Abstract
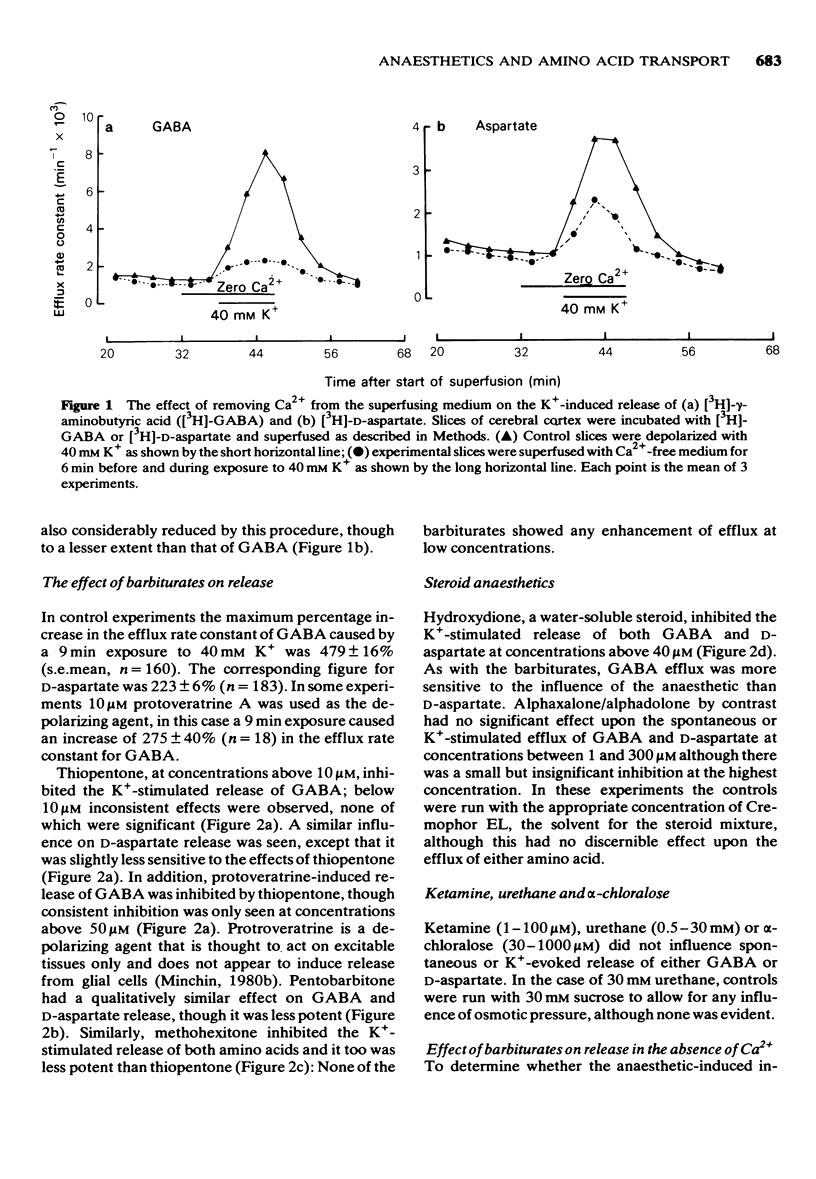
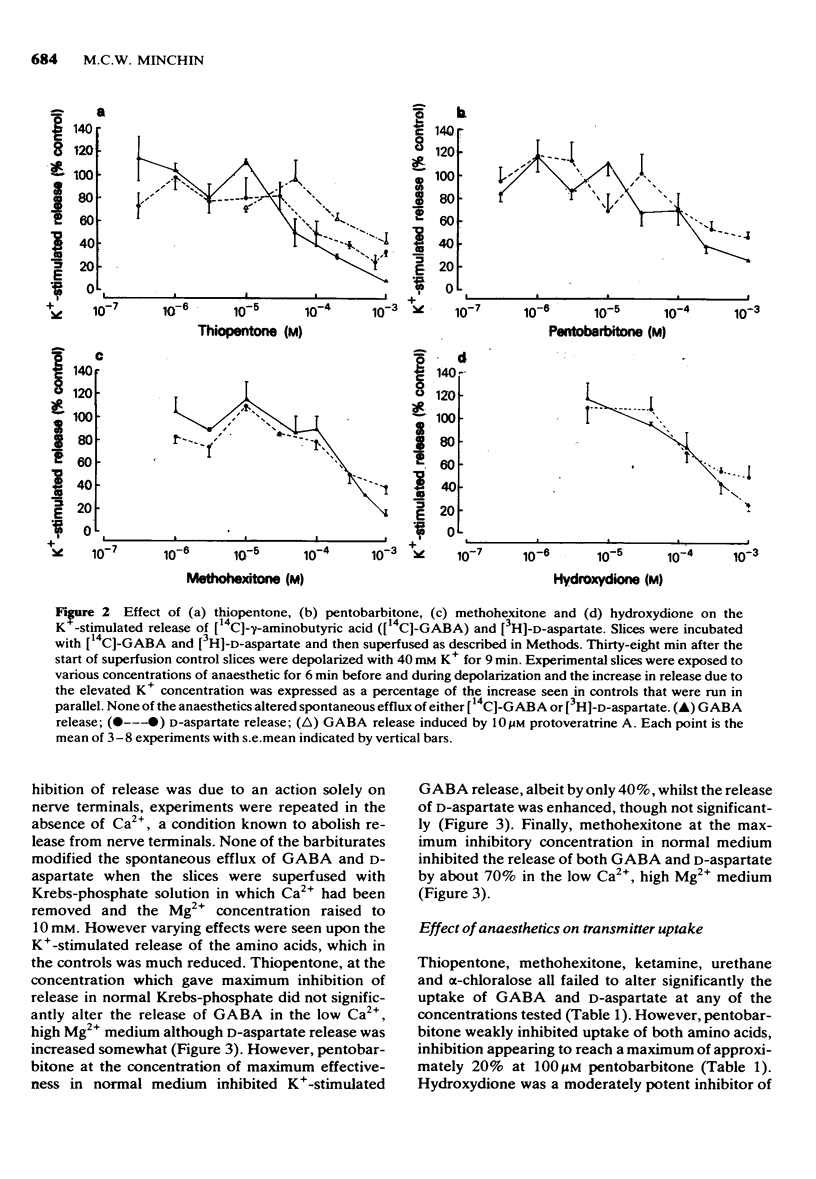
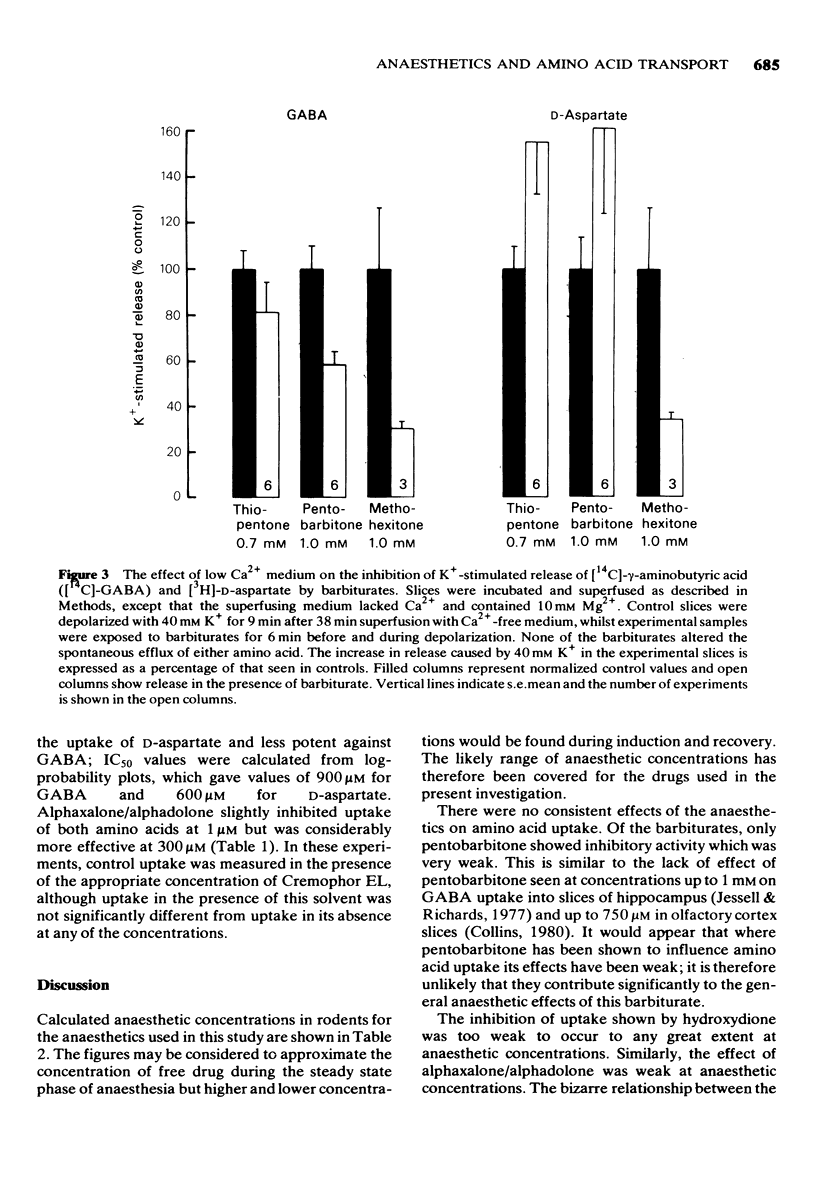
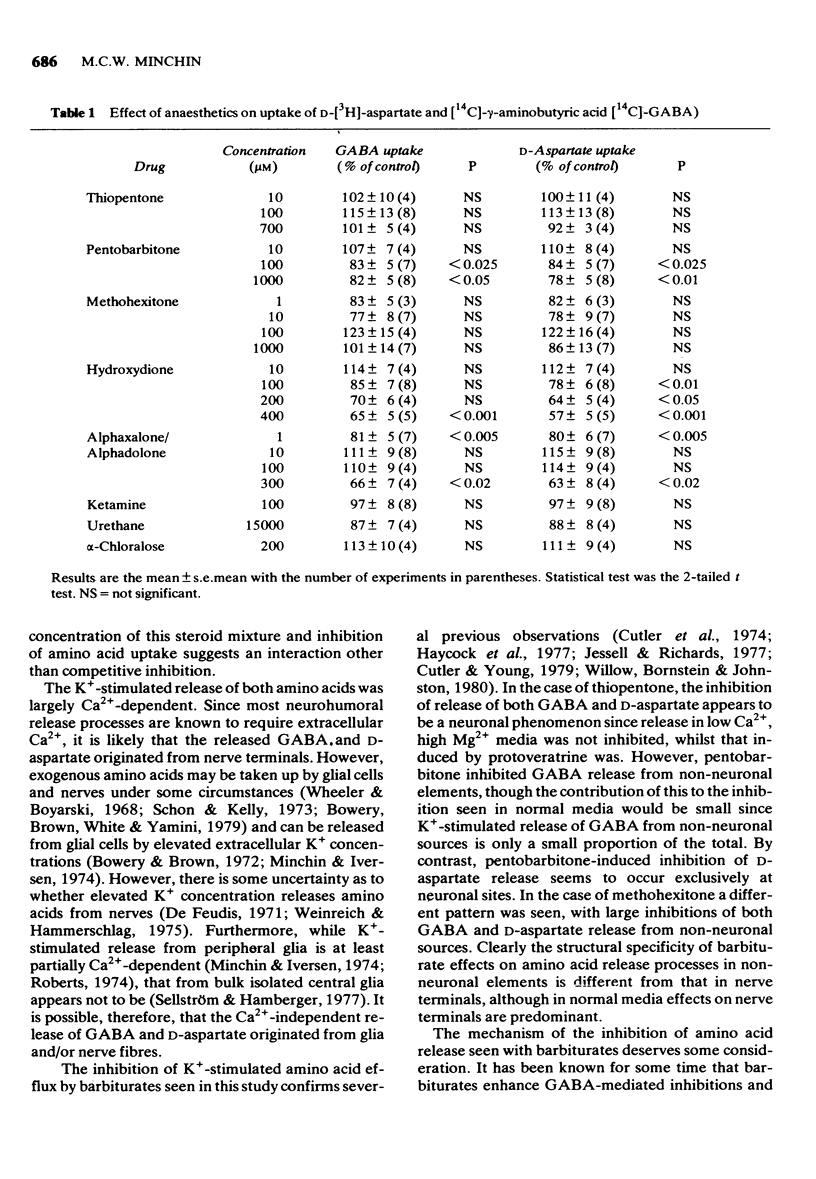
1 The effect of various concentrations of thiopentone, pentobarbitone, methohexitone, hydroxydione, alphaxalone/alphadolone, ketamine, alpha-chloralose, and urethane on the transport of radiolabelled gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and D-aspartate was investigated. 2 Uptake of the amino acids was weakly inhibited, if at all, by the anaesthetics and it is unlikely that such effects contribute significantly to their physiological function. 3 The spontaneous efflux of GABA and D-aspartate was not detectably altered by any of the drugs tested. 4 Thiopentone, pentobarbitone, methohexitone and hydroxydione inhibited K+-stimulated GABA and D-aspartate release. The other anaesthetics had no effect on K+-stimulated amino acid release. 5 The rank order of potency of the inhibitors of K+-stimulated amino acid release did not correlate with their anaesthetic potency. Furthermore not all inhibitors appeared to be very effective at anaesthetic concentrations. 6 It is concluded that although it is possible that inhibition of excitatory transmitter release may be involved in the anaesthetic action of some anaesthetics, for many of the substances tested in this study such as mechanism does not appear to be implicated.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. L., Ransom B. R. Pentobarbitone pharmacology of mammalian central neurones grown in tissue culture. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:355–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A. -Aminobutyric acid uptake by sympathetic ganglia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):89–91. doi: 10.1038/newbio238089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Brown D. A., White R. D., Yamini G. [3H]gamma-Aminobutyric acid uptake into neuroglial cells of rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A. Interaction of pentobarbitone and gamma-aminobutyric acid on mammalian sympathetic ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child K. J., Currie J. P., Dis B., Dodds M. G., Pearce D. R., Twissell D. J. The pharmacological properties in animals of CT1341--a new steroid anaesthetic agent. Br J Anaesth. 