Abstract
1 Transmurally stimulated segments of the guinea-pig ileum have been used to analyse the different adrenoceptors in the terminal (0 to 3 cm) and the proximal (> 50 cm from the ileocaecal valve) ileum.
2 The prejunctional adrenoceptors (located on the final, cholinergic, motor nerve terminals) and postjunctional adrenoceptors (located on the smooth muscle membrane) have been characterized according to their sensitivity to α- and β-agonists and antagonists.
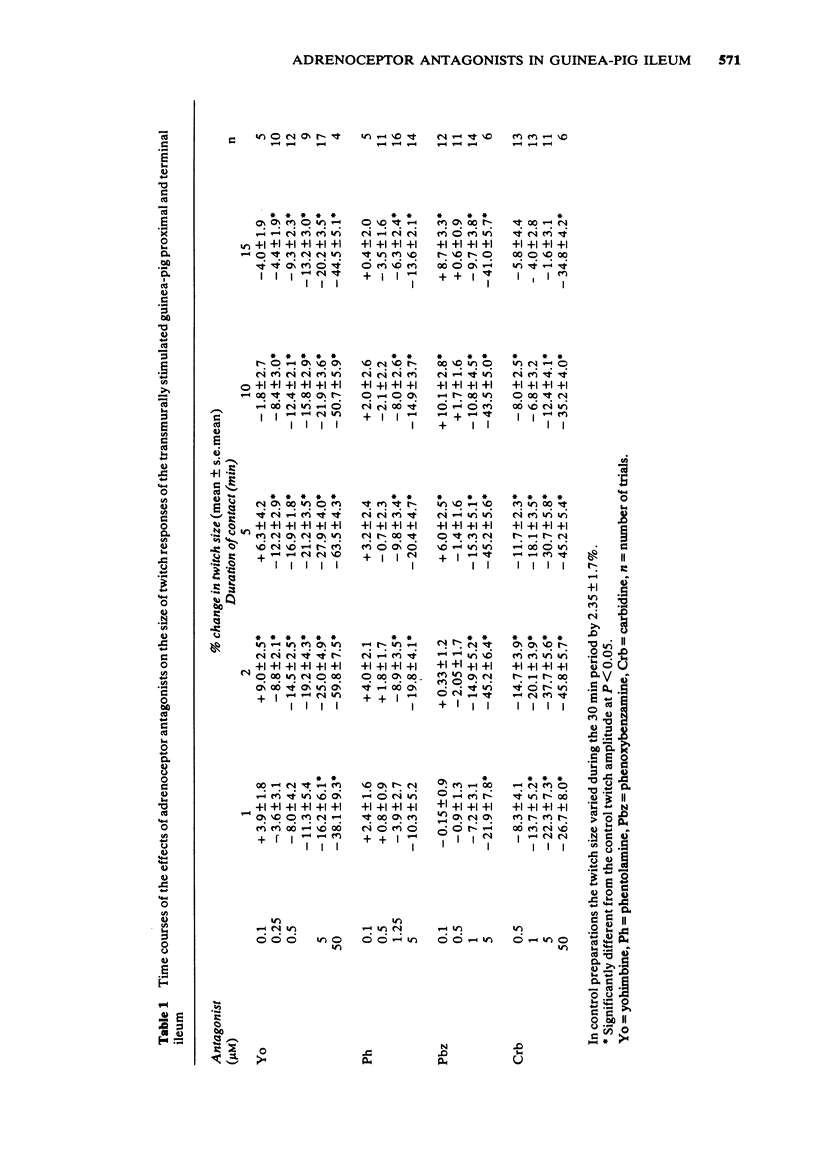
3 Phentolamine, phenoxybenzamine and yohimbine, in concentrations of 0.1 μM, transiently enhanced (up to 10%) the twitch response. At higher concentrations all the α- and β-antagonists studied depressed the neurogenic twitches and relaxed the smooth muscle.
