Abstract
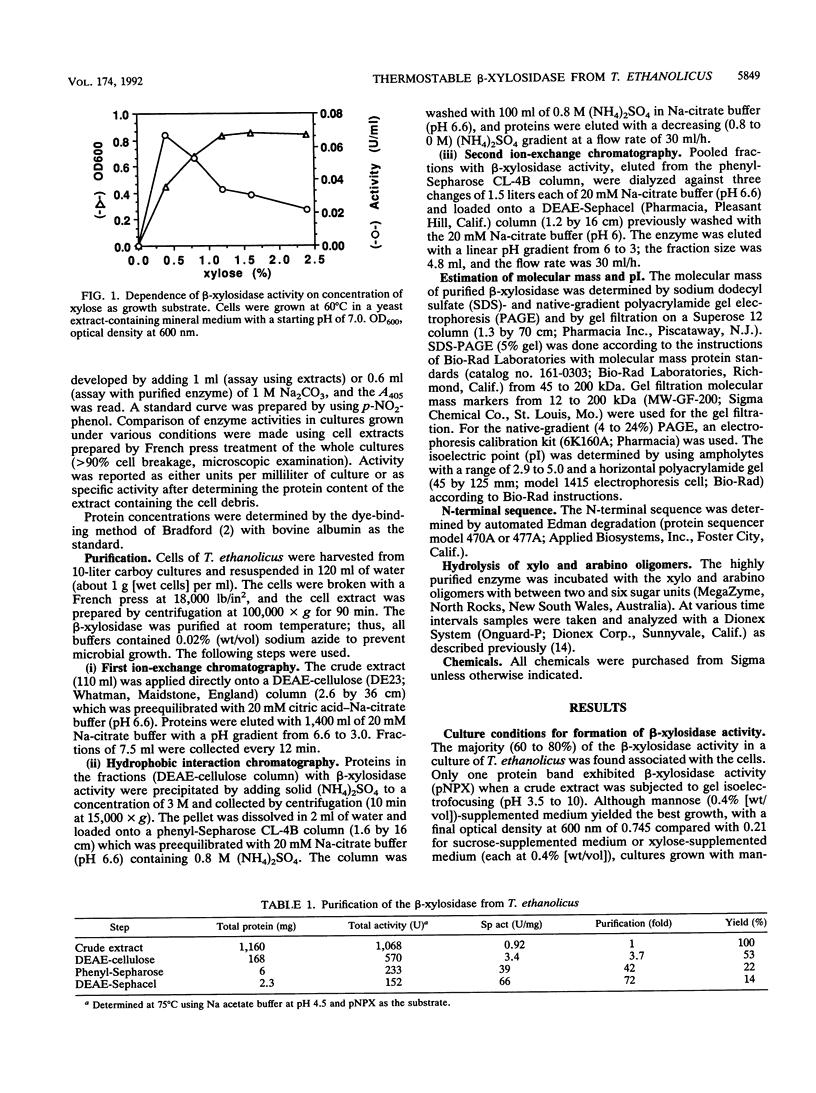
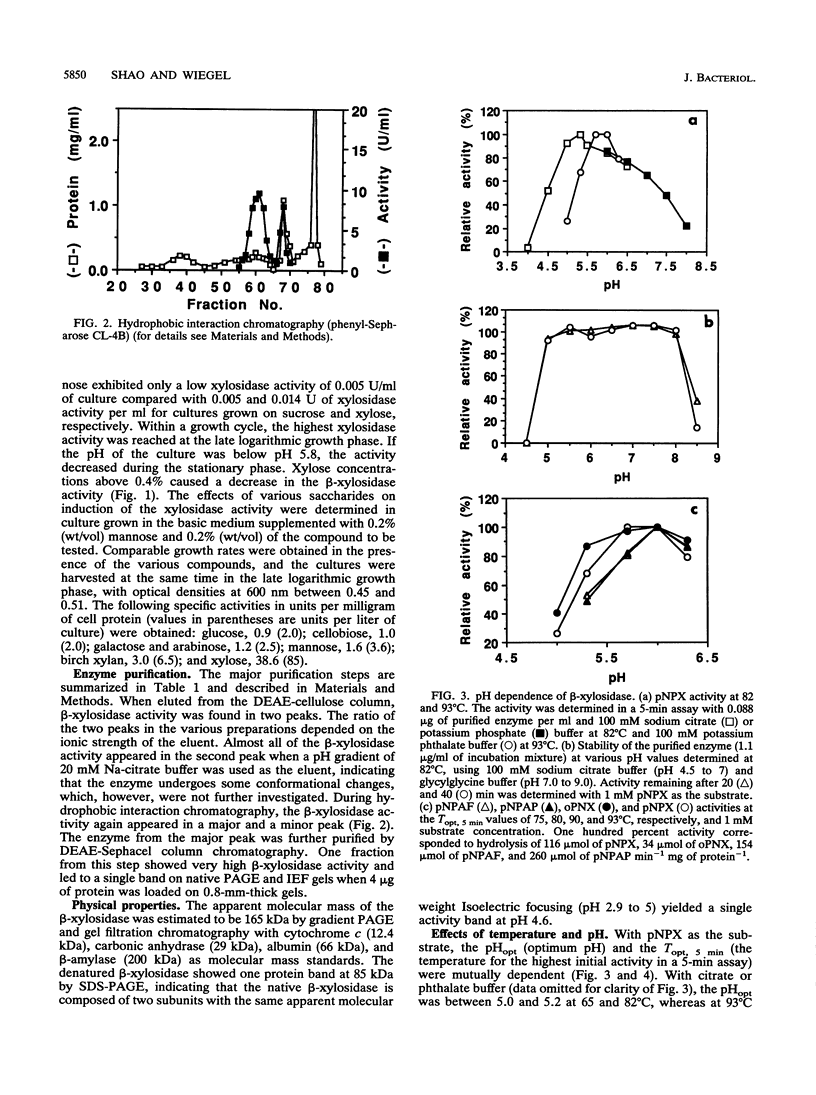
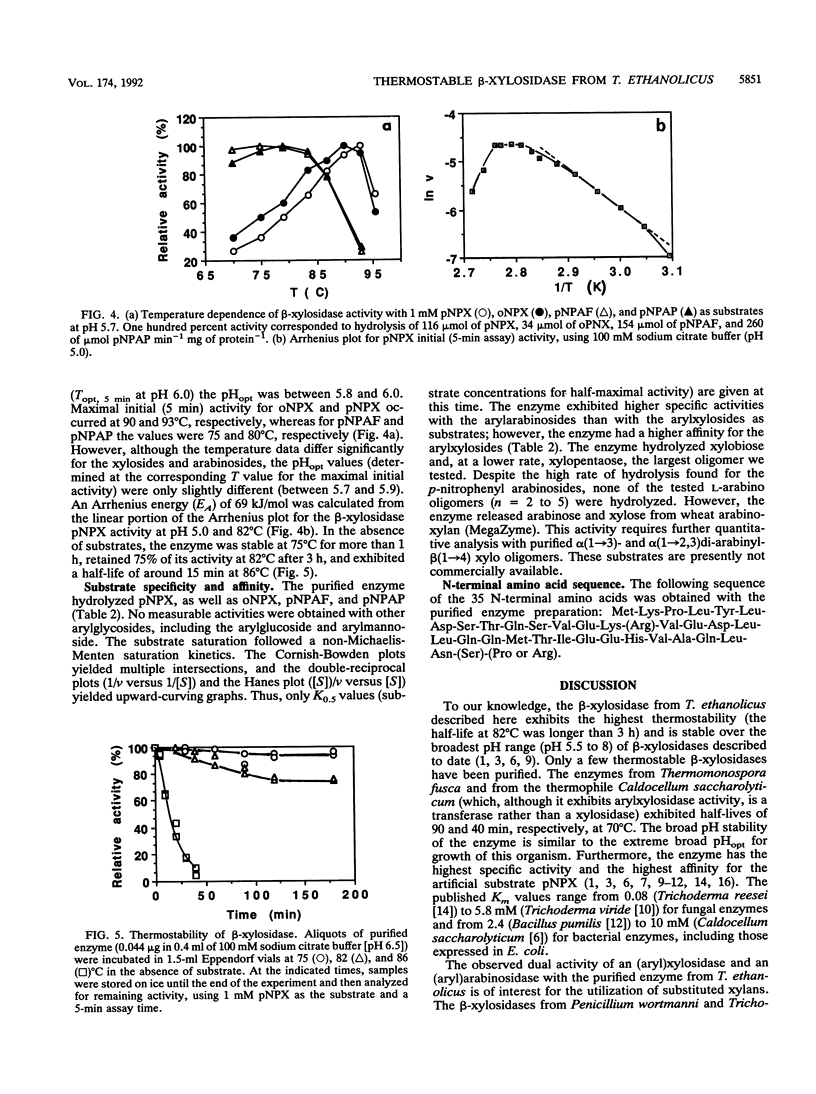
A highly thermostable beta-xylosidase, exhibiting similarly high activities for arylxylose and arylarabinose, was purified (72-fold) to gel electrophoretic homogeneity from the ethanologenic thermophilic anaerobe Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. The isoelectric point is pH 4.6; the apparent molecular weight is around 165,000 for the native enzyme (gel filtration and gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) and 85,000 for the two subunits (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). The enzyme exhibited the highest affinity towards p-NO2-phenyl xyloside (pNPX) (substrate concentration for half-maximal activity = 0.018 mM at 82 degrees C and pH 5.0) but the highest specific activity with p-NO2-phenylarabinofuranoside. T(opt), 5 min, the temperature for the maximum initial activity in a 5-min assay of the purified enzyme, was observed around pH 5.9 and 93 degrees C; however at 65 and 82 degrees C, the pH optimum was 5.0 to 5.2, and at this pH the maximal initial activity was observed at 82 degrees C (pH 5.0 to 5.5). The pH curves and temperature curves for arylxylosides as substrates differed significantly from those for arylarabinosides as substrates. An incubation for 3 h at 82 degrees C in the absence of substrate reduced the activity to around 