Abstract
We present sequences of the glnB gene of Escherichia coli and of two open reading frames (ORFs) located directly upstream of glnB and transcribed in the same direction. The major transcriptional start sites for glnB are located between ORF-2 and glnB, but some transcription of glnB is initiated at the promoter for ORF-1. The putative amino acid sequence of the ORF-2 product has high homology to that of response regulators which by phosphorylation acquire the ability to activate transcription of sigma 54-dependent promoters. The product of ORF-1 showed no similarity to other known proteins. The product of neither ORF-1 nor ORF-2 is necessary for the ability of PII, the product of glnB, to bring about the repression of glutamine synthetase in response to nitrogen excess. On the other hand, the product of hmpA, a gene located on the other side of glnB and transcribed in the opposite direction, appears to play an auxiliary role in this process.
Full text
PDF

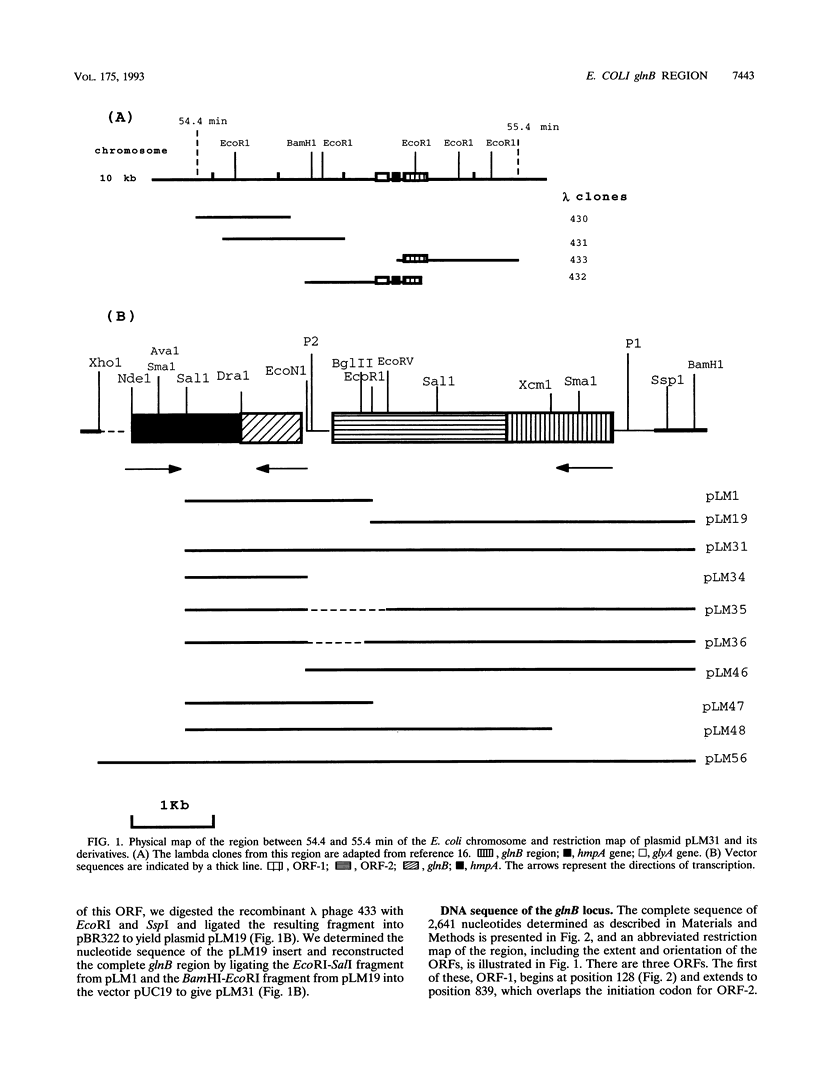

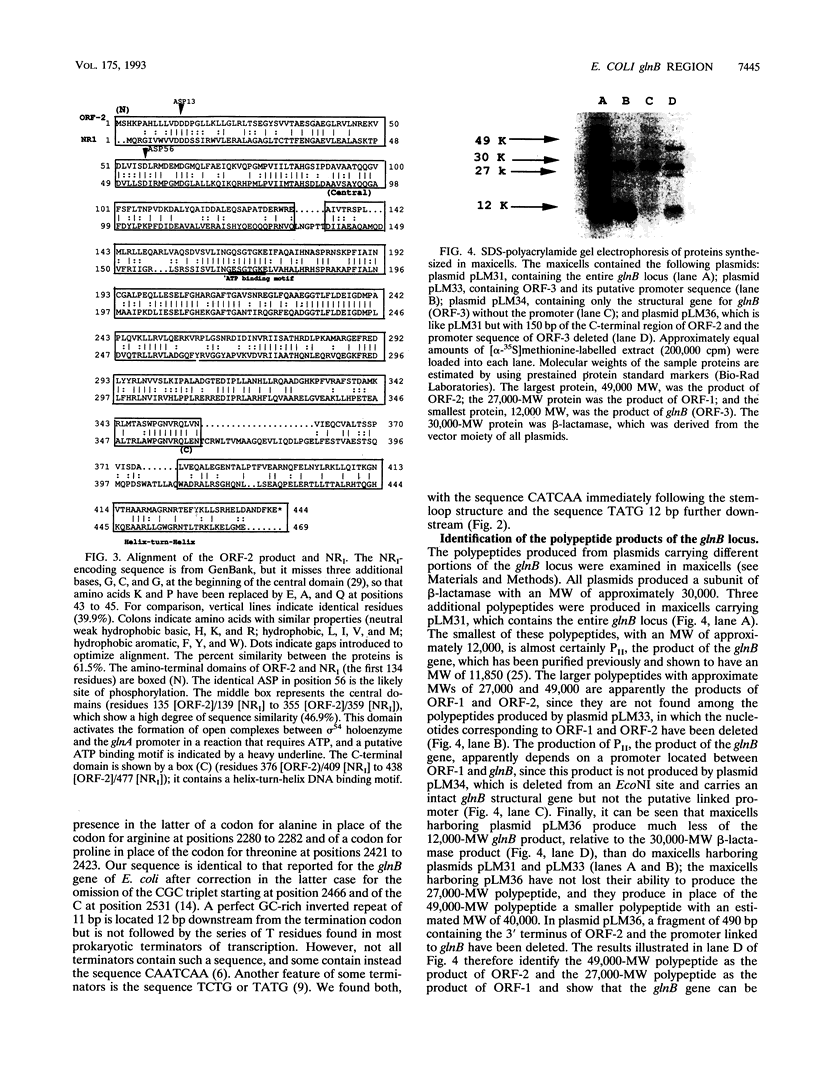



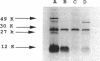
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S. P., Purich D., Stadtman E. R. Cascade control of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Properties of the PII regulatory protein and the uridylyltransferase-uridylyl-removing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6264–6272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Transcription and DNA sequence of the BamHI L fragment of B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1083–1090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. R., Levin M. S., Foor F., Tyler B. Regulation of glutamine synthetase formation in Escherichia coli: characterization of mutants lacking the uridylyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):569–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.569-577.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Trifonov E. N. A computer algorithm for testing potential prokaryotic terminators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4411–4427. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno R., Pahel G., Magasanik B. Role of glnB and glnD gene products in regulation of the glnALG operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.816-822.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Backman K., Magasanik B. Characterization of a gene, glnL, the product of which is involved in the regulation of nitrogen utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):214–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.214-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides J., Magasanik B., Gralla J. D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):371–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.371-394.