Abstract
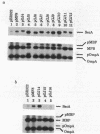
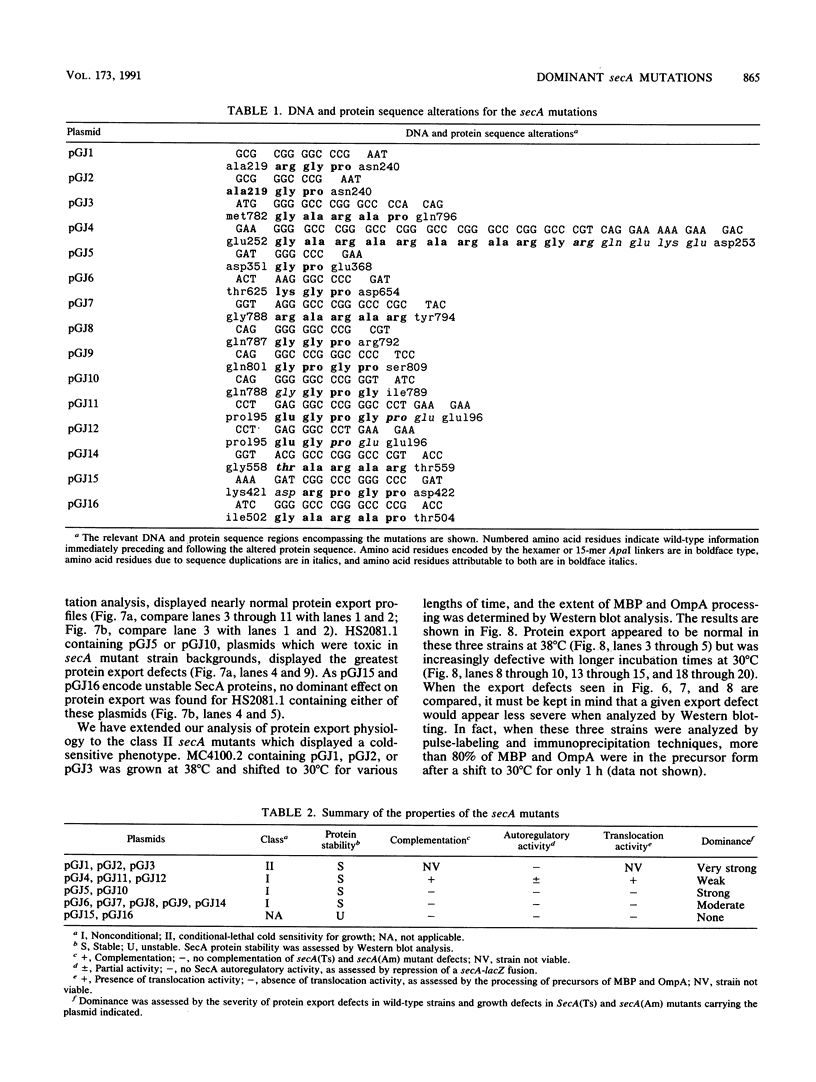
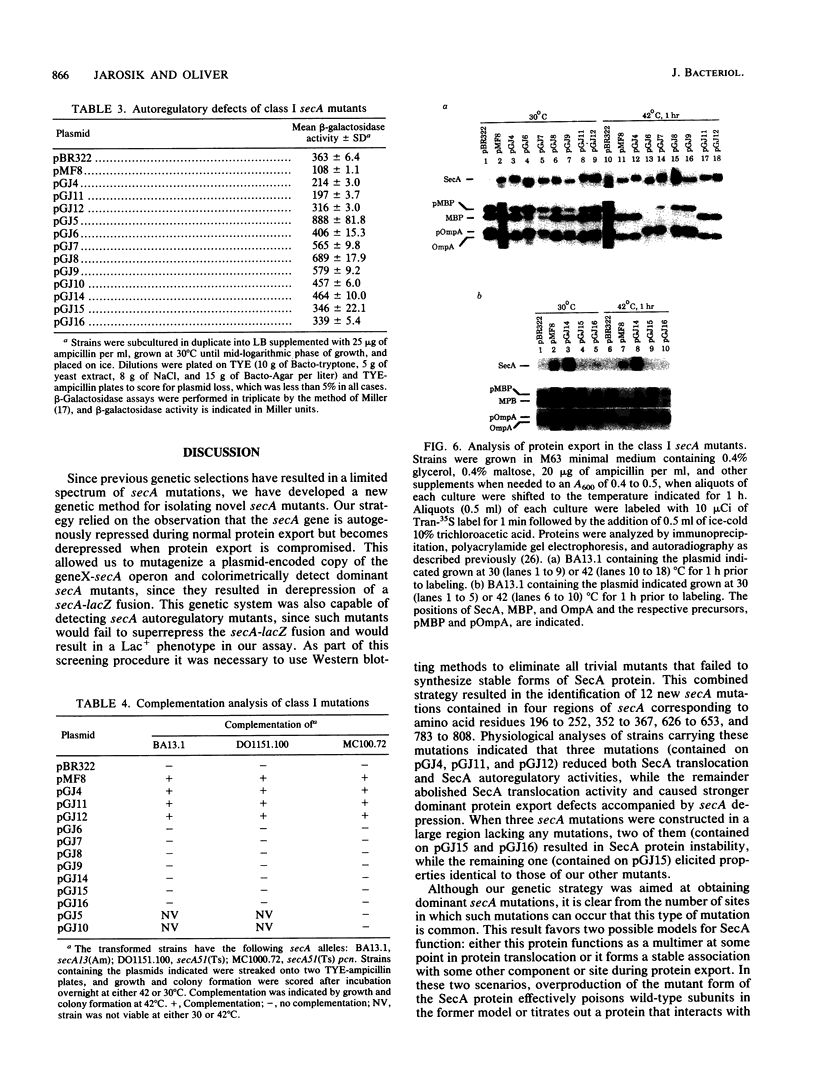
The secA gene product is an autoregulated, membrane-associated ATPase which catalyzes protein export across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Previous genetic selective strategies have yielded secA mutations at a limited number of sites. In order to define additional regions of the SecA protein that are important in its biological function, we mutagenized a plasmid-encoded copy of the secA gene to create small internal deletions or duplications marked by an oligonucleotide linker. The mutagenized plasmids were screened in an E. coli strain that allowed the ready detection of dominant secA mutations by their ability to derepress a secA-lacZ protein fusion when protein export is compromised. Twelve new secA mutations were found to cluster into four regions corresponding to amino acid residues 196 to 252, 352 to 367, 626 to 653, and 783 to 808. Analysis of these alleles in wild-type and secA mutant strains indicated that three of them still maintained the essential functions of SecA, albeit at a reduced level, while the remainder abolished SecA translocation activity and caused dominant protein export defects accompanied by secA depression. Three secA alleles caused dominant, conditional-lethal, cold-sensitive phenotypes and resulted in some of the strongest defects in protein export characterized to date. The abundance of dominant secA mutations strongly favors certain biochemical models defining the function of SecA in protein translocation. These new dominant secA mutants should be useful in biochemical studies designed to elucidate SecA protein's functional sites and its precise role in catalyzing protein export across the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barany F. Two-codon insertion mutagenesis of plasmid genes by using single-stranded hexameric oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4202–4206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J., Ferro-Novick S. Genetic studies on protein export in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:5–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Chen L., Tai P. C., Oliver D. B. SecA protein is required for secretory protein translocation into E. coli membrane vesicles. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C. ATP is essential for protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. T., Goff S. A., Webster T., Smith T., Goldberg A. L. Sequence of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. A heat-shock gene which encodes the ATP-dependent protease La. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11718–11728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Lill R., Crooke E., Rice M., Moore K., Wickner W., Oliver D. SecA protein, a peripheral protein of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane, is essential for the functional binding and translocation of proOmpA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):955–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fandl J. P., Cabelli R., Oliver D., Tai P. C. SecA suppresses the temperature-sensitive SecY24 defect in protein translocation in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8953–8957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fandl J. P., Tai P. C. Biochemical evidence for the secY24 defect in Escherichia coli protein translocation and its suppression by soluble cytoplasmic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7448–7452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Novel secA alleles improve export of maltose-binding protein synthesized with a defective signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):402–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.402-409.