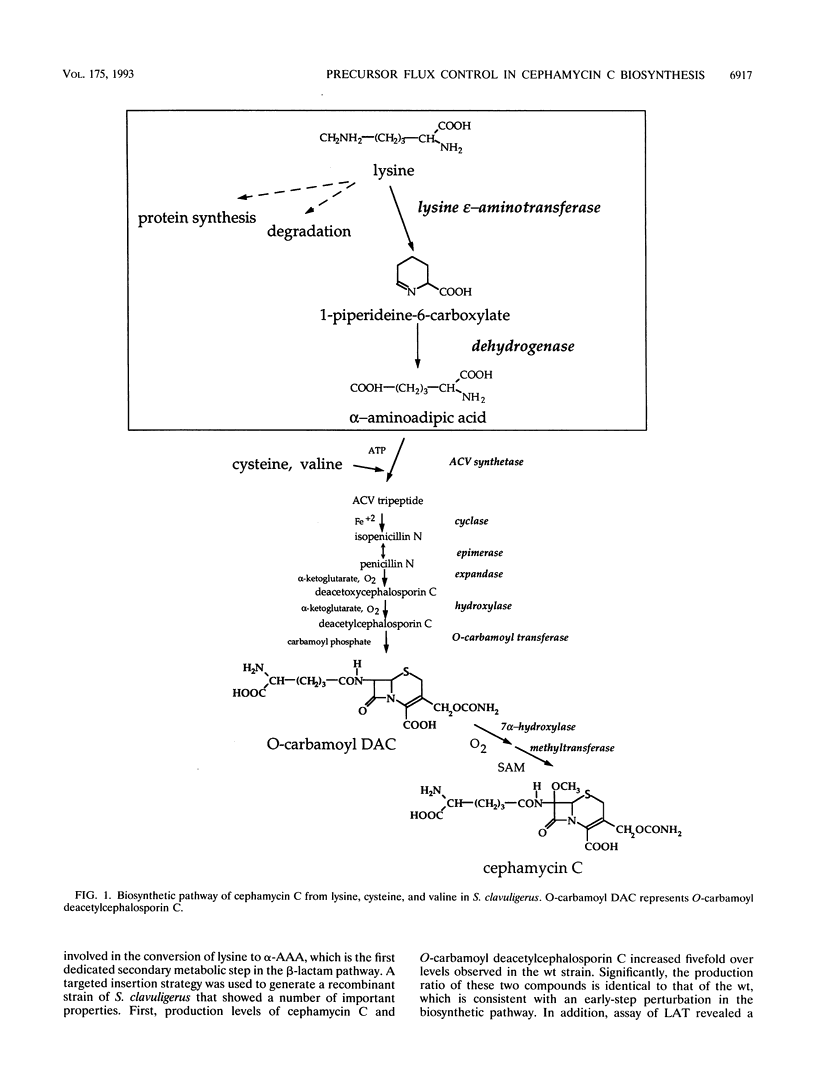

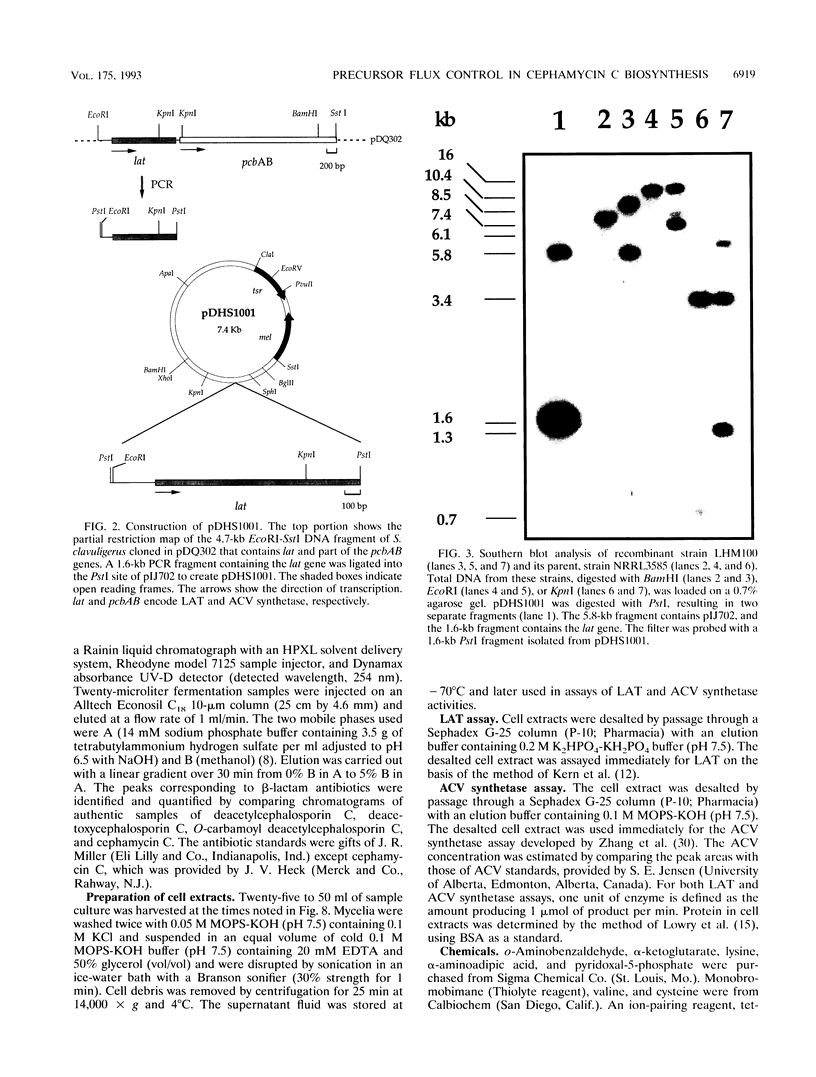


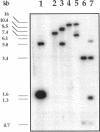
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonowitz Y., Demain A. L. Nitrogen nutrition and regulation of cephalosporin production in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):61–67. doi: 10.1139/m79-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharonowitz Y., Mendelovitz S., Kirenberg F., Kuper V. Regulatory mutants of Streptomyces clavuligerus affected in free diaminopimelic acid content and antibiotic biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):337–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.337-340.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. R., Winstanley D. J. Inhibition of restriction in Streptomyces clavuligerus by heat treatment. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Oct;132(10):2945–2947. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-10-2945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew S. W., Demain A. L. Effect of primary metabolites on secondary metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:343–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzhauer-Rieger K., Zhou W., Schügerl K. On-line high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of cephalosporin C and by-products in complex fermentation broths. J Chromatogr. 1990 Jan 19;499:609–615. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhang J., Wolfe S., Demain A. L. Phosphate regulation of ACV synthetase and cephalosporin biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K. J., Cohen S. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 and correlation of the sequence with genetic properties. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4634–4651. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4634-4651.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern B. A., Hendlin D., Inamine E. L-lysine epsilon-aminotransferase involved in cephamycin C synthesis in Streptomyces lactamdurans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):679–685. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick J. R., Doolin L. E., Godfrey O. W. Lysine biosynthesis in Streptomyces lipmanii: implications in antibiotic biosynthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Nov;4(5):542–550. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.5.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskiw B. K., Aharonowitz Y., Mevarech M., Wolfe S., Vining L. C., Westlake D. W., Jensen S. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Gene. 1988;62(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luengo J. M., Revilla G., López M. J., Villanueva J. R., Martín J. F. Inhibition and repression of homocitrate synthase by lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):869–876. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.869-876.