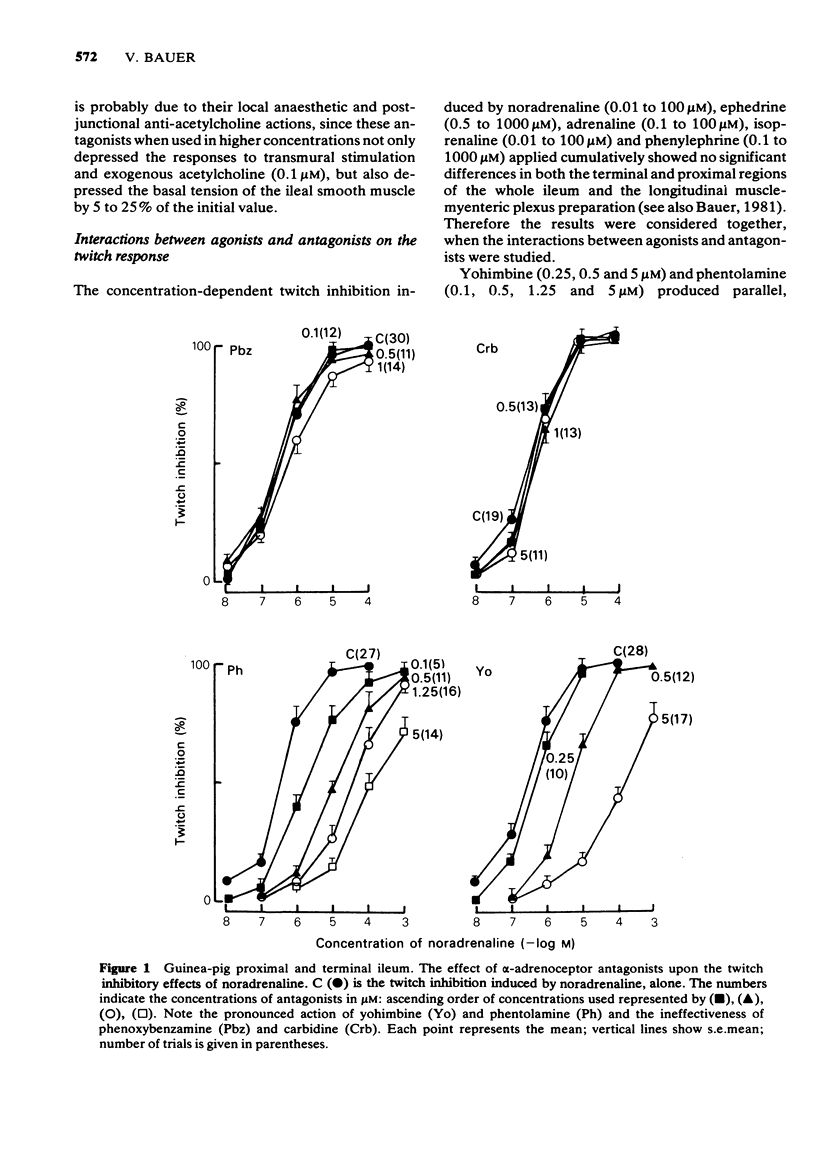
4 The twitch-inhibitory effects of adrenoceptor agonists (noradrenaline, adrenaline and ephedrine) were not antagonized by phenoxybenzamine (0.1, 0.5 and 1 μM), carbidine (0.5, 1 and 5 μM) and propranolol (0.5, 1 and 5 μM); however, they were depressed by phentolamine (0.1, 0.5, 1.25 and 5 μM) and yohimbine (0.25, 0.5 and 5 μM).
