Abstract
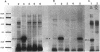
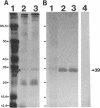
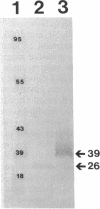
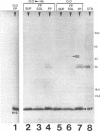
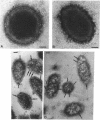
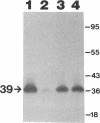
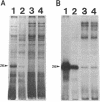
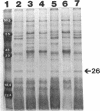
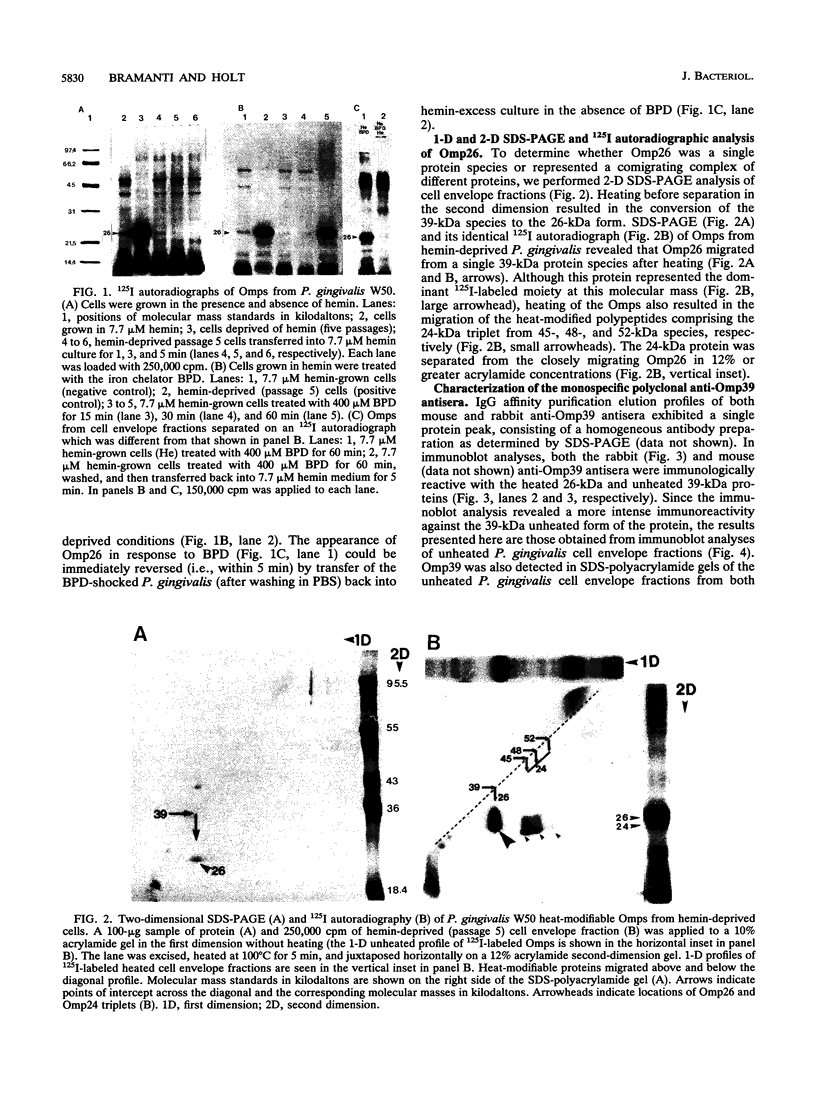
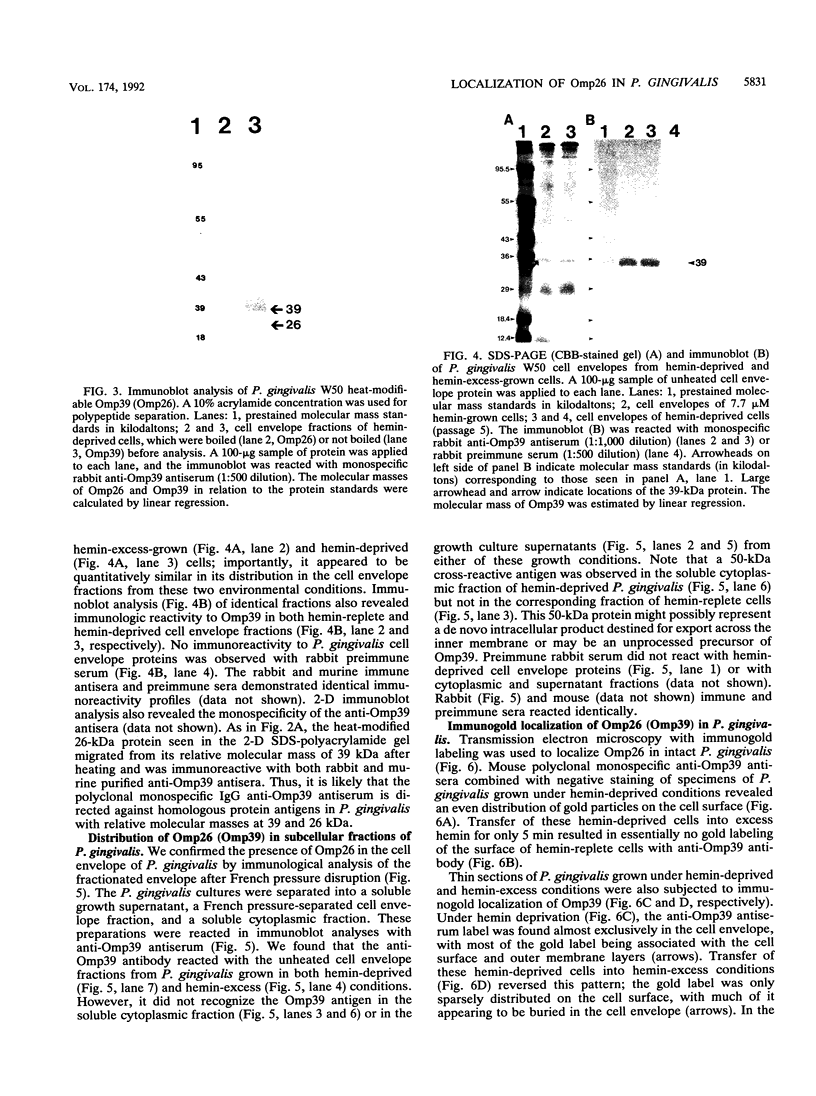
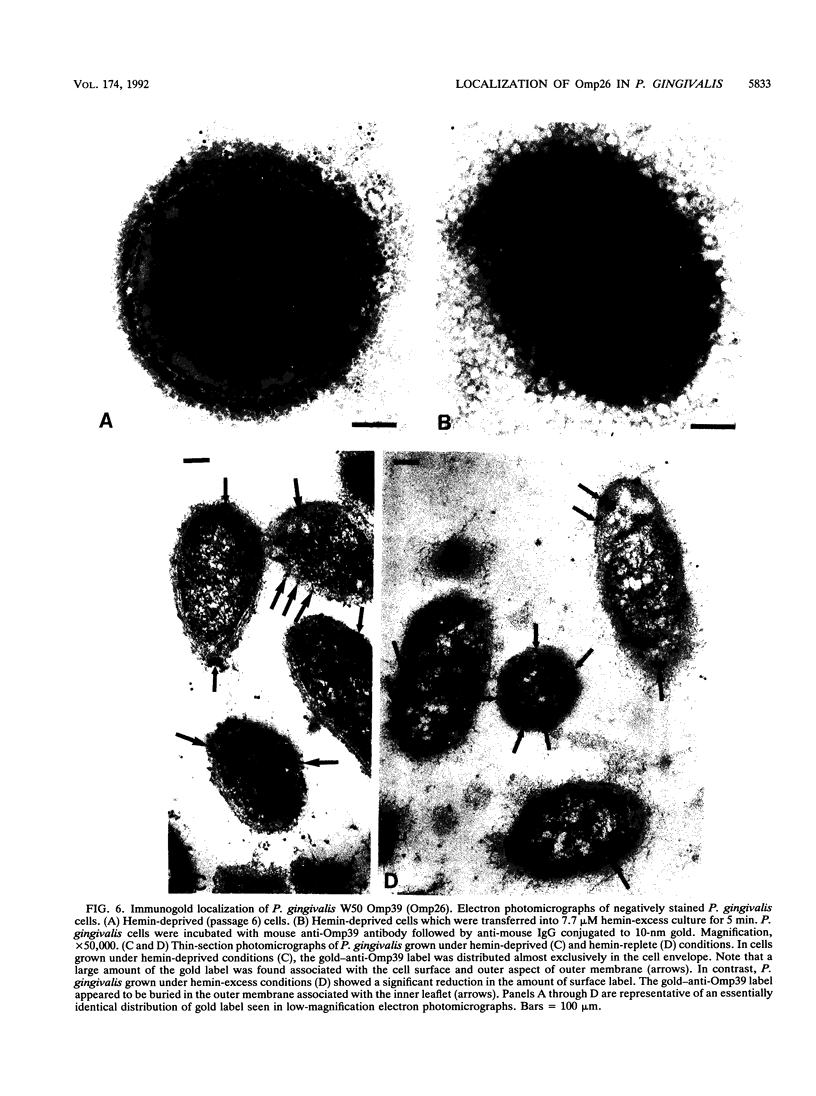
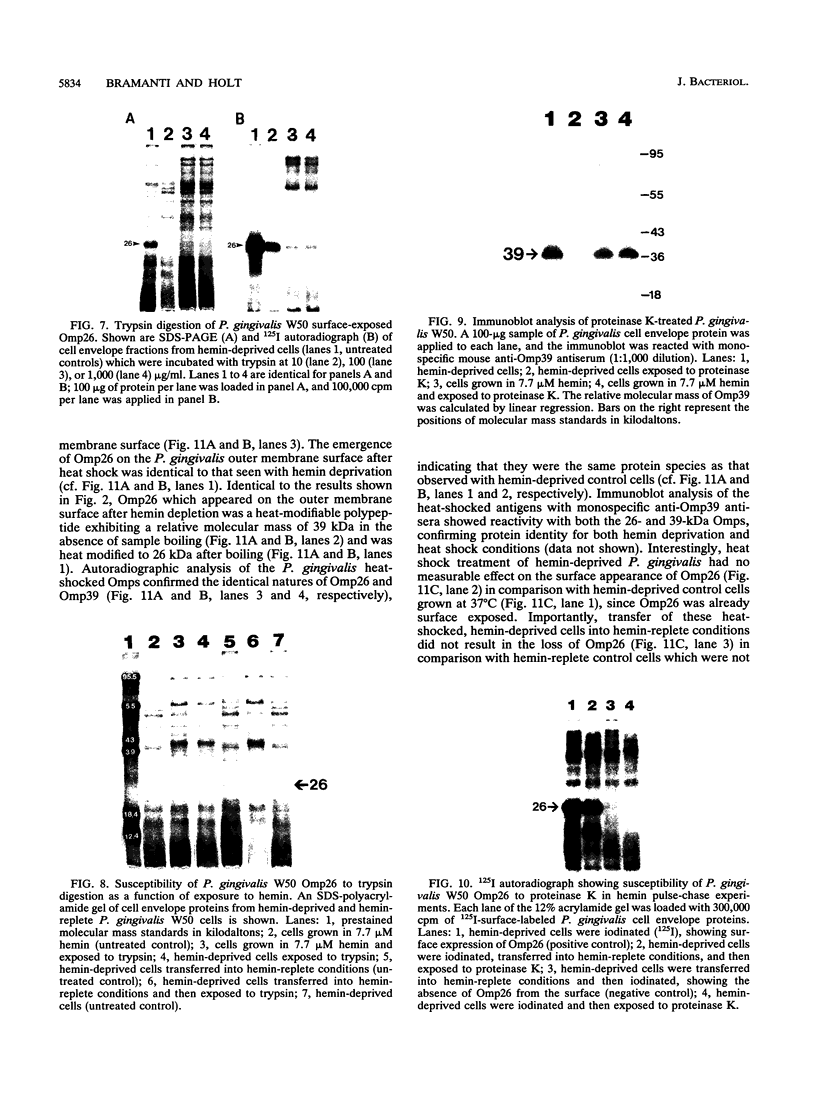
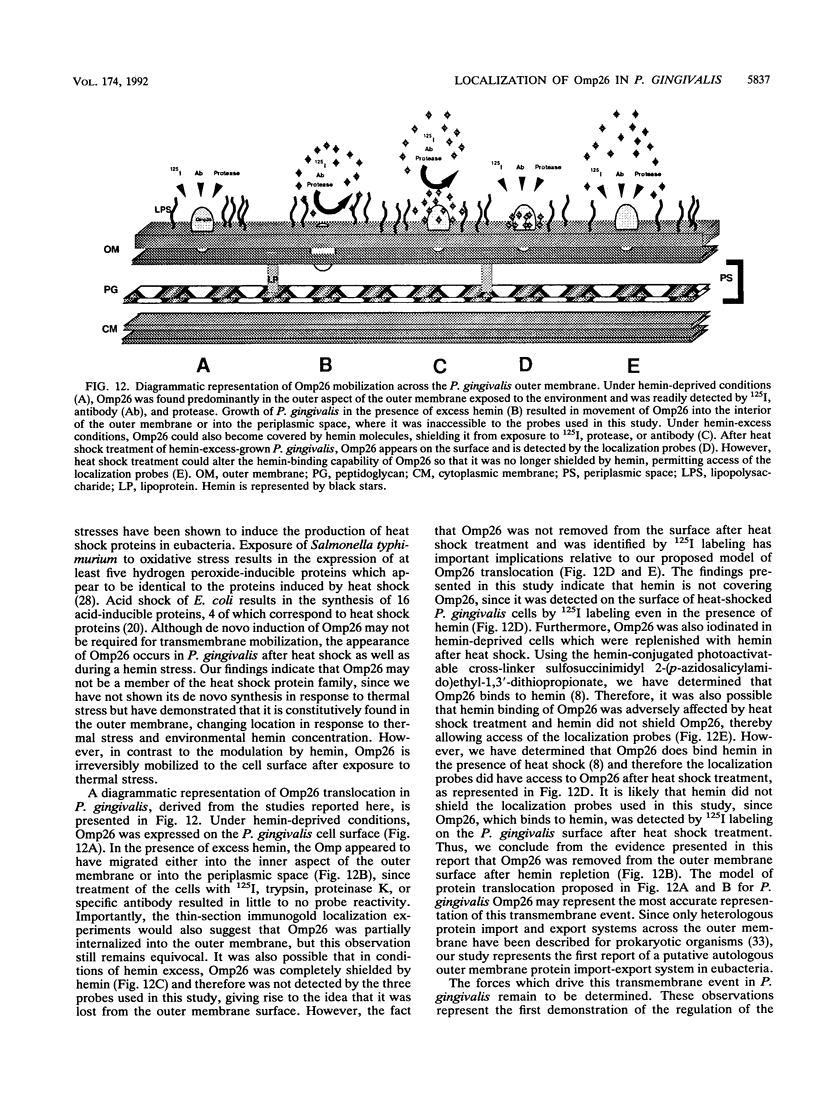
We recently identified a 26-kDa hemin-repressible outer membrane protein (Omp26) expressed by the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. We report the localization of Omp26, which may function as a component of a hemin transport system in P. gingivalis. Under hemin-deprived conditions, P. gingivalis expressed Omp26, which was then lost from the surface after a shift back into hemin-rich conditions. Experiments with 125I labeling of surface proteins to examine the kinetics of mobilization of Omp26 determined that it was rapidly (within less than 1 min) lost from the cell surface after transfer into a hemin-excess environment. When cells grown under conditions of hemin excess were treated with the iron chelator 2,2'-bipyridyl, Omp26 was detected on the cell surface after 60 min. One- and two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analyses using purified anti-Omp26 monospecific polyclonal immunoglobulin G antisera established that Omp26 was heat modifiable (39 kDa unheated) and consisted of a single protein species. Immunogold labeling of negatively stained and chemically fixed thin-section specimens indicated that Omp26 was associated with the cell surface and outer leaflet of the P. gingivalis outer membrane in hemin-deprived conditions but was buried in the deeper recesses of the outer membrane in hemin-excess