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Benson S., Hunt J., Michaelis S., Beckwith J. secD, a new gene involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1286-1290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K. Identification of the secY (prlA) gene product involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00330964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Evidence for specificity at an early step in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):267–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.267-274.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Chen L., Fandl J., Tai P. C. Purification of the Escherichia coli secB gene product and demonstration of its activity in an in vitro protein translocation system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2242–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Dowhan W., Wickner W. The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopilato J., Bortner S., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new chromosomal gene of Escherichia coli K-12, pcnB, reduce plasmid copy number of pBR322 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00430440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Cabelli R. J., Dolan K. M., Jarosik G. P. Azide-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli alter the SecA protein, an azide-sensitive component of the protein export machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Cabelli R. J., Jarosik G. P. SecA protein: autoregulated initiator of secretory precursor protein translocation across the E. coli plasma membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):311–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00763170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs P. D., Derman A. I., Beckwith J. A mutation affecting the regulation of a secA-lacZ fusion defines a new sec gene. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):571–579. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollo E. E., Oliver D. B. Regulation of the Escherichia coli secA gene by protein secretion defects: analysis of secA, secB, secD, and secY mutants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3281–3282. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3281-3282.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Riggs P. D., Jacq A., Fath M. J., Beckwith J. The secE gene encodes an integral membrane protein required for protein export in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1035–1044. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. G., Oliver D. B. SecA protein autogenously represses its own translation during normal protein secretion in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):643–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.643-649.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. G., Rollo E. E., Grodberg J., Oliver D. B. Nucleotide sequence of the secA gene and secA(Ts) mutations preventing protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3404–3414. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3404-3414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Loranger J. M., Wu H. C. Prolipoprotein modification and processing enzymes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3825–3830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Blobel G. Cytosolic factor purified from Escherichia coli is necessary and sufficient for the export of a preprotein and is a homotetramer of SecB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Purified secB protein of Escherichia coli retards folding and promotes membrane translocation of the maltose-binding protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8978–8982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng Q. P., Chen L. L., Tai P. C. Requirement of heat-labile cytoplasmic protein factors for posttranslational translocation of OmpA protein precursors into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):126–131. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.126-131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Wickner W., Goodman J. M. Sequence of the leader peptidase gene of Escherichia coli and the orientation of leader peptidase in the bacterial envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12073–12080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]