75%. At 86 degrees C the half-life was around 15 min. With pNPX as the substrate, an Arrhenius energy of 69 kJ/mol was determined. The N-terminal sequence did not reveal a high similarity to those from other published enzyme sequences.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleyn F., Claeyssens M., Van Beeumen J., De Bruyne C. K. Purification and properties of beta-xylosidase from Penicillium wortmanni. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jan;56(1):43–50. doi: 10.1139/o78-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier Doris, Mothershed Cheryle P., Wiegel Juergen. Characterization of Clostridium thermocellum JW20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.204-211.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. C., Schofield L. R., Coolbear T., Daniel R. M., Morgan H. W. Purification and properties of an aryl beta-xylosidase from a cellulolytic extreme thermophile expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):645–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2730645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt B., Schmidt J. Purification and some properties of five endo-1,4-beta-D-xylanases and a beta-D-xylosidase produced by a strain of Aspergillus niger. Can J Biochem. 1979 Feb;57(2):125–134. doi: 10.1139/o79-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. F., Forsberg C. W. Isolation and Some Properties of a beta-d-Xylosidase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):651–654. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.651-654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanmori T., Watanabe T., Shinke R., Kohno A., Kawamura Y. Purification and properties of thermostable xylanase and beta-xylosidase produced by a newly isolated Bacillus stearothermophilus strain. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6669–6672. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6669-6672.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panbangred W., Kawaguchi O., Tomita T., Shinmyo A., Okada H. Isolation of two beta-xylosidase genes of Bacillus pumilus and comparison of their gene products. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utt E. A., Eddy C. K., Keshav K. F., Ingram L. O. Sequencing and expression of the Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens xylB gene encoding a novel bifunctional protein with beta-D-xylosidase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase activities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1227-1234.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegel J., Mothershed C. P., Puls J. Differences in Xylan Degradation by Various Noncellulolytic Thermophilic Anaerobes and Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):656–659. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.656-659.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