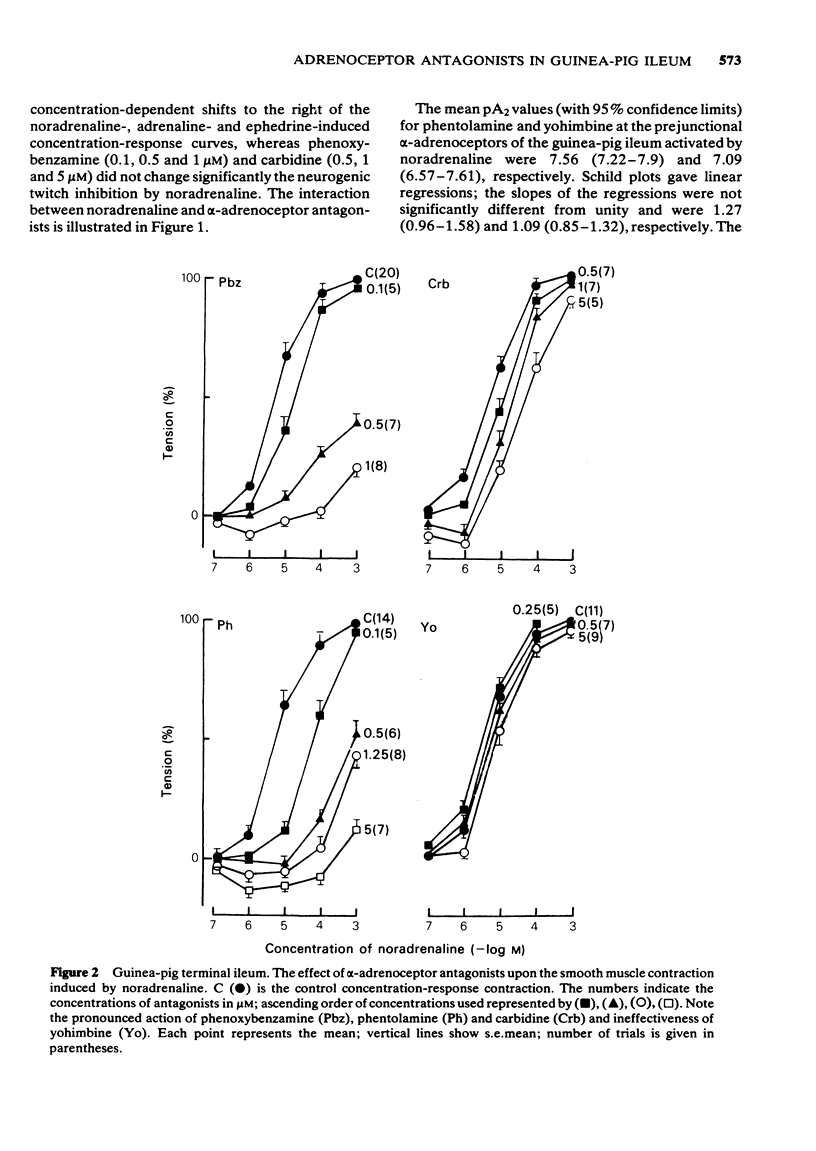
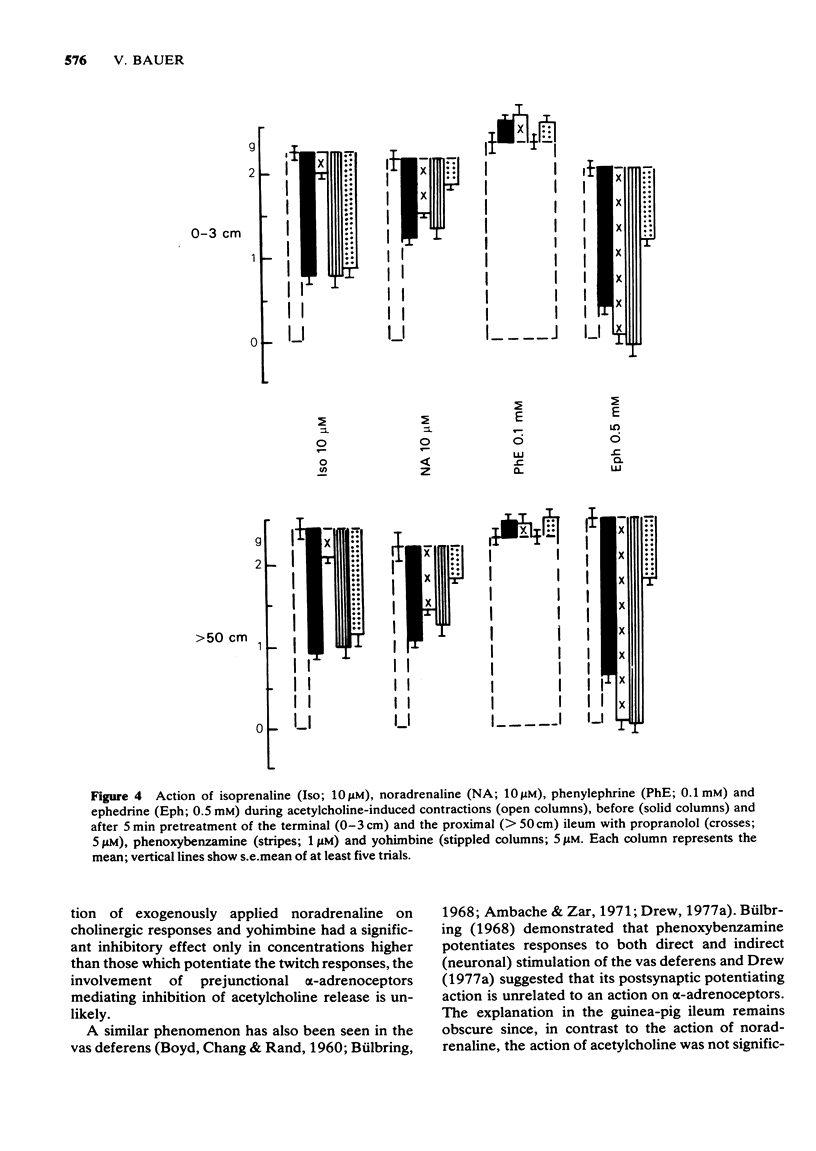
5 The smooth muscle contractions induced by noradrenaline and adrenaline in the terminal ileum and by phenylephrine in both the terminal and proximal ileum were antagonized by phenoxybenzamine, carbidine and phentolamine but were not influenced by yohimbine and propranolol.
