Abstract
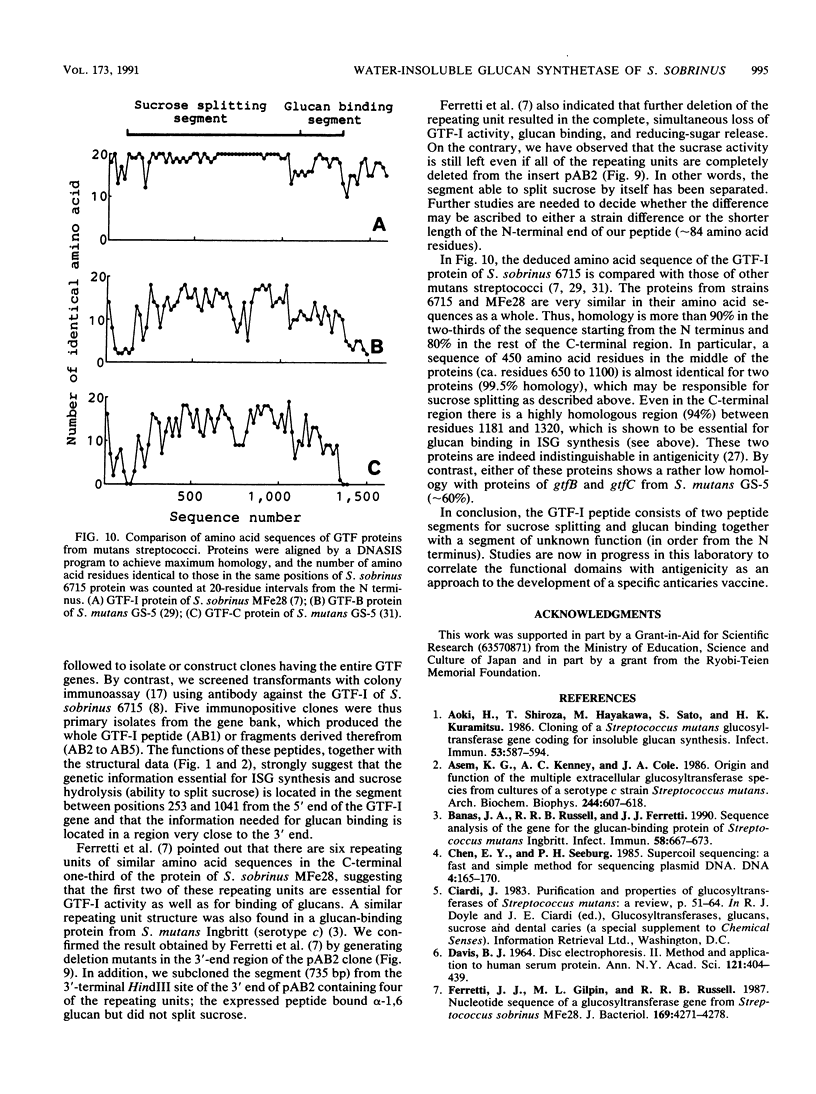
The gene encoding glucosyltransferase responsible for water-insoluble glucan synthesis (GTF-I) of Streptococcus sobrinus (formerly Streptococcus mutans 6715) was cloned, expressed, and sequenced. A gene bank from S. sobrinus 6715 DNA was constructed in vector pUC18 and screened with anti-GTF-I antibody to detect clones producing GTF-I peptide. Five immunopositive clones were isolated, all of which produced peptides that bound alpha-1,6 glucan. GTF-I activity was found in only two large peptides: one stretching over the full length of the GTF-I peptide and composed of about 1,600 amino acid residues (AB1 clone) and the other lacking about 80 N-terminal residues and about 260 C-terminal residues (AB2 clone). A deletion study of the AB2 clone indicated that specific glucan binding, which is essential for water-insoluble glucan synthesis, was lost prior to sucrase activity with an increase in deletion from the 3' end of the GTF-I gene. These results suggest that the GTF-I peptide consists of three segments: that for sucrose splitting (approximately 1,100 residues), that for glucan binding (approximately 240 residues), and that of unknown function (approximately 260 residues), in order from the N terminus. The primary structure of the GTF-I peptide, deduced by DNA sequencing of the AB1 clone, was found to be very similar to that of the homologous protein from another strain of S. sobrinus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asem K. G., Kenney A. C., Cole J. A. Origin and function of the multiple extracellular glucosyltransferase species from cultures of a serotype c strain of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):607–618. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90629-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banas J. A., Russell R. R., Ferretti J. J. Sequence analysis of the gene for the glucan-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):667–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.667-673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Nucleotide sequence of a glucosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus sobrinus MFe28. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4271-4278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Kokeguchi S., Kato K., Miyake Y., Nogami R., Moriyama T. Immunochemical properties of glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):762–766. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.762-766.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Moriyama T., Miyake Y., Mizutani K., Tanaka O. Purification and properties of glucosyltransferase responsible for water-insoluble glucan synthesis from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.1-9.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R., Morrissey P. Cloning and expression of two Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):414–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.414-416.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Horikoshi T., Minami T., Okahashi N., Koga T. Purification and characterization of cell-associated glucosyltransferase synthesizing water-insoluble glucan from serotype c Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):335–344. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfC gene, coding for synthesis of both soluble and insoluble glucans. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1999–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1999-2005.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfD gene, coding for primer-dependent soluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2079–2085. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2079-2085.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa H., Gengyo K., McLachlan A. D., Brenner S., Karn J. Paramyosin gene (unc-15) of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and models for thick filament structure. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):311–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Koga K., Hayashida O., Nakano Y., Hasegawa Y. Glucan-binding domain of a glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus sobrinus: isolation of a 55-kilodalton peptide from a trypsin digest of glucosyltransferase prebound to insoluble glucan. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2210–2213. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2210-2213.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser G., Wong C. Isolation of a glucan-binding domain of glucosyltransferase (1,6-alpha-glucan synthase) from Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):880–884. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.880-884.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Purification and characterization of cell-associated glucosyltransferase synthesizing insoluble glucan from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):2055–2063. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-2055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Jones K. R., Kuramitsu H. K., Macrina F. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the glucosyltransferase C gene (gtfC) from Streptococcus mutans LM7. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2176–2182. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2176-2182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Gilpin M. L., Mukasa H., Dougan G. Characterization of glucosyltransferase expressed from a Streptococcus sobrinus gene cloned in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):935–944. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Ueda S., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfB gene from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4263–4270. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4263-4270.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsumori H., Kumada H., Umemoto T., Shimamura A., Mukasa H. Purification and characterization of extracellular glucosyltransferase synthesizing water-insoluble glucan from Streptococcus rattus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):325–333. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Shiroza T., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfC gene from Streptococcus mutans GS-5. Gene. 1988 Sep 15;69(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Hanada N., Takehara T. Purification of a fourth glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus sobrinus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6265–6270. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6265-6270.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






