Abstract
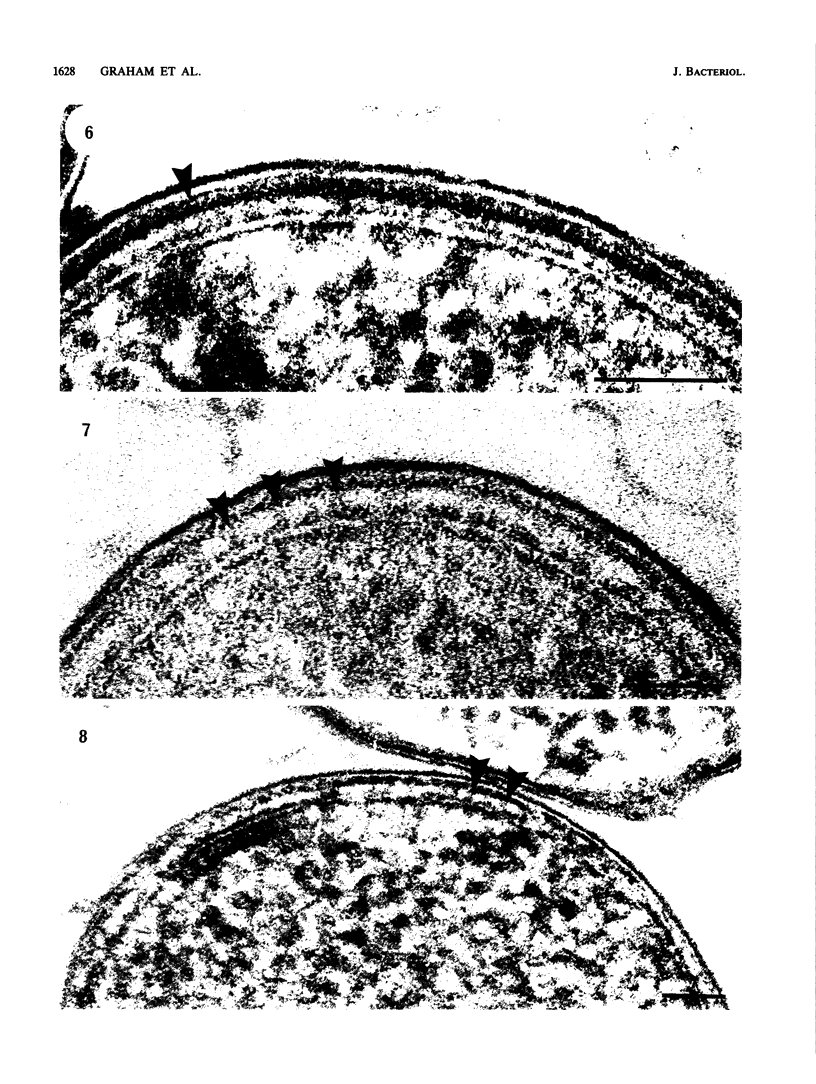
Freeze-substitution was performed on strains of Escherichia coli, Pasteurella multocida, Campylobacter fetus, Vibrio cholerae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida, Aeromonas salmonicida, Proteus mirabilis, Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae, Caulobacter crescentus, and Leptothrix discophora with a substitution medium composed of 2% osmium tetroxide and 2% uranyl acetate in anhydrous acetone. A thick periplasmic gel ranging from 10.6 to 14.3 nm in width was displayed in E. coli K-12, K30, and His 1 (a K-12 derivative containing the K30 capsule genes), P. multocida, C. fetus, P. putida, A. salmonicida, H. pleuropneumoniae, and P. mirabilis. The other bacteria possessed translucent periplasms in which a thinner peptidoglycan layer was seen. Capsular polysaccharide, evident as electron-dense fibers radiating outward perpendicular to the cell surface, was observed on E. coli K30 and His 1 and P. mirabilis cells. A more random arrangement of fibers forming a netlike structure was apparent surrounding cells of H. pleuropneumoniae. For the first time a capsule, distinct from the sheath, was observed on L. discophora. In all instances, capsular polysaccharide was visualized in the absence of stabilizing agents such as homologous antisera or ruthenium red. Other distinct envelope structures were observed external to the outer membrane including the sheath of L. discophora and the S layers of A. salmonicida A450 and C. crescentus CB15A. We believe that the freeze-substitution technique presents a more accurate image of the structural organization of these cells and that it has revealed complex ultrastructural relationships between cell envelope constituents previously difficult to visualize by more conventional means of preparation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker G., Bitter-Suermann D., Meier-Dieter U., Peters H., Mayer H. Immunocytochemical localization of enterobacterial common antigen in Escherichia coli and Yersinia enterocolitica cells. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):348–356. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.348-356.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams L. F., Ghiorse W. C. Influence of Manganese on Growth of a Sheathless Strain of Leptothrix discophora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):556–562. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.556-562.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Meno Y., Takade A. Fine structures of the capsules of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4960–4962. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4960-4962.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Okada K., Miake S. Evidence for the presence of a capsule in Vibrio vulnificus. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Oct;130(10):2741–2743. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-10-2741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Takade A. The fine structure of Bacillus subtilis revealed by the rapid-freezing and substitution-fixation method. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1985;34(1):13–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. H., Costello G. P., Bayer M. E. Isolation and partial characterization of membrane vesicles carrying markers of the membrane adhesion sites. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):758–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.758-767.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope G. H., Williams M. A. Quantitative studies on neutral lipid preservation in electron microscopy. J R Microsc Soc. 1968;88(2):259–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1968.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope G. H., Williams M. A. Quantitative studies on the preservation of choline and ethanolamine phosphatides during tissue preparation for electron microscopy. I. Glutaraldehyde, osmium tetroxide, Araldite methods. J Microsc. 1969;90(1):31–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope G. H., Williams M. A. Quantitative studies on the preservation of choline and ethanolamine phosphatides during tissue preparation for electron microscopy. II. Other preparative methods. J Microsc. 