Abstract
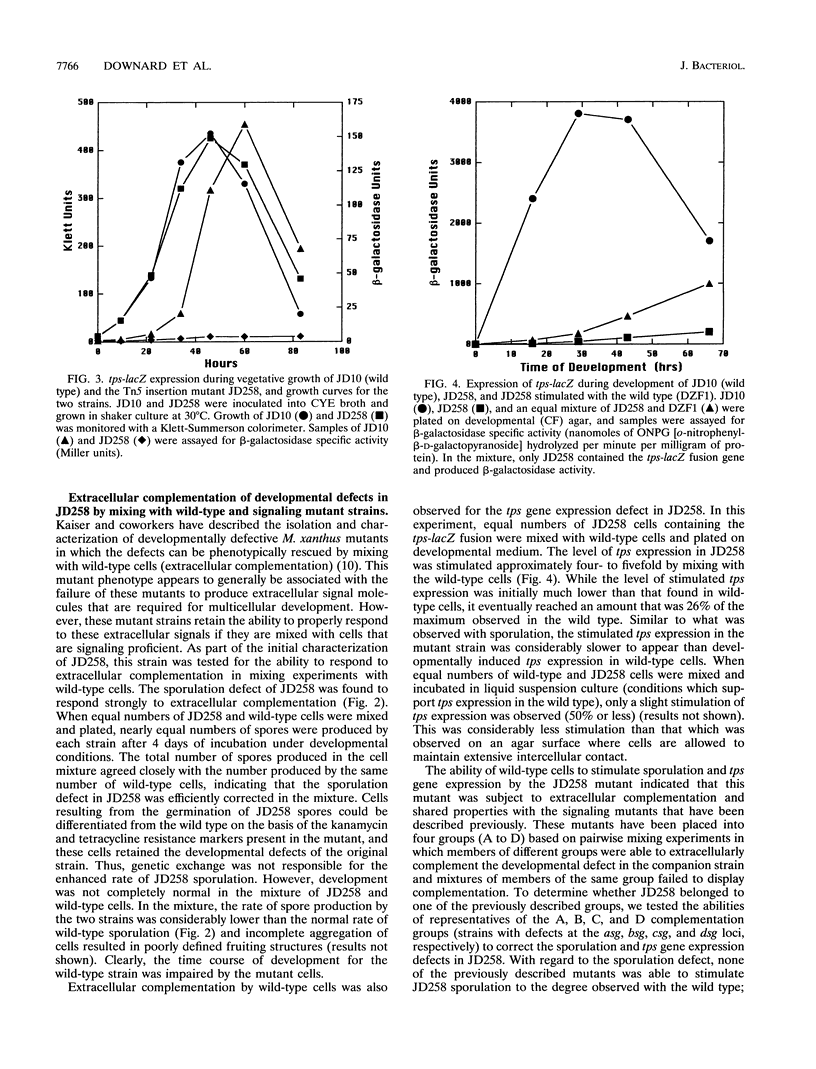
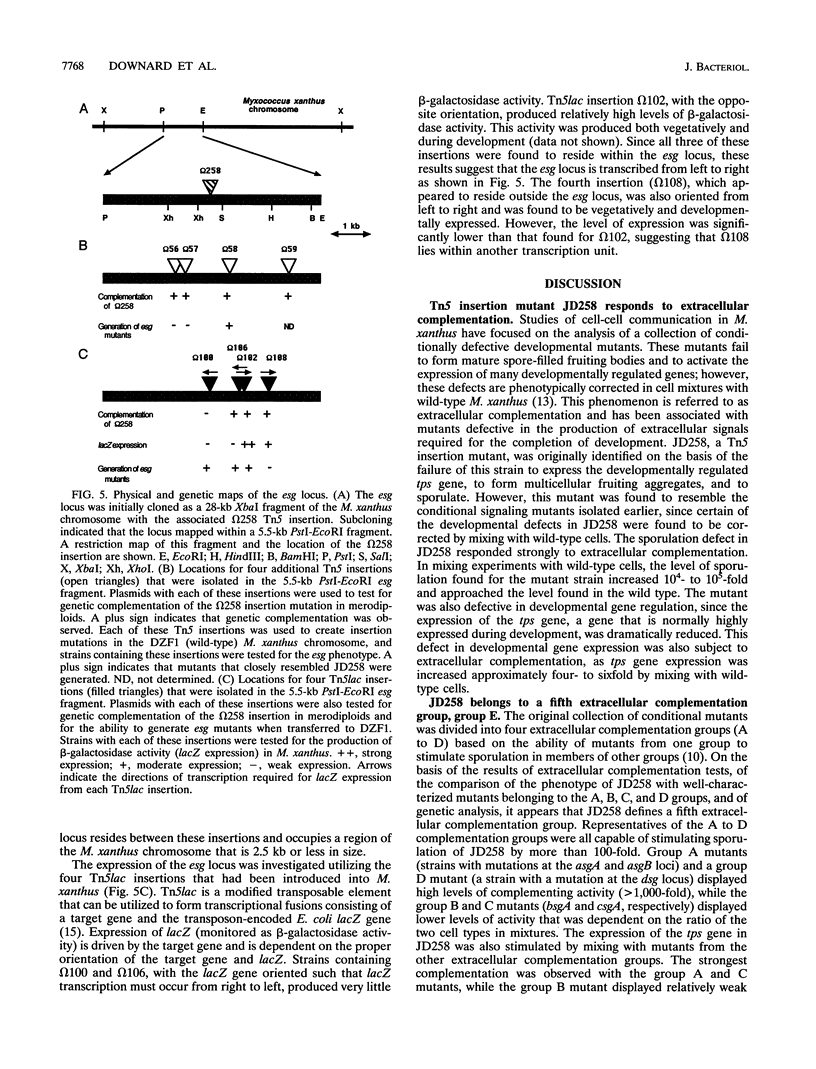
JD258, a Tn5 insertion mutant of Myxococcus xanthus, was shown to have major defects in three development-associated properties: expression of the developmentally regulated tps gene, spore formation, and production of multicellular fruiting bodies. The defects in tps gene expression and sporulation could be substantially corrected, at the phenotypic level, by mixing JD258 with wild-type cells (extracellular complementation). By this criterion, JD258 appeared to be a new member of a group of conditional developmental mutants that were previously characterized and placed in four extracellular complementation groups (A to D) based on the ability of mutants in one group to stimulate development in mutants belonging to a different group (D. C. Hagen, A. P. Bretscher, and D. Kaiser, Dev. Biol. 64:284-296, 1978). Mutants from groups A, B, C, and D all displayed extracellular complementation activity when mixed with JD258. These results, and other aspects of the phenotype of JD258, indicate that this mutant defines a fifth extracellular complementation group, group E. The M. xanthus esg locus identified by the Tn5 insertion in JD258 was cloned in Escherichia coli and used for further genetic analysis of the locus. These studies indicated that the esg locus resides within a 2.5-kb region of the M. xanthus chromosome and that the locus contains at least two genetic complementation groups. Our results are consistent with a model in which the esg locus controls the production of a previously unrecognized extracellular signal that must be transmitted between cells for the completion of M. xanthus development.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avery L., Kaiser D. In situ transposon replacement and isolation of a spontaneous tandem genetic duplication. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):99–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00330896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Kaiser D. dsg, a gene required for Myxococcus development, is necessary for cell viability. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3727–3731. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3727-3731.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Kaiser D. dsg, a gene required for cell-cell interaction early in Myxococcus development. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3719–3726. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3719-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S. Identification of the RNA products of the ops gene of Myxococcus xanthus and mapping of ops and tps RNAs. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1522–1528. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1522-1528.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Kupfer D., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus. Analysis of the genes for protein S. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):469–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Zusman D. R. Differential expression of protein S genes during Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1146–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1146-1155.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. E., Cull M. G. Control of developmental gene expression by cell-to-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. E., Cull M. G., Fly S. Genetic identification and cloning of a gene required for developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5279–5288. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5279-5288.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D. C-factor: a cell-cell signaling protein required for fruiting body morphogenesis of M. xanthus. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90211-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Kaiser D., Kuspa A. Control of cell density and pattern by intercellular signaling in Myxococcus development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:117–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Furuichi T., Teintze M., Inouye M., Inouye S. Effects of deletion of the gene for the development-specific protein S on differentiation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1195–1197. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1195-1197.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Introduction of transposon Tn5 into Myxococcus for analysis of developmental and other nonselectable mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):425–429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Genes required for developmental signalling in Myxococcus xanthus: three asg loci. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2762-2772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Plamann L., Kaiser D. A-signalling and the cell density requirement for Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7360–7369. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7360-7369.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Plamann L., Kaiser D. Identification of heat-stable A-factor from Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3319–3326. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3319-3326.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. A., Kaiser D. asgB, a gene required early for developmental signalling, aggregation, and sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):409–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00332403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zusman D. R. Transport and localization of protein S, a spore coat protein, during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):547–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.547-553.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Coliphage P1-mediated transduction of cloned DNA from Escherichia coli to Myxococcus xanthus: use for complementation and recombinational analyses. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):317–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.317-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Proteins that rescue A-signal-defective mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3311–3318. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3311-3318.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Asher S. J. Use of recombination techniques to examine the structure of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00338394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Gill R. E., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus and the spoC locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Rafiee H. CsgA, an extracellular protein essential for Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5299–5306. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5299-5306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



