Abstract
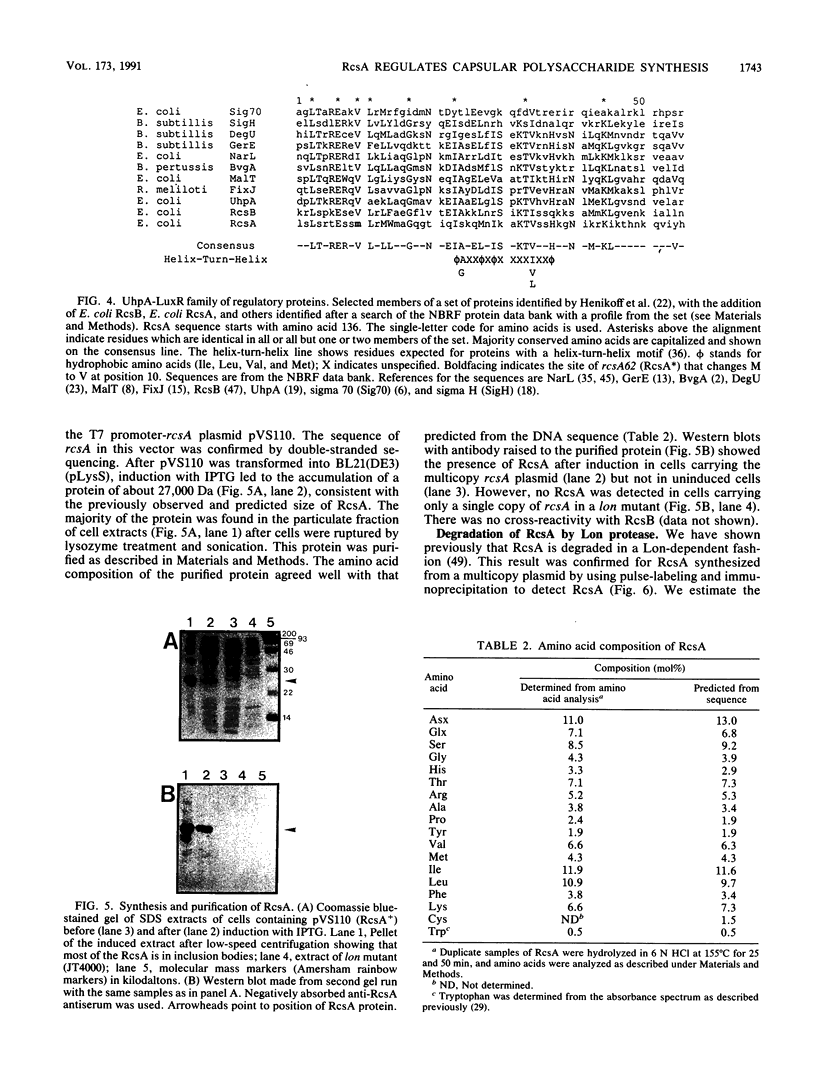
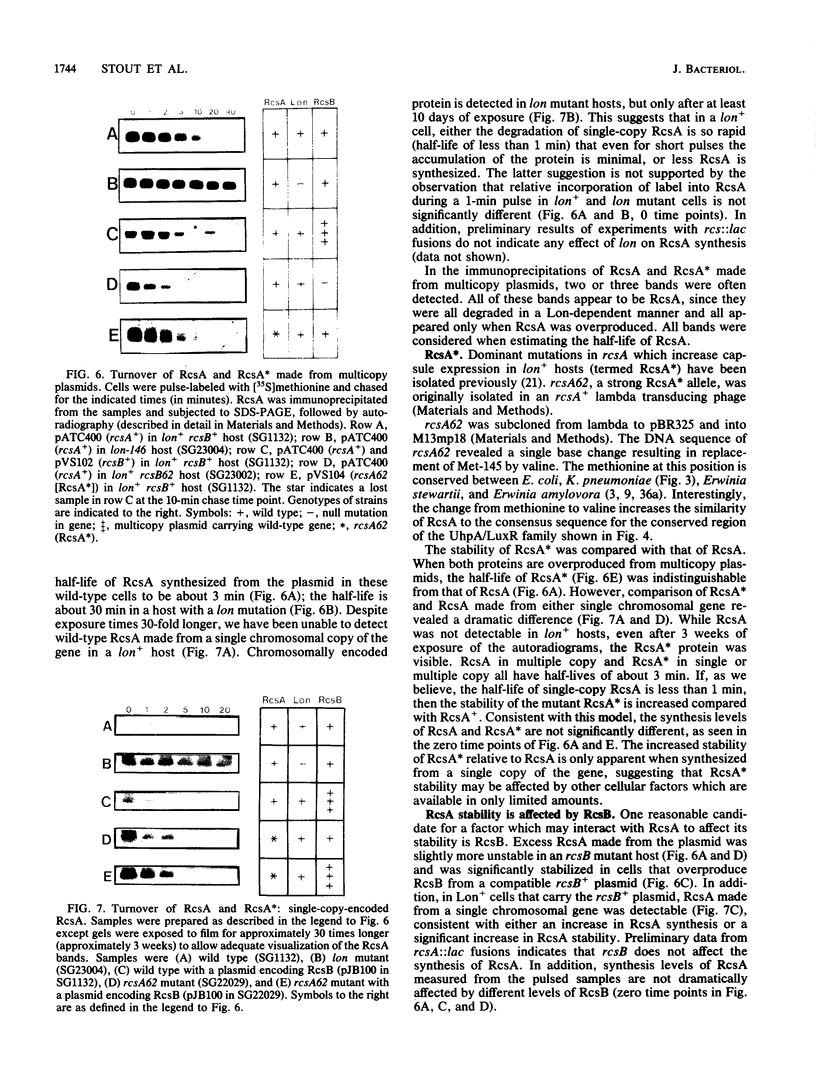
RcsA is an unstable positive regulator required for the synthesis of colanic acid capsular polysaccharide in Escherichia coli. Degradation of the RcsA protein in vivo depends on the ATP-dependent Lon protease. DNA sequence analysis of the rcsA gene reveals a single open reading frame for a 23,500-Da highly basic protein (pI = 9.9), consistent with the observed size of the purified subunit of RcsA. The DNA and protein sequences are highly homologous to the rcsA gene and protein from Klebsiella pneumoniae and other species. The carboxy-terminal region of RcsA contains a possible helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif that resembles sequences found at the carboxy terminus of RcsB, another positive regulator of capsule synthesis, and in several other transcriptional regulators including members of the LuxR family. rcsA62, a mutation in rcsA that leads to increased capsule synthesis, encodes a protein designated RcsA*, which differs from wild-type RcsA only in the replacement of Met-145 by valine. The RcsA* protein is subject to Lon-dependent degradation. The stability of wild-type RcsA in vivo is increased by multicopy RcsB. Conversely, RcsA is degraded more rapidly in rcsB mutant hosts than in wild-type hosts. These results suggest that RcsA and RcsB interact in vivo and are consistent with genetic experiments that indicate an interaction between RcsA and RcsB. Based on these experiments, we propose a model for capsule regulation in which RcsA interacts directly with RcsB to promote transcription of the genes for capsule synthesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P., Hart C. A., Saunders J. R. Isolation from Klebsiella and characterization of two rcs genes that activate colanic acid capsular biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):331–340. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard F., Poetter K., Geider K., Coplin D. L. The rcsA gene from Erwinia amylovora: identification, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Nov-Dec;3(6):429–437. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill J. A., Quinlan-Walshe C., Gottesman S. Fine-structure mapping and identification of two regulators of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2599–2611. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2599-2611.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Raibaud O. The nucleotide sequence of the malT gene encoding the positive regulator of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon. Gene. 1986;42(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M., Pearce R., Hitchin E., Busfield F., Mansfield J. W., Roberts I. S. Molecular cloning, expression and nucleotide sequence of the rcsA gene of Erwinia amylovora, encoding a positive regulator of capsule expression: evidence for a family of related capsule activator proteins. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Sep;136(9):1799–1806. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-9-1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coplin D. L., Cook D. Molecular genetics of extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis in vascular phytopathogenic bacteria. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Sep-Oct;3(5):271–279. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coplin D. L., Frederick R. D., Majerczak D. R., Haas E. S. Molecular cloning of virulence genes from Erwinia stewartii. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):619–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.619-623.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Mandelstam J. The nucleotide sequence and the transcription during sporulation of the gerE gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):3013–3024. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Majerczak D. R., Coplin D. L. Characterization of a gene cluster for exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and virulence in Erwinia stewartii. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):865–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.865-871.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Weir J., Nair G., Carter L., 3rd, Moran C., Jr, Smith I. Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for sigma 30 (sigma H). J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1054-1062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich M. J., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the uhp region of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3556–3563. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3556-3563.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Castellazzi M., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. III. Mutations sfiA and sfiB restore division in tif and lon strains and permit the expression of mutator properties of tif. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):309–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Trisler P., Torres-Cabassa A. Regulation of capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12: characterization of three regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1111–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1111-1119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Wallace J. C., Brown J. P. Finding protein similarities with nucleotide sequence databases. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:111–132. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Ferrari E. Localization of Bacillus subtilis sacU(Hy) mutations to two linked genes with similarities to the conserved procaryotic family of two-component signalling systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5102–5109. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5102-5109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R., Gottesman S. Cell-division control in Escherichia coli: specific induction of the SOS function SfiA protein is sufficient to block septation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Holland I. B. Role of the SulB (FtsZ) protein in division inhibition during the SOS response in Escherichia coli: FtsZ stabilizes the inhibitor SulA in maxicells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., Gottesman S., Pumphrey J., Rudikoff S., Clark W. P., Maurizi M. R. The two-component, ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. Purification, cloning, and mutational analysis of the ATP-binding component. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15226–15236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. L., Federici M. M. Quantitation of aromatic residues in proteins: model compounds for second-derivative spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2600–2606. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J., Sanjanwala B., Lowe M. Overproduction of FtsZ suppresses sensitivity of lon mutants to division inhibition. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):756–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.756-762.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Trisler P., Gottesman S. Insertional mutagenesis of the lon gene in Escherichia coli: lon is dispensable. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1124–1135. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1124-1135.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum K. L., Whitfield C. The rcsA gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae O1:K20 is involved in expression of the serotype-specific K (capsular) antigen. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):494–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.494-502.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Court D., Gottesman S. Transcription of the sulA gene and repression by LexA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 15;171(3):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Gottesman S. Protein degradation in Escherichia coli: the lon gene controls the stability of sulA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):358–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Noji S., Taniguchi S., Saito T. The narX and narL genes encoding the nitrate-sensing regulators of Escherichia coli are homologous to a family of prokaryotic two-component regulatory genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):2947–2957. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Raibaud O. MalT, the regulatory protein of the Escherichia coli maltose system, is an ATP-dependent transcriptional activator. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):981–987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J. G. Functional antibody lacking a variable-region disulfide bridge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7875–7878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker J. M., Gayda R. C., Markovitz A. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli: SOS induction and cellular location of the sulA protein, a key to lon-associated filamentation and death. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):551–561. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.551-561.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Parales J., Jr, Merkel S. M. Structure of genes narL and narX of the nar (nitrate reductase) locus in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2229–2234. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2229-2234.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Gottesman S. RcsB and RcsC: a two-component regulator of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):659–669. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.659-669.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Cabassa A. S., Gottesman S. Capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12 is regulated by proteolysis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):981–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.981-989.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Cabassa A., Gottesman S., Frederick R. D., Dolph P. J., Coplin D. L. Control of extracellular polysaccharide synthesis in Erwinia stewartii and Escherichia coli K-12: a common regulatory function. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4525–4531. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4525-4531.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trisler P., Gottesman S. lon transcriptional regulation of genes necessary for capsular polysaccharide synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):184–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.184-191.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trun N. J., Silhavy T. J. PrlC, a suppressor of signal sequence mutations in Escherichia coli, can direct the insertion of the signal sequence into the membrane. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):665–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkewich-Péotti K., Fraser J. M. New locus for exopolysaccharide overproduction in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1405–1407. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1405-1407.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]