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He B., Choi K. Y., Zalkin H. Regulation of Escherichia coli glnB, prsA, and speA by the purine repressor. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3598–3606. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3598-3606.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtel A., Merrick M. Identification of the Klebsiella pneumoniae glnB gene: nucleotide sequence of wild-type and mutant alleles. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):134–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00331314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener J., Kustu S. Protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase activities of nitrogen regulatory proteins NTRB and NTRC of enteric bacteria: roles of the conserved amino-terminal domain of NTRC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Reversible phosphorylation of an enhancer binding protein regulates the transcription of bacterial nitrogen utilization genes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Dec;13(12):475–479. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann M. D., Stauffer G. V. Characterization of the Escherichia coli gene for serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Phosphorylation site of NtrC, a protein phosphatase whose covalent intermediate activates transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5117–5122. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5117-5122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Son H. S., Rhee S. G. Cascade control of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase. Purification and properties of PII protein and nucleotide sequence of its structural gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8690–8695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer G. V., Plamann M. D., Stauffer L. T. Construction and expression of hybrid plasmids containing the Escherichia coli glyA genes. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weglenski P., Ninfa A. J., Ueno-Nishio S., Magasanik B. Mutations in the glnG gene of Escherichia coli that result in increased activity of nitrogen regulator I. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4479–4485. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4479-4485.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Batut J., Klose K. E., Keener J., Kustu S. The phosphorylated form of the enhancer-binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity that is essential for activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90579-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Scholl R., Browse J., Somerville C. Double stranded DNA sequencing as a choice for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1220–1220. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]