Abstract
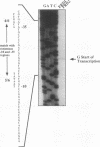
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a strict aerobe which is likely exposed to oxygen reduction products including superoxide and hydrogen peroxide during the metabolism of molecular oxygen. To counterbalance the potentially hazardous effects of elevated endogenous levels of superoxide, most aerobic organisms possess one or more superoxide dismutases or compounds capable of scavenging superoxide. We have previously shown that P. aeruginosa possesses both an iron- and a manganese-cofactored superoxide dismutase (D. J. Hassett, L. Charniga, K. A. Bean, D. E. Ohman, and M. S. Cohen, Infect. Immun. 60:328-336, 1992). In this study, the genes encoding manganese (sodA)- and iron (sodB)- cofactored superoxide dismutase were cloned by using a cosmid library of P. aeruginosa FRD which complemented an Escherichia coli (JI132) strain devoid of superoxide dismutase activity. The sodA and sodB genes of P. aeruginosa, when cloned into a high-copy-number vector (pKS-), partially restored the aerobic growth rate defect, characteristic of the Sod- strain, to that of the wild type (AB1157) when grown in Luria broth. The nucleotide sequences of sodA and sodB have open reading frames of 612 and 579 bp that encode dimeric proteins of 22.9 and 21.2 kDa, respectively. These data were also supported by the results of in vitro expression studies. The deduced amino acid sequence of the P. aeruginosa manganese and iron superoxide dismutase revealed approximately 50 and 67% similarity with manganese and iron superoxide dismutases from E. coli, respectively. There was also remarkable similarity with iron and manganese superoxide dismutases from other phyla. The mRNA start site of sodB was mapped to 174 bp upstream of the ATG codon. A likely promoter with similarity to the -10 and -35 consensus sequence of E. coli was observed upstream of the ATG start codon of sodB. Regions sequenced 519 bp upstream of the sodA electrophoresis, sodA gene revealed no such promoter, suggesting an alternative mode of control for sodA. By transverse field electrophoresis, sodA and sodB were mapped to the 71- to 75-min region on the P. aeruginosa PAO1 chromosome. Strikingly, mucoid alginate-producing bacteria generated greater levels of manganese superoxide dismutase than nonmucoid revertants, suggesting that mucoid P. aeruginosa is responding to oxidative stress and/or changes in the redox status of the cell.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer W., Imlay J., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:221–253. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60843-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlioz A., Touati D. Isolation of superoxide dismutase mutants in Escherichia coli: is superoxide dismutase necessary for aerobic life? EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis C. E., Ohman D. E. Cloning of Pseudomonas aeruginosa algG, which controls alginate structure. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2894–2900. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2894-2900.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare D. A., Duong M. N., Darr D., Archibald F., Fridovich I. Effects of molecular oxygen on detection of superoxide radical with nitroblue tetrazolium and on activity stains for catalase. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):532–537. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene algD coding for GDPmannose dehydrogenase is transcriptionally activated in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.351-358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Ohman D. E. Use of a gene replacement cosmid vector for cloning alginate conversion genes from mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains: algS controls expression of algT. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3228–3236. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3228-3236.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. R., Fridovich I. Superoxide sensitivity of the Escherichia coli aconitase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19328–19333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. A global response induced in Escherichia coli by redox-cycling agents overlaps with that induced by peroxide stress. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3933–3939. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3933-3939.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Intracellular production of superoxide radical and of hydrogen peroxide by redox active compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Sep;196(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Mechanism of the antibiotic action pyocyanine. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):156–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.156-163.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Moody C. S. Regulation of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. Anaerobic induction by nitrate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17173–17177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Sun H. C. Regulatory roles of Fnr, Fur, and Arc in expression of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3217–3221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett D. J., Charniga L., Bean K., Ohman D. E., Cohen M. S. Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to pyocyanin: mechanisms of resistance, antioxidant defenses, and demonstration of a manganese-cofactored superoxide dismutase. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):328–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.328-336.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett D. J., Cohen M. S. Bacterial adaptation to oxidative stress: implications for pathogenesis and interaction with phagocytic cells. FASEB J. 1989 Dec;3(14):2574–2582. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.14.2556311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg D. P., Bass J. A., Mattingly S. J. Aeration selects for mucoid phenotype of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):986–990. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.986-990.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. F., Mashino T., Fridovich I. alpha, beta-Dihydroxyisovalerate dehydratase. A superoxide-sensitive enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4724–4727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liochev S. I., Fridovich I. Effects of overproduction of superoxide dismutase on the toxicity of paraquat toward Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8747–8750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. S., Hassan H. M. Anaerobic biosynthesis of the manganese-containing superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12821–12825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa Hassan H., Fridovich I. Regulation of superoxide dismutase synthesis in Escherichia coli: glucose effect. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):505–510. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.505-510.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig D. O., Imlay K., Touati D., Hallewell R. A. Human copper-zinc superoxide dismutase complements superoxide dismutase-deficient Escherichia coli mutants. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14697–14701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederhoffer E. C., Naranjo C. M., Bradley K. L., Fee J. A. Control of Escherichia coli superoxide dismutase (sodA and sodB) genes by the ferric uptake regulation (fur) locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1930–1938. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1930-1938.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalle C. T., Fridovich I. Induction of superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli by heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2723–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalle C. T., Fridovich I. Inductions of superoxide dismutases in Escherichia coli under anaerobic conditions. Accumulation of an inactive form of the manganese enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4274–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Touati D. Cloning of the iron superoxide dismutase gene (sodB) in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):418–420. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.418-420.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Meshnick S. R., Eaton J. W. Superoxide dismutase-rich bacteria. Paradoxical increase in oxidant toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3640–3645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortridge V. D., Pato M. L., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Physical mapping of virulence-associated genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by transverse alternating-field electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3596–3603. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3596-3603.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. A., Smith S. E., Dean R. T. Scavenging by alginate of free radicals released by macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;6(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(89)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smidsrod O., Haug A. Dependence upon the gel-sol state of the ion-exchange properties of alginates. Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(5):2063–2074. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P. Host defenses in patients with cystic fibrosis: modulation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1985;4(1):14–33. doi: 10.1159/000156962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman H. M. Bacteriocuprein superoxide dismutases in pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1255–1260. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1255-1260.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Gatzy J. T., Boucher R. C. Oxygen consumption and ouabain binding sites in cystic fibrosis nasal epithelium. Pediatr Res. 1986 Dec;20(12):1316–1320. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198612000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry J. M., Piña S. E., Mattingly S. J. Role of energy metabolism in conversion of nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the mucoid phenotype. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1329–1335. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1329-1335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase biosynthesis in Escherichia coli, studied with operon and protein fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2511–2520. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2511-2520.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Iglewski B. H. Codon usage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9323–9335. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak D. J., Ohman D. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgB, a two-component response regulator of the NtrC family, is required for algD transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1406–1413. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1406-1413.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]