1969;90(1):47–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., McDowall A. W., Menge B., Schmid E. N., Lickfeld K. G. Electron microscopy of frozen-hydrated bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.381-390.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J. Physicochemical roles of soluble metal cations in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K-12. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jul;32(7):594–601. doi: 10.1139/m86-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J. Site specificity of metallic ion binding in Escherichia coli K-12 lipopolysaccharide. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Jan;32(1):52–55. doi: 10.1139/m86-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L., Beveridge T. J. Effect of chemical fixatives on accurate preservation of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis structure in cells prepared by freeze-substitution. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2150–2159. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2150-2159.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. L., Beveridge T. J. Evaluation of freeze-substitution and conventional embedding protocols for routine electron microscopic processing of eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2141–2149. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2141-2149.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Villiger W., Escaig J., Maeder M., Ryter A., Kellenberger E. Shape and fine structure of nucleoids observed on sections of ultrarapidly frozen and cryosubstituted bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):960–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.960-971.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Graham L. Improved preservation of bacterial capsule for electron microscopy. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1989 Feb;11(2):167–169. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060110212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Buckley J. T., Ishiguro E. E., Phipps B. M., Monette J. P., Trust T. J. Purification and disposition of a surface protein associated with virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1077–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1077-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E. The 'Bayer bridges' confronted with results from improved electron microscopy methods. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):697–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. J., Downey J., Clapham L., Nickel J. C. A simple technique for studying struvite crystal growth in vitro. Urol Res. 1990;18(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00294580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meno Y., Amako K. Morphological evidence for penetration of anti-O antibody through the capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1421–1428. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1421-1428.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Grano D. A., Glaeser R. M., Agabian N. Periodic surface array in Caulobacter crescentus: fine structure and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1135–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1135-1150.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda A., Ueki Y., Amako K. Structure of the Staphylococcus aureus cell wall determined by the freeze-substitution method. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2482–2487. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2482-2487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibull C., Christiansson A., Carlemalm E. Extraction of membrane lipids during fixation, dehydration and embedding of Acholeplasma laidlawii-cells for electron microscopy. J Microsc. 1983 Feb;129(Pt 2):201–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Schoenhals G., Graham L. Mutants of Escherichia coli O9:K30 with altered synthesis and expression of the capsular K30 antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Oct;135(10):2589–2599. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-10-2589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]