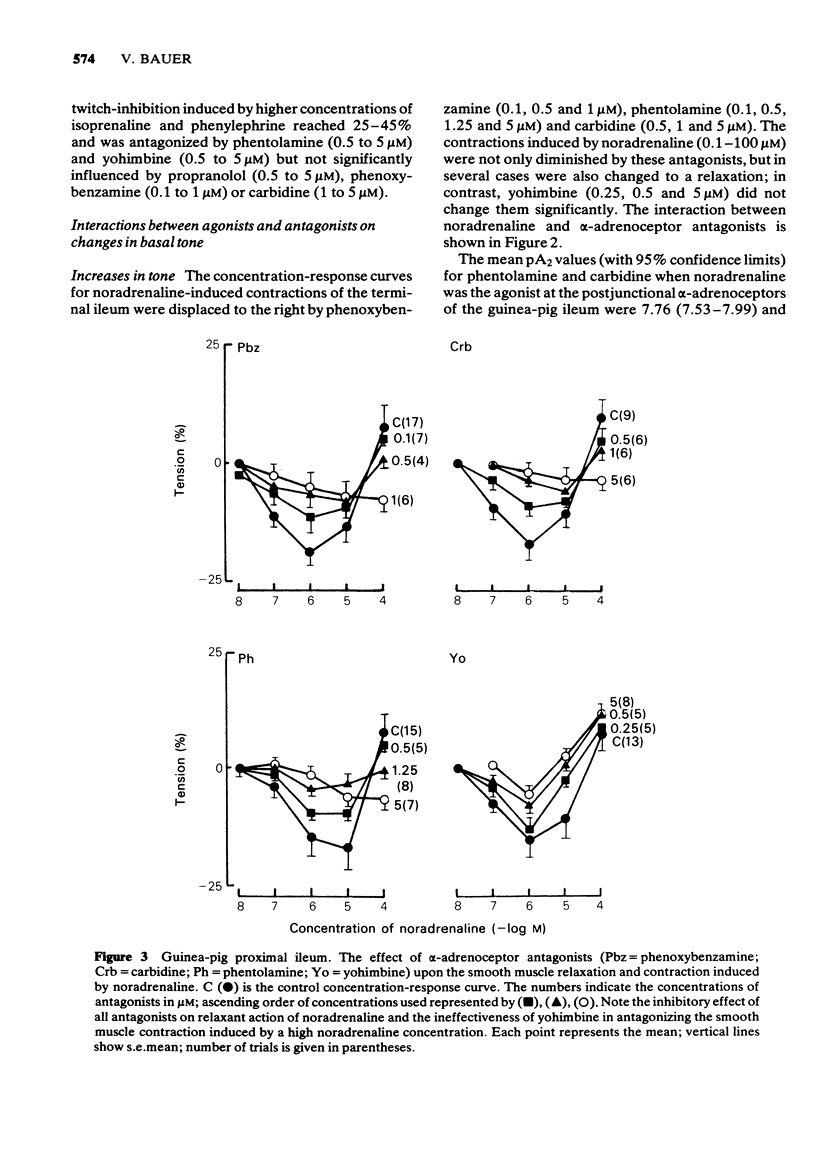
6 The smooth muscle relaxations of the proximal ileum induced by noradrenaline, adrenaline and ephedrine were inhibited by yohimbine, phentolamine, carbidine and phenoxybenzamine, and the isoprenaline-induced relaxation was antagonized by propranolol.