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madduri K., Stuttard C., Vining L. C. Cloning and location of a gene governing lysine epsilon-aminotransferase, an enzyme initiating beta-lactam biosynthesis in Streptomyces spp. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):985–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.985-988.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg L. H., Hu W. S. Identification of rate-limiting steps in cephalosporin C biosynthesis in Cephalosporium acremonium: a theoretical analysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Oct;38(1):122–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00169431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg L. H., Sherman D. H., Hu W. S. Analysis of rate-limiting reactions in cephalosporin biosynthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Oct 13;665:16–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb42570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masurekar P. S., Demain A. L. Lysine control of penicillin biosynthesis. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):1045–1048. doi: 10.1139/m72-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelovitz S., Aharonowitz Y. Regulation of cephamycin C synthesis, aspartokinase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthetase, and homoserine dehydrogenase by aspartic acid family amino acids in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):74–84. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelovitz S., Aharonowitz Y. beta-lactam antibiotic production by Streptomyces clavuligerus mutants impaired in regulation of aspartokinase. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2063–2069. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piret J., Resendiz B., Mahro B., Zhang J. Y., Serpe E., Romero J., Connors N., Demain A. L. Characterization and complementation of a cephalosporin-deficient mutant of Streptomyces clavuligerus NRRL 3585. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990 Feb;32(5):560–567. doi: 10.1007/BF00173728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. I., Cove J. H., Baumberg S., Jones C. A., Rudd B. A. Plasmid effects on secondary metabolite production by a streptomycete synthesizing an anthelmintic macrolide. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2331–2337. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin M. B., Kovacevic S., Madduri K., Hoskins J. A., Skatrud P. L., Vining L. C., Stuttard C., Miller J. R. Localization of the lysine epsilon-aminotransferase (lat) and delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase (pcbAB) genes from Streptomyces clavuligerus and production of lysine epsilon-aminotransferase activity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6223–6229. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6223-6229.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbarger H. E. Amino acid biosynthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:532–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]