1971 Jan;43(1):2–13. doi: 10.1093/bja/43.1.2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child K. J., Gibson W., Harnby G., Hart J. W. Metabolism and excretion of Althesin (CT 1341) in the rat. Postgrad Med J. 1972 Jun;48(Suppl):37–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. M. Anaesthetic agents and the chemical sensitivity of cortical neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1970 Jan;9(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. W., Markowitz D., Dudzinski D. S. The effect of barbiturates on (3H)GABA transport in rat cerebral cortex slices. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 6;81(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90935-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. W., Young J. Effect of barbiturates on release endogenous amino acids from rat cortex slices. Neurochem Res. 1979 Jun;4(3):319–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00963802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L. P., Johnston G. A. Uptake and release of D- and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):1007–1014. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. Noninhalational anaesthetics. Adv Drug Res. 1975;10:1–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeudis F. V. Effects of electrical stimulation on the efflux of L-glutamate from peripheral nerve in vitro. Exp Neurol. 1971 Feb;30(2):291–296. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(71)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., SCHMIDT R., WILLIS W. D. PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDIES ON PRESYNAPTIC INHIBITION. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:500–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C., Faber D. S., Táboríková H. The action of a parallel fiber volley on the antidromic invasion of Purkyne cells of cat cerebellum. Brain Res. 1971 Jan 22;25(2):335–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo A. Effects of procaine, pentobarbital and halothane on synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Oct;169(2):185–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Levy