Abstract
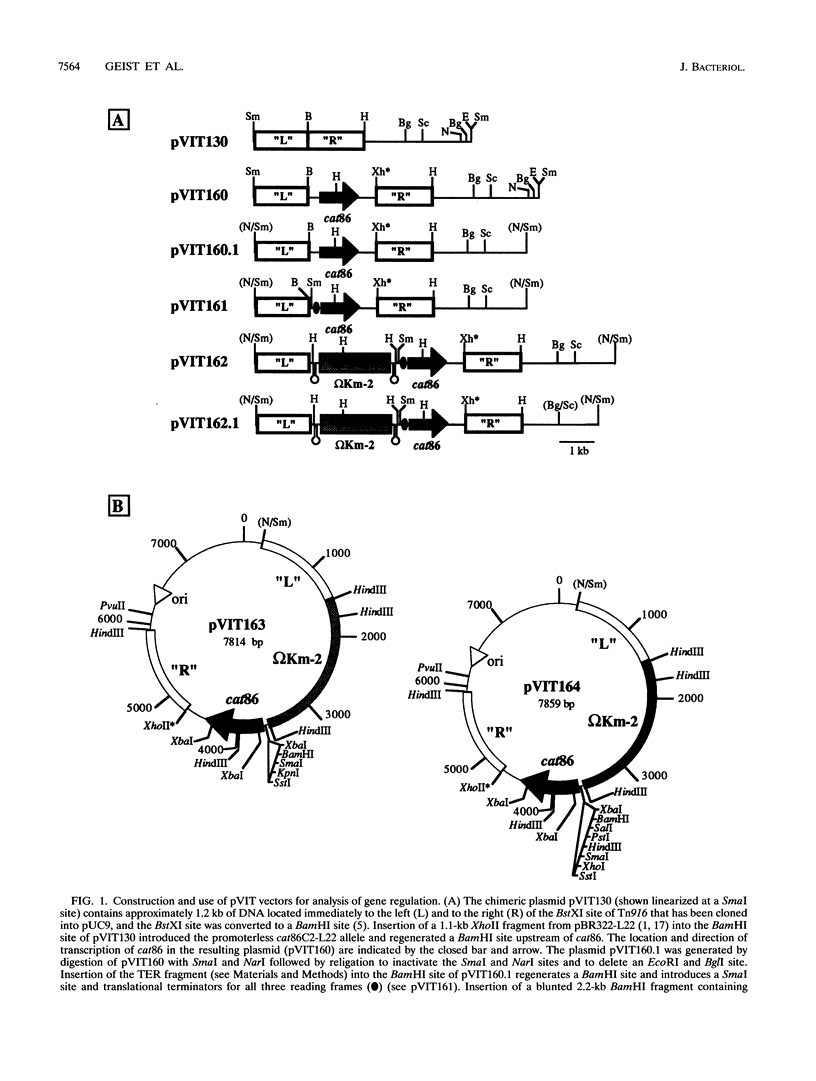
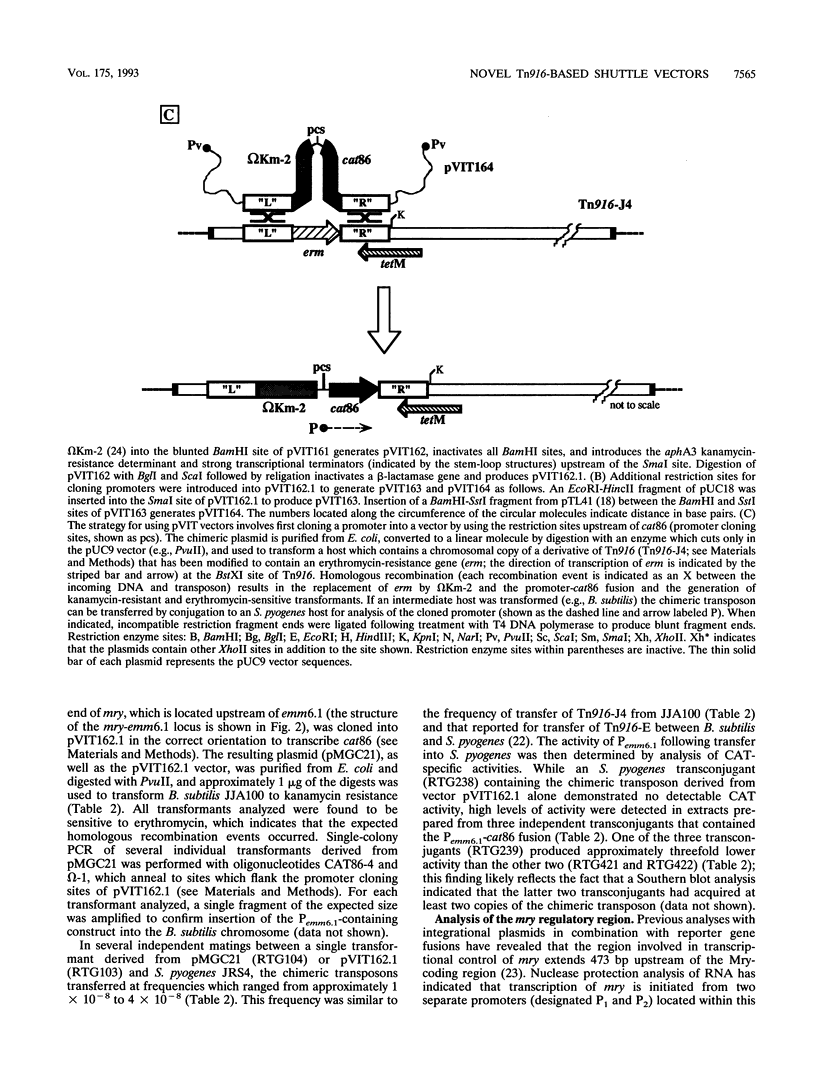
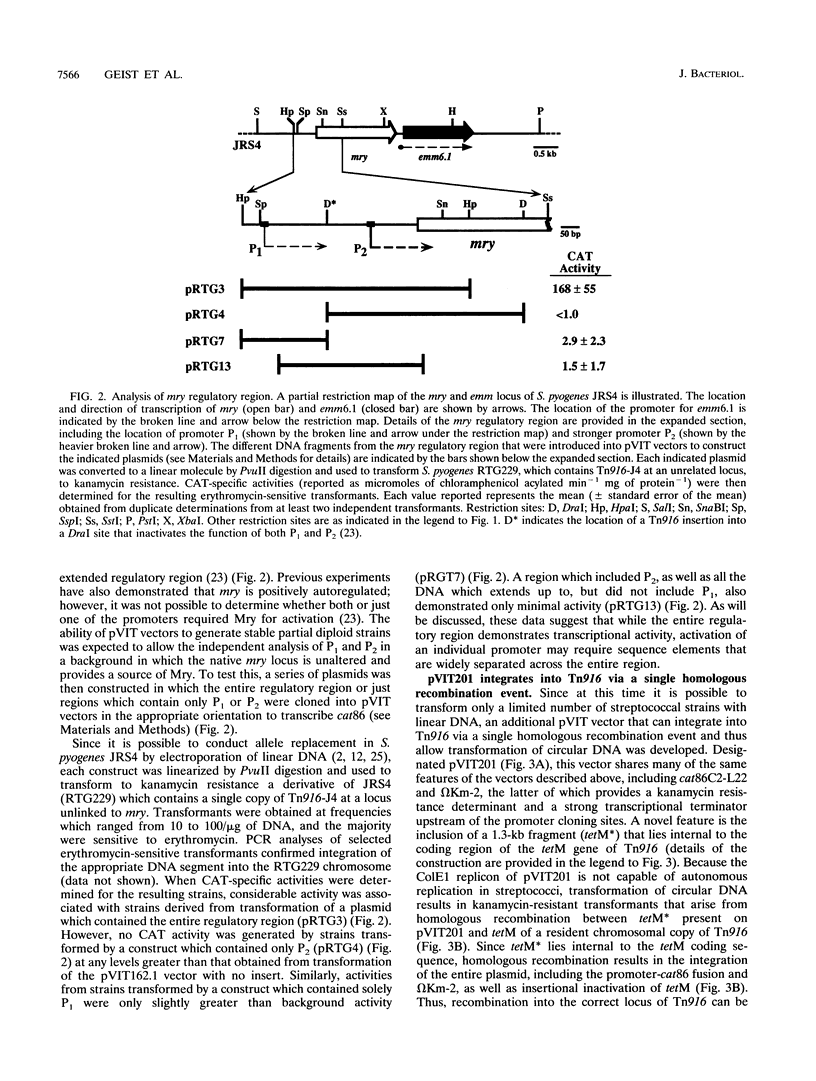
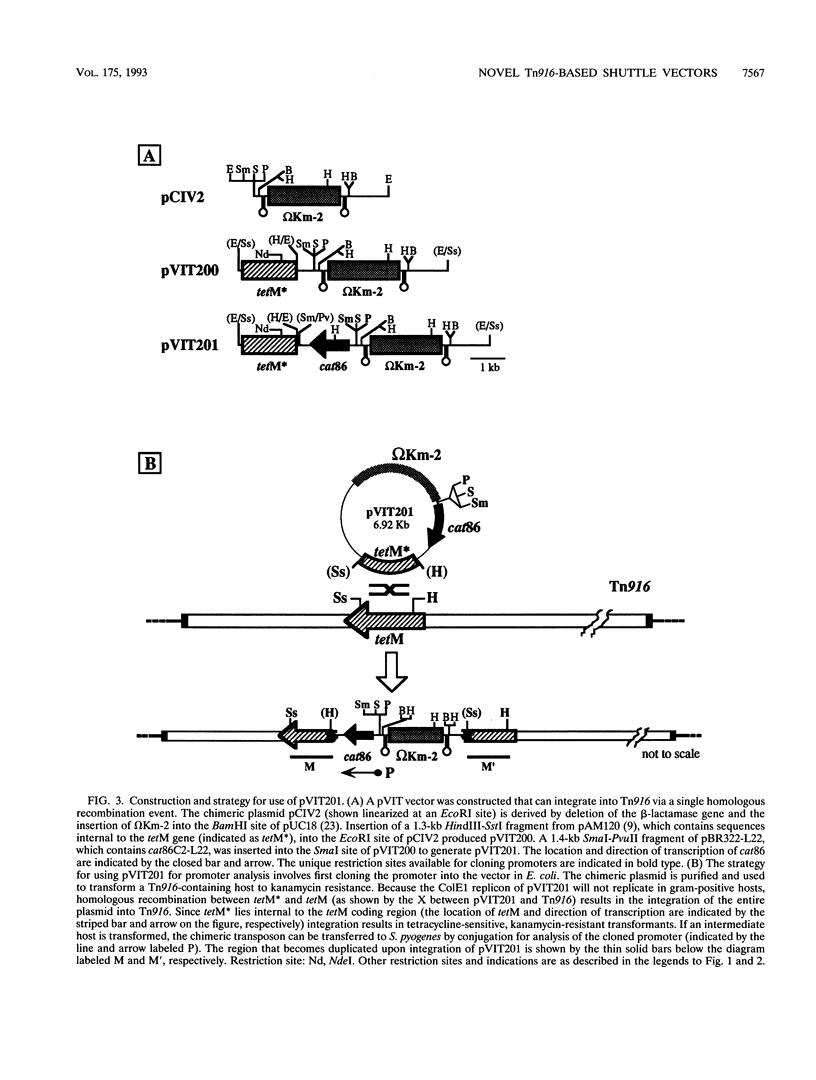
We have developed a series of shuttle vectors based on the conjugative transposon Tn916 that have been designed for the analysis of transcriptional regulation in Streptococcus pyogenes and other gram-positive bacteria. Designated the pVIT vectors (vectors for integration into Tn916), the vectors are small, stable plasmids in Escherichia coli to facilitate the fusion of promoters from cloned S. pyogenes genes to a promoterless gene which encodes chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. The vectors each contain one or more small regions of Tn916 to direct the integration of the transcriptional fusion into the transposon via homologous recombination following transformation of S. pyogenes or other suitable gram-positive hosts. Integration can be monitored by the inactivation or replacement of an antibiotic resistance determinant in modified derivatives of Tn916. Promoter activity can then be quantitated by the determination of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase-specific activity. In addition, since integration is into loci that do not disrupt the conjugative transpositional functions of Tn916, the vectors are useful for analysis of regulation in strains that are difficult or impossible to transform and can be introduced into these strains by conjugation following transformation of an intermediate host. The promoters for the genes which encode both the M protein and protein F of S. pyogenes were active in pVIT vectors, as was the region which controls transcription of mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of M protein expression. However, neither of the two characterized promoters for mry demonstrated activity when independently analyzed in pVIT-generated partial diploid strains, suggesting that regulation of mry is more complex than predicted by current models. The broad host range of Tn916 should make the pVIT vectors useful for analysis of regulation in numerous other bacterial species.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Smith T., Mulbry W., Lovett P. S. CUG as a mutant start codon for cat-86 and xylE in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90478-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Geist R. T., Perez-Casal J., Scott J. R. Environmental regulation of virulence in group A streptococci: transcription of the gene encoding M protein is stimulated by carbon dioxide. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5693–5701. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5693-5701.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Excision and insertion of the conjugative transposon Tn916 involves a novel recombination mechanism. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1027–1034. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90759-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Genetic manipulation of pathogenic streptococci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:556–586. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04028-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Identification of a gene that regulates expression of M protein, the major virulence determinant of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8677–8681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Gawron-Burke C. Conjugative transposons and the dissemination of antibiotic resistance in streptococci. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:635–659. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Brown B. L., Clewell D. B. Induced cell aggregation and mating in Streptococcus faecalis: evidence for a bacterial sex pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. Regeneration of insertionally inactivated streptococcal DNA fragments after excision of transposon Tn916 in Escherichia coli: strategy for targeting and cloning of genes from gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):214–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.214-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Caparon M. Protein F, a fibronectin-binding protein, is an adhesin of the group A streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan B. R., Blakesley R. W., Berg D. E. Linear amplification DNA sequencing directly from single phage plaques and bacterial colonies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1153–1153. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laredo J., Wolff V. L., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase specified by cat-86: relationship between the gene and the protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T., St Pierre R. Improved vector system for constructing transcriptional fusions that ensures independent translation of lacZ. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1077–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1077-1084.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Tobian J. A., Jones K. R., Evans R. P., Clewell D. B. A cloning vector able to replicate in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus sanguis. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews K. S. DNA looping. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):123–136. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.123-136.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. A method for allelic replacement that uses the conjugative transposon Tn916: deletion of the emm6.1 allele in Streptococcus pyogenes JRS4. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3846–3850. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3846-3850.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren M., Scott J. R. The presence of conjugative transposon Tn916 in the recipient strain does not impede transfer of a second copy of the element. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):319–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.319-324.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Geist R. T., Caparon M. G. Positive transcriptional control of mry regulates virulence in the group A streptococcus. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):893–903. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Introduction of the emm6 gene into an emm-deleted strain of Streptococcus pyogenes restores its ability to resist phagocytosis. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of the M protein gene of Streptococcus pyogenes with similarity to the receptor proteins of two-component regulatory systems. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2617–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2617-2624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Price J. A., Maguin E., Scott J. R. An M protein with a single C repeat prevents phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes: use of a temperature-sensitive shuttle vector to deliver homologous sequences to the chromosome of S. pyogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):809–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podbielski A., Peterson J. A., Cleary P. Surface protein-CAT reporter fusions demonstrate differential gene expression in the vir regulon of Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2253–2265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzi G., Musmanno R. A., Renzoni E. A., Oggioni M. R., Cusi M. G. Host-vector system for integration of recombinant DNA into chromosomes of transformable and nontransformable streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1969–1972. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1969-1972.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Guenthner P. C., Malone L. M., Fischetti V. A. Conversion of an M- group A streptococcus to M+ by transfer of a plasmid containing an M6 gene. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1641–1651. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R. Sex and the single circle: conjugative transposition. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6005–6010. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6005-6010.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senghas E., Jones J. M., Yamamoto M., Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. Genetic organization of the bacterial conjugative transposon Tn916. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):245–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.245-249.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Ferretti J. J. Electrotransformation of Streptococcus pyogenes with plasmid and linear DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Aug 1;66(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu-Cuot P., Carlier C., Poyart-Salmeron C., Courvalin P. An integrative vector exploiting the transposition properties of Tn1545 for insertional mutagenesis and cloning of genes from gram-positive bacteria. Gene. 1991 Sep 30;106(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90561-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G., Moscoso M., Espinosa M. Rolling circle-replicating plasmids from gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria: a wall falls. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):789–796. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