conditions. Analysis of subcellular fractions of P. gingivalis grown either in hemin-excess or hemin-deprived conditions detected Omp26 only in the cell envelope fraction, not in the cytoplasmic fraction or culture supernatant. Limited proteolytic digestion of hemin-deprived P. gingivalis with trypsin and proteinase K verified the surface location of Omp26 as well as its susceptibility to proteolytic digestion. Heat shock treatment of hemin-excess-grown P. gingivalis also resulted in Omp26 translocation onto the outer membrane surface even in the presence of hemin. Furthermore, hemin repletion of heat-shocked, hemin-deprived P. gingivalis did not result in Omp26 translocation off the outer membrane surface, suggesting that thermal stress inactivates this transmembrane event. This newly described outer membrane protein appears to be associated primarily with the outer membrane, in which it is exported to the outer membrane surface for hemin binding and may be imported across the outer membrane for intracellular hemin transport.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berryman M. A., Rodewald R. D. An enhanced method for post-embedding immunocytochemical staining which preserves cell membranes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Feb;38(2):159–170. doi: 10.1177/38.2.1688894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostford J. L. Analysis of protein expression in response to osmotic stress in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):355–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramanti T. E., Holt S. C. Iron-regulated outer membrane proteins in the periodontopathic bacterium, Bacteroides gingivalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1146–1154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90986-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramanti T. E., Holt S. C. Roles of porphyrins and host iron transport proteins in regulation of growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis W50. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7330–7339. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7330-7339.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Williams P. The influence of environment on envelope properties affecting survival of bacteria in infections. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:527–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Höfling J. F., Sundqvist G. K. Degradation of albumin, haemopexin, haptoglobin and transferrin, by black-pigmented Bacteroides species. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L., Bramanti T. E., Ebersole J. L., Holt S. C. Hemolytic activity in the periodontopathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis: kinetics of enzyme release and localization. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1932–1940. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1932-1940.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneer H. G., Potter A. A. Effect of iron restriction on the outer membrane proteins of Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):798–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.798-804.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Sciortino C. V., McIntosh M. A. Role of iron in microbe-host interactions. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S759–S777. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Chao G., McBride B. C. Characterization of sodium dodecyl sulfate-stable Bacteroides gingivalis proteases by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.95-99.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Hansen E. J. Molecular cloning, partial purification, and characterization of a haemin-binding lipoprotein from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde M., Portalier R. Acid shock proteins of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90406-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. M., Birss A. J., Smalley J. W. Haemagglutinating and haemolytic activity of the extracellular vesicles of Bacteroides gingivalis W50. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Oct;5(5):269–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Porphyrin binding by the surface array virulence protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1332–1336. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1332-1336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell W. L., Holt S. C. Extraction, purification, and characterization of major outer membrane proteins from Wolinella recta ATCC 33238. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3740–3749. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3740-3749.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell W., Holt S. C. Comparative studies of the outer membranes of Bacteroides gingivalis, strains ATCC 33277, W50, W83, 381. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Jun;5(3):121–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez J. L., Delgado-Iribarren A., Baquero F. Mechanisms of iron acquisition and bacterial virulence. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;6(1):45–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Christman M. F., Jacobson F. S., Storz G., Ames B. N. Hydrogen peroxide-inducible proteins in Salmonella typhimurium overlap with heat shock and other stress proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8059–8063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B. R., Sparrius M., Verweij-van Vught A. M., MacLaren D. M. Iron-regulated outer membrane protein of Bacteroides fragilis involved in heme uptake. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3954–3958. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3954-3958.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Iron and virulence in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;16(2):81–111. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Payne S. M. Effect of iron limitation on growth, siderophore production, and expression of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.148-155.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence J., Cegielska A., Georgopoulos C. Role of Escherichia coli heat shock proteins DnaK and HtpG (C62.5) in response to nutritional deprivation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7157–7166. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7157-7166.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stugard C. E., Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. A 101-kilodalton heme-binding protein associated with congo red binding and virulence of Shigella flexneri and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3534–3539. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3534-3539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Holt S. C. Chemical and biological activities of a 64-kilodalton outer sheath protein from Treponema denticola strains. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6935–6947. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6935-6947.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron withholding: a defense against infection and neoplasia. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):65–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatvin M. B., Clark A. W., Siegel F. L. Major E. coli heat-stress protein do not translocate: implications for cell survival. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1987 Oct;52(4):603–613. doi: 10.1080/09553008714552091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]