W. B., Cotman C. W. Pentobarbital depression of stimulus-secretion coupling in brain--selective inhibition of depolarization-induced calcium-dependent release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jan 15;26(2):159–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Richards C. D. Barbiturate potentiation of hippocampal i.p.s.p.s is not mediated by blockade of GABA uptake [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):42P–44P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Mitchell J. F. The effect of bicuculline, metrazol, picrotoxin and strychnine on the release of ( 3 H)GABA from rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2441–2446. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin M. C., Iversen L. L. Release of (3H)gamma-aminobutyric acid from glial cells in rat dorsal root ganglia. J Neurochem. 1974 Sep;23(3):533–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb06056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin M. C. The effect of some anaesthetic agents on [3H]-GABA release from rat brain slices [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;68(1):131P–131P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchin M. C. Veratrum alkaloids as transmitter-releasing agents. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Apr;2(2):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. R., Martin I. L. Is GABA release modulated by presynaptic receptors? Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):904–905. doi: 10.1038/274904a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Eccles J. C., Oshima T., Rubia F. Prolongation of hippocampal inhibitory postsynaptic potentials by barbiturates. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):625–627. doi: 10.1038/258625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. Pentobarbital: action on frog motoneurons. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 10;96(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90582-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. The effects of anaesthetics on synaptic excitation and inhibition in the olfactory bulb. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):803–814. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D. On the mechanism of barbiturate anaesthesia. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):749–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Smaje J. C. Anaesthetics depress the sensitivity of cortical neurones to L-glutamate. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):347–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J. Amino acid release from isolated rat dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 1974 Jul 12;74(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90586-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellström A., Hamberger A. Potassium-stimulated gamma-aminobutyric acid release from neurons and glia. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 1;119(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass S. R. Use of 3H-muscimol for GABA receptor studies. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):392–394. doi: 10.1038/273392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Olsen R. W. Interaction of barbiturates with dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites related to the GABA receptor-ionophore system. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1643–1651. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weakly J. N. Effect of barbiturates on 'quantal' synaptic transmission in spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):63–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D., Hammerschlag R. Nerve impulse-enhanced release of amino acids from non-synaptic regions of peripheral and central nerve trunks of bullfrog. Brain Res. 1975 Jan 24;84(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90807-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler D. D., Boyarsky L. L. Influx of glutamic acid in peripheral nerve--characteristics in influx. J Neurochem. 1968 Sep;15(9):1019–1031. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willow M., Bornstein J. C., Johnston G. A. The effects of anaesthetic and convulsant barbiturates on the efflux of [3H]D-aspartate from brain minislices. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jun;18(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


