Abstract
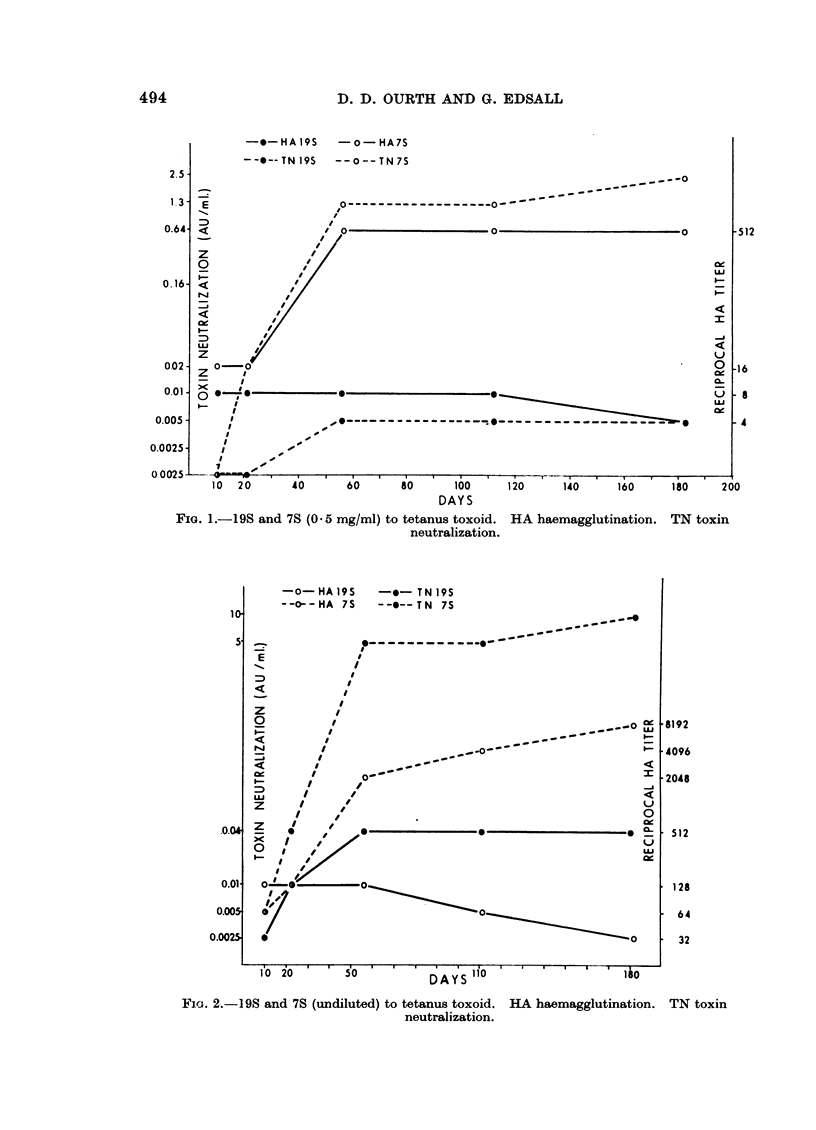
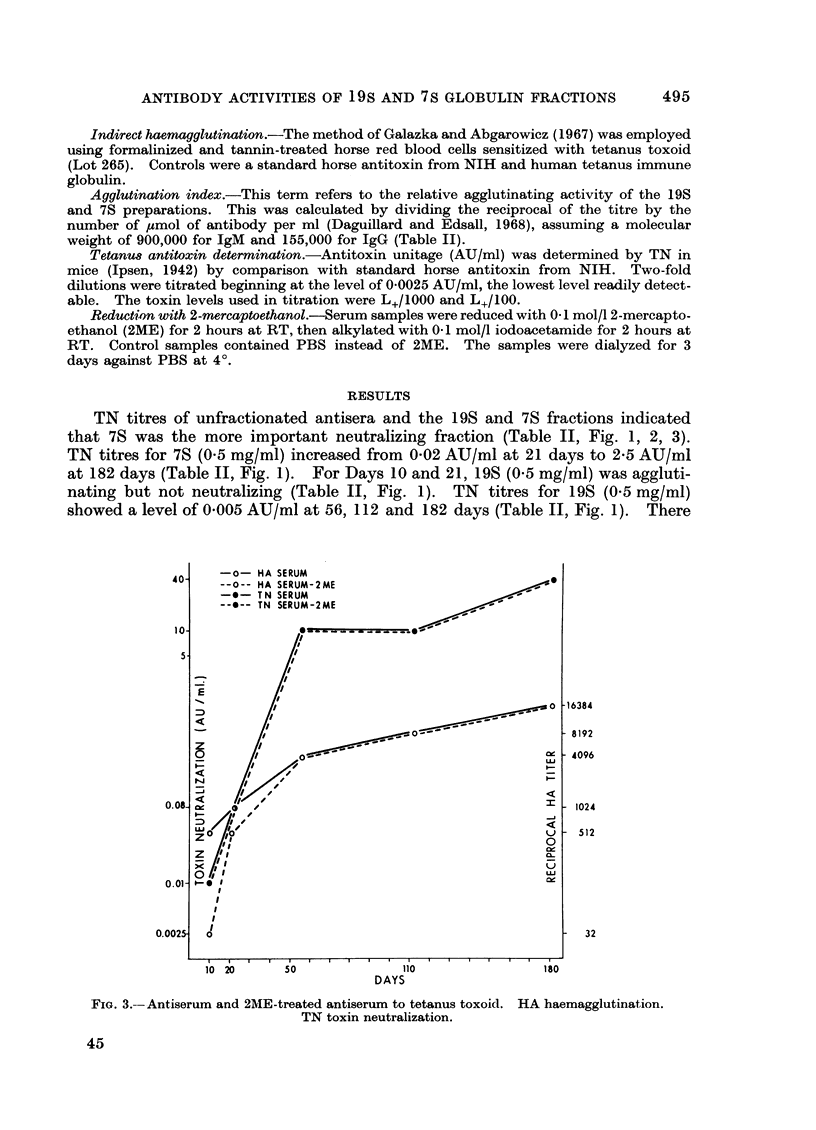
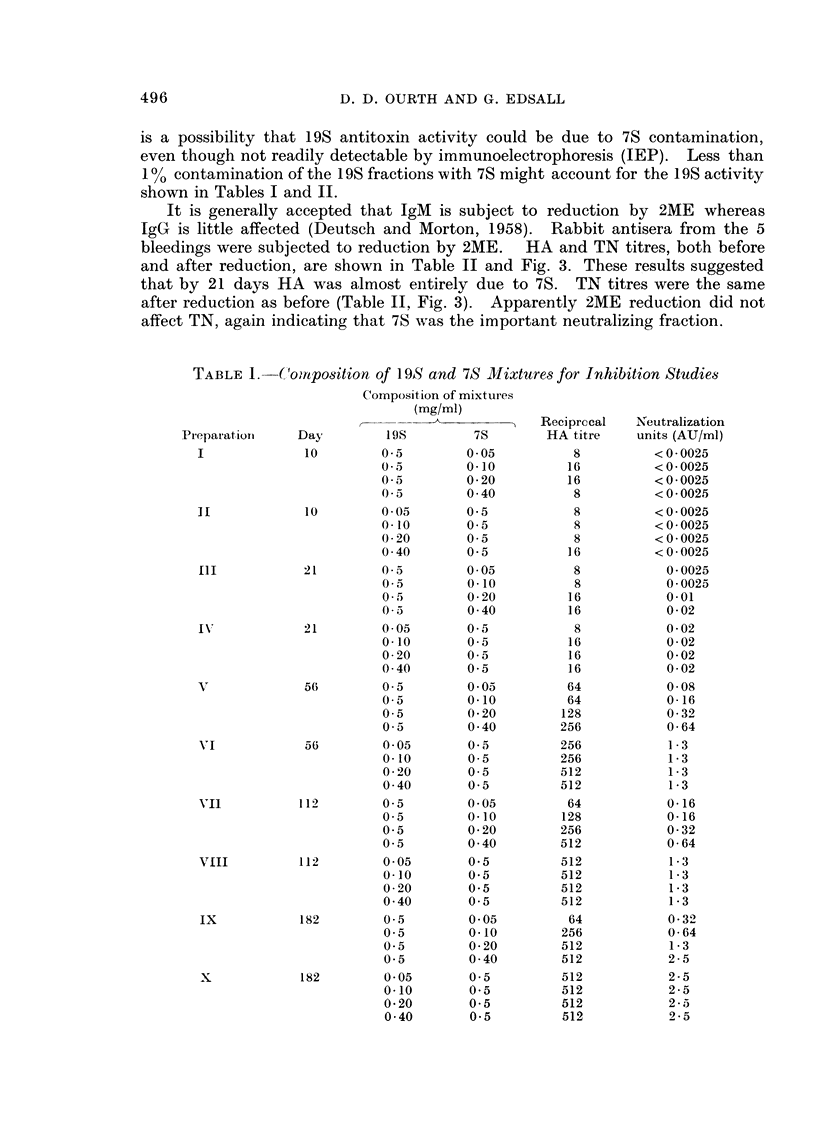
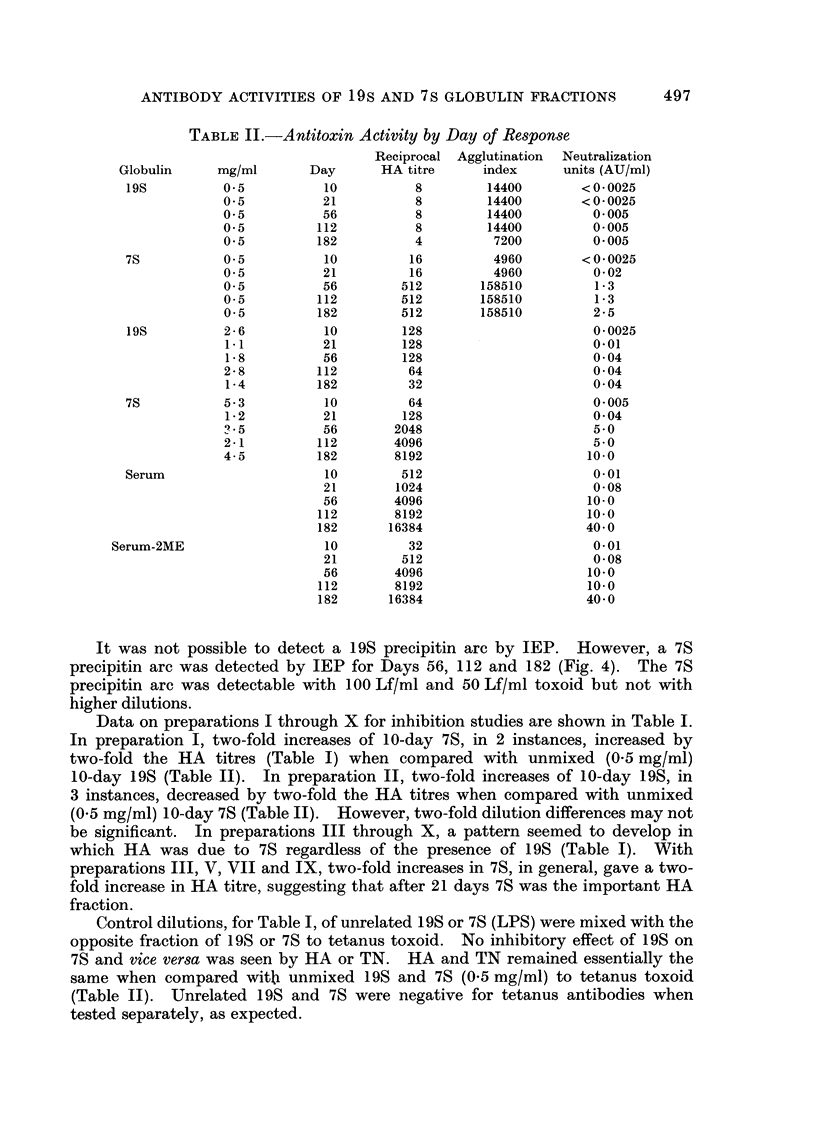
The immune response in rabbits to tetanus toxoid was followed from 10 to 182 days. It was found that 7S became 500 times more efficient in toxin neutralization (TN) and 11 times greater in haemagglutination (HA) than 19S during this time period. No evidence that 19S inhibited 7S and vice versa by TN or HA was apparent at the concentrations tested. Precipitation in gel of tetanus toxoid was demonstrated only with 7S.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer D. C., Stavitsky A. B. ON THE DIFFERENT MOLECULAR FORMS OF ANTIBODY SYNTHESIZED BY RABBITS DURING THE EARLY RESPONSE TO A SINGLE INJECTION OF PROTEIN AND CELLULAR ANTIGENS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct;47(10):1667–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH H. F., MORTON J. I. Human serum macroglobulins and dissociation units. I. Physicochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):1107–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daguillard F., Edsall G. The agglutinating and bactericidal activity of IgM and IgG antibodies to the 9 and 12 factors of Salmonella typhi O 901. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):1112–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolby J. M., Dolby D. E. The antibody activities of 19S and 7S fractions from rabbit antisera to Bordetella pertussis. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):737–747. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M. STUDIES ON CHANGES IN THE QUALITY OF RABBIT-BOVINE SERUM ALBUMIN ANTIBODY FOLLOWING IMMUNIZATION. Immunology. 1964 Jan;7:82–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R., Garvey J. S. Prolonged antibody production in rats after single injection of KLH coated on bentonite. Immunochemistry. 1969 Sep;6(5):766–767. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEREMANS J. F., VAERMAN J. P., VAERMAN C. STUDIES ON THE IMMUNE GLOBULINS OF HUMAN SERUM. II. A STUDY OF THE DISTRIBUTION OF ANTI-BRUCELLA AND ANTI-DIPHTHERIA ANTIBODY ACTIVITIES AMONG GAMMA-SS, GAMMA-IM AND GAMMA-1A-GLOBULIN FRACTIONS. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist K. J. A unique class of rabbit immunoglobulins eliciting passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in homologous skin. Immunochemistry. 1968 Nov;5(6):525–542. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist K., Bauer D. C. Precipitin activity of rabbit macroglobulin antibody. Immunochemistry. 1966 Sep;3(5):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDY W. J., RIVERS M. M., NISONOFF A. Recombination of univalent subunits derived from rabbit antibody. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3221–3226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osler A. G., Mulligan J. J., Jr, Rodriguez E. Weight estimates of rabbit anti-human serum albumin based on antigen-binding and precipitin analyses: specific hemagglutinating activities of 7 S and 19 S components. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):334–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M. Antibody heterogeneity and serological reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):157–174. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.157-174.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. B., KENNY K., SUTER E. THE ISOLATION AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF RABBIT GAMMA M- AND GAMMA G-ANTI-SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM ANTIBODIES. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:385–402. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALIAFERRO W. H., TALIAFERRO L. G. Intercellular transfer of gamma-1 and gamma-2 Forssman hemolysins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 May 15;47:713–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.5.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner K. J., Krishnapillai V. The influence of IgM antibody on the neutralisation of T4r bacteriophage by IgG antibody. Immunochemistry. 1968 Jan;5(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Finkelstein M. S. The kinetics of antibody formation. Prog Allergy. 1967;10:37–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G. The immune response to influenza virus. 3. Changes in the avidity and specificity of early IgM and IgG antibodies. Immunology. 1968 Jan;14(1):39–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., Liu C. T., Adler F. L. Studies on passive hemagglutination. I. Titration of "early" and "late" antibodies with tanned red cells sensitized with native or denatured bovine serum albumin. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):879–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]