7 All the agonists studied, except phenylephrine, elicited relaxations of the acetylcholine-induced sustained contraction of both proximal and terminal ileum. The relaxation induced by isoprenaline was antagonized by propranolol, and the effects of noradrenaline and ephedrine by yohimbine.
8 It is concluded that in the guinea-pig ileum there are postsynaptic β-adrenoceptors and at least two types of α-adrenoceptors: α1-excitatory postjunctional adrenoceptors activated by phenylephrine, noradrenaline and adrenaline and antagonized by phenoxybenzamine, carbidine and phentolamine; α2-inhibitory prejunctional adrenoceptors activated by ephedrine, noradrenaline and adrenaline and inhibited by yohimbine and phentolamine. The inhibitory postjunctional α-adrenoceptors are more close to the α2-adrenoceptors, since they were stimulated predominantly by ephedrine and noradrenaline and inhibited by yohimbine.
9 It has been shown that all α-adrenoceptor subtypes are to be found at every distance (0 to 70 cm) from the ileocaecal valve and that they can be activated in the resting or in the acetylcholine-contracted states.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Evidence against adrenergic motor transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):359–389. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. A., Lees G. M. Investigation of occurrence of tolerance to bronchodilator drugs in chronically pretreated guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):331–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD H., BURNSTOCK G., CAMPBELL G., JOWETT A., O'SHEA J., WOOD M. The cholinergic blocking action of adrenergic blocking agents in the pharmacological analysis of autonomic innervation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:418–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer V. Distribution and types of adrenoceptors in the guinea-pig ileum: the action of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):201–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman W. C., Hall M. T. Inhibition of rabbit intestine mediated by alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Feb;38(2):399–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb08528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Smith C. F., Walker J. M. Selectivity of blocking agents for pre-and postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterisation of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 21;42(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors which regulate-cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):513P–513P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Pharmacological characterization of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors regulating cholinergic activity in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;64(2):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innes I. R., Kohli J. D. Excitatory action of sympathomimetic amines on 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors of gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;35(3):383–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Lydon R. J., Watt A. J. The effects of adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on inhibitory alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;39(2):398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb12903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of catecholamine release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Jul 1;23(13):1793–1800. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The response of the guineapig ileum to electrical stimulation by coaxial electrodes. J Physiol. 1955 Feb 28;127(2):40–1P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and adrenaline on acetylcholine output by guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle strip. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):10–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Vizi E. S., Zar M. A. The mechanism of acetylcholine release from parasympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;215(3):819–848. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Pre- and postsynaptic components in effect of drugs with alpha adrenoceptor affinity. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):440–441. doi: 10.1038/254440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida R. J., Cowan A., Adler M. W. pA2 and receptor differentiation: a statistical analysis of competitive antagonism. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):637–654. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Differentiation between pre- and postjunctional alpha-receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit aorta. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):225–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Localization of adrenergic receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit jejunum to cholinergic neurons and to smooth muscle cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Feb;99(2):190–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


