Abstract
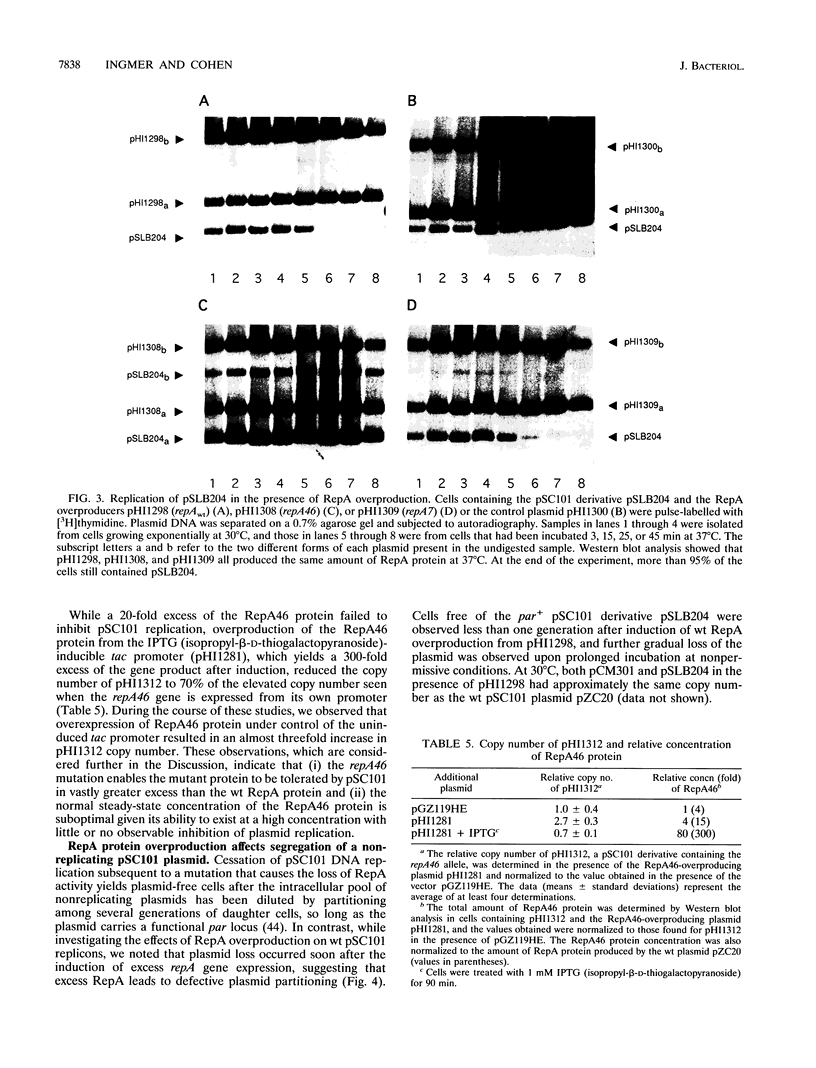
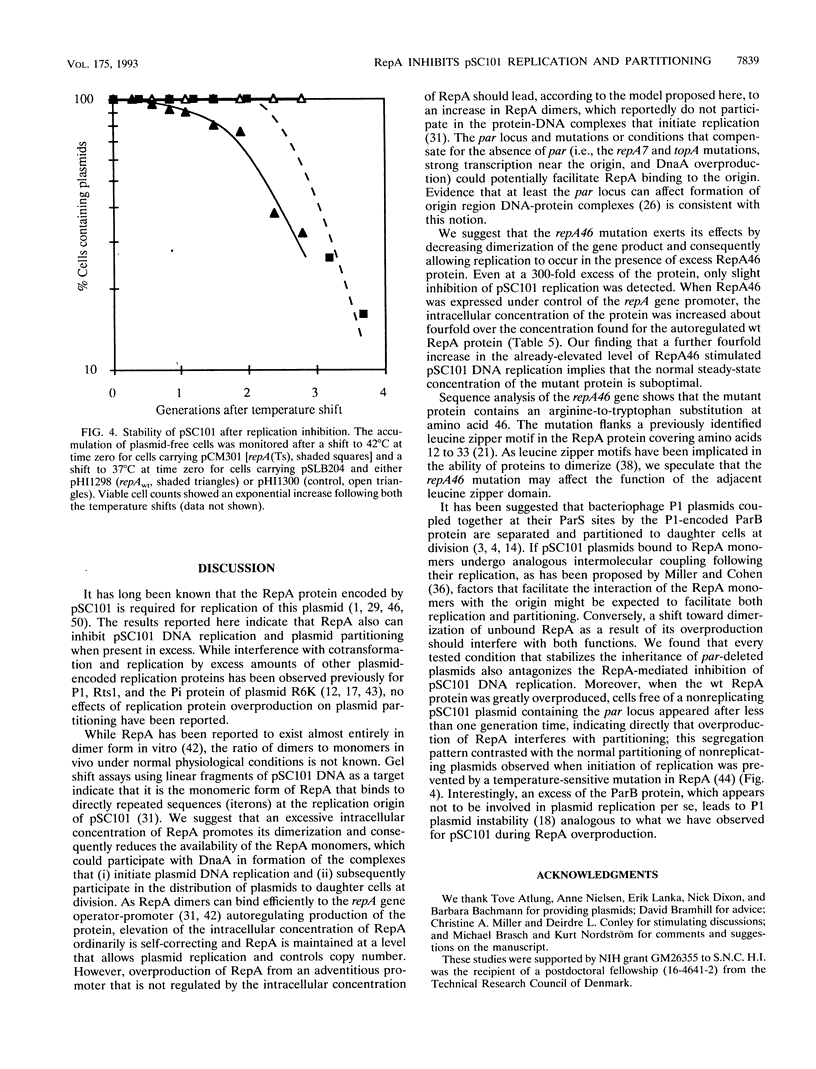
RepA, a plasmid-encoded gene product required for pSC101 replication in Escherichia coli, is shown here to inhibit the replication of pSC101 in vivo when overproduced 4- to 20-fold in trans. Unlike plasmids whose replication is prevented by mutations in the repA gene, plasmids prevented from replicating by overproduction of the RepA protein were lost rapidly from the cell population instead of being partitioned evenly between daughter cells. Removal of the partition (par) locus increased the inhibitory effect of excess RepA on replication, while host and plasmid mutations that compensate for the absence of par, or overproduction of the E. coli DnaA protein, diminished it. A repA mutation (repA46) that elevates pSC101 copy number almost entirely eliminated the inhibitory effect of RepA at high concentration and stimulated replication when the protein was moderately overproduced. As the RepA protein can exist in both monomer and dimer forms, we suggest that overproduction promotes RepA dimerization, reducing the formation of replication initiation complexes that require the RepA monomer and DnaA; we propose that the repA46 mutation alters the ability of the mutant protein to dimerize. Our discovery that an elevated intracellular concentration of RepA specifically impedes plasmid partitioning implies that the RepA-containing complexes initiating pSC101 DNA replication participate also in the distribution of plasmids at cell division.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong K. A., Acosta R., Ledner E., Machida Y., Pancotto M., McCormick M., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. A 37 X 10(3) molecular weight plasmid-encoded protein is required for replication and copy number control in the plasmid pSC101 and its temperature-sensitive derivative pHS1. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):331–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlung T., Clausen E. S., Hansen F. G. Autoregulation of the dnaA gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):442–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00425729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S. J. Plasmid partition. Plasmid. 1988 Jul;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Nordström K. Partition-mediated incompatibility of bacterial plasmids. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90584-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaucage S. L., Miller C. A., Cohen S. N. Gyrase-dependent stabilization of pSC101 plasmid inheritance by transcriptionally active promoters. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2583–2588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Cohen S. N. Involvement of integration host factor (IHF) in maintenance of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli: characterization of pSC101 mutants that replicate in the absence of IHF. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2056–2065. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2056-2065.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Cohen S. N. Involvement of integration host factor (IHF) in maintenance of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli: mutations in the topA gene allow pSC101 replication in the absence of IHF. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2066–2074. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2066-2074.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Cohen S. N. Propagation of pSC101 plasmids defective in binding of integration host factor. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):785–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.785-792.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Snyder K. M., Abeles A. L. P1 plasmid replication: multiple functions of RepA protein at the origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Austin S. J. Recognition of the P1 plasmid centromere analog involves binding of the ParB protein and is modified by a specific host factor. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1881–1888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubendorff J. W., Studier F. W. Controlling basal expression in an inducible T7 expression system by blocking the target T7 promoter with lac repressor. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):45–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90856-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely S., Wright A. Maintenance of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli requires the host primase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):484–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.484-486.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filutowicz M., McEachern M. J., Helinski D. R. Positive and negative roles of an initiator protein at an origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9645–9649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funnell B. E. Mini-P1 plasmid partitioning: excess ParB protein destabilizes plasmids containing the centromere parS. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):954–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.954-960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamas P., Burger A. C., Churchward G., Caro L., Galas D., Chandler M. Replication of pSC101: effects of mutations in the E. coli DNA binding protein IHF. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00330192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo R., Nieto C., Fernandez-Tresguerres M. E., Diaz R. Bacterial zipper. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):866–866. doi: 10.1038/342866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma K., Sekiguchi M. Effect of dna mutations on the replication of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1095–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1095-1099.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma K., Sekiguchi M. Replication of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli K12: requirement for dnaA function. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 9;154(3):225–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00571277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingmer H., Cohen S. N. The pSC101 par locus alters protein-DNA interactions in vivo at the plasmid replication origin. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):6046–6048. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.6046-6048.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Balzer D., Lurz R., Waters V. L., Guiney D. G., Lanka E. Dissection of IncP conjugative plasmid transfer: definition of the transfer region Tra2 by mobilization of the Tra1 region in trans. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2493–2500. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2493-2500.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Churchward G., Caro L. Plasmid pSC101 replication mutants generated by insertion of the transposon Tn1000. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):287–303. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Churchward G., Xia G. X., Yu Y. Y., Caro L. An essential replication gene, repA, of plasmid pSC101 is autoregulated. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen D., Upegui-Gonzalez L. C., Caro L. Monomers and dimers of the RepA protein in plasmid pSC101 replication: domains in RepA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8923–8927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClary J. A., Witney F., Geisselsoder J. Efficient site-directed in vitro mutagenesis using phagemid vectors. Biotechniques. 1989 Mar;7(3):282–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock P. A., Cohen S. N. Genetic analysis of the inter-relationship between plasmid replication and incompatibility. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 13;174(2):135–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00268351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock P. A., Cohen S. N. Partitioning of bacterial plasmids during cell division: a cis-acting locus that accomplishes stable plasmid inheritance. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):529–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90639-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. A., Beaucage S. L., Cohen S. N. Role of DNA superhelicity in partitioning of the pSC101 plasmid. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90246-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. A., Cohen S. N. The partition (par) locus of pSC101 is an enhancer of plasmid incompatibility. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):695–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel T. T., MacAllister T., Bastia D. Cooperativity at a distance promoted by the combined action of two replication initiator proteins and a DNA bending protein at the replication origin of pSC101. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1453–1463. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura S., Tanaka M., Masamune Y., Yamaguchi K. DNA binding properties of purified replication initiator protein (Rep) encoded by plasmid pSC101. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):369–376. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terawaki Y., Nozue H., Zeng H., Hayashi T., Kamio Y., Itoh Y. Effects of mutations in the repA gene of plasmid Rts1 on plasmid replication and autorepressor function. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.786-792.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker W. T., Miller C. A., Cohen S. N. Structural and functional analysis of the par region of the pSC 10 1 plasmid. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vocke C., Bastia D. DNA-protein interaction at the origin of DNA replication of the plasmid pSC101. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):495–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vocke C., Bastia D. Primary structure of the essential replicon of the plasmid pSC101. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6557–6561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vocke C., Bastia D. The replication initiator protein of plasmid pSC101 is a transcriptional repressor of its own cistron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2252–2256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia G. X., Manen D., Goebel T., Linder P., Churchward G., Caro L. A copy-number mutant of plasmid pSC101. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):631–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Masamune Y. Autogenous regulation of synthesis of the replication protein in plasmid pSC101. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):362–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00425718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]