Abstract
We isolated and sequenced a clone for Candida albicans enolase from a C. albicans cDNA library by using molecular genetic techniques. The 1.4-kbp cDNA encoded one long open reading frame of 440 amino acids which was 87 and 75% similar to predicted enolases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and enolases from other organisms, respectively. The cDNA included the entire coding region and predicted a protein of molecular weight 47,178. The codon usage was highly biased and similar to that found for the highly expressed EF-1 alpha proteins of C. albicans. Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed that the enolase cDNA hybridized to an abundant C. albicans mRNA of 1.5 kb present in both yeast and hyphal growth forms. The polypeptide product of the cloned cDNA, which was purified as a recombinant protein fused to glutathione S-transferase, had enolase enzymatic activity and inhibited radioimmunoprecipitation of a single C. albicans protein of molecular weight 47,000. Analysis of the predicted C. albicans enolase showed strong conservation in regions of alpha helices, beta sheets, and beta turns, as determined by comparison with the crystal structure of apo-enolase A of S. cerevisiae. The lack of cysteine residues and a two-amino-acid insertion in the main domain differentiated C. albicans enolase from S. cerevisiae enolase. Immunofluorescence of whole C. albicans cells by using a mouse antiserum generated against the purified fusion protein showed that enolase is not located on the surface of C. albicans. Recombinant C. albicans enolase will be useful in understanding the pathogenesis and host immune response in disseminated candidiasis, since enolase is an immunodominant antigen which circulates during disseminated infections.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. G., Corces V. G. The nucleotide sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster enolase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):191–191. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseret F., Keith G., Rihn B., Amiri I., Werneburg B., Girardot R., Baldacini O., Green G., Nguyen V. K., Monteil H. Clostridium difficile toxin B: characterization and sequence of three peptides. J Chromatogr. 1989 May 5;490(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)82764-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer J. M. Yeast enolase: mechanism of activation by metal ions. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;11(3):209–254. doi: 10.3109/10409238109108702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle P. K., Holland J. P., Willett C. E., Innis M. A., Holland M. J. Multiple factors bind the upstream activation sites of the yeast enolase genes ENO1 and ENO2: ABFI protein, like repressor activator protein RAP1, binds cis-acting sequences which modulate repression or activation of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4872–4885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calì L., Feo S., Oliva D., Giallongo A. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the human muscle-specific enolase (MSE). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1893–1893. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin C. C., Brewer J. M., Wold F. The amino acid sequence of yeast enolase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1377–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Yokoi T., Holland J. P., Pepper A. E., Holland M. J. Transcription of the constitutively expressed yeast enolase gene ENO1 is mediated by positive and negative cis-acting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2753–2761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklyn K. M., Warmington J. R., Ott A. K., Ashman R. B. An immunodominant antigen of Candida albicans shows homology to the enzyme enolase. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;68(Pt 3):173–178. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giallongo A., Feo S., Moore R., Croce C. M., Showe L. C. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for human alpha enolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6741–6745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudot-Crozel V., Caillol D., Djabali M., Dessein A. J. The major parasite surface antigen associated with human resistance to schistosomiasis is a 37-kD glyceraldehyde-3P-dehydrogenase. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2065–2080. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P. Isolation and identification of yeast messenger ribonucleic acids coding for enolase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and phosphoglycerate kinase. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4900–4907. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P., Thill G. P., Jackson K. A. The primary structures of two yeast enolase genes. Homology between the 5' noncoding flanking regions of yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1385–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaghad M., Dumont X., Chalon P., Lelias J. M., Lamandé N., Lucas M., Lazar M., Caput D. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs alpha and gamma enolase mRNAs from mouse brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3638–3638. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz M. B., Cortelyou M. W., Kirsch D. R. Integrative transformation of Candida albicans, using a cloned Candida ADE2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal S. K., Johnson S., Conway T., Kelley P. M. Characterization of a maize cDNA that complements an enolase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):787–795. doi: 10.1007/BF00015071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebioda L., Stec B., Brewer J. M. The structure of yeast enolase at 2.25-A resolution. An 8-fold beta + alpha-barrel with a novel beta beta alpha alpha (beta alpha)6 topology. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3685–3693. doi: 10.2210/pdb2enl/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebioda L., Stec B. Mapping of isozymic differences in enolase. Int J Biol Macromol. 1991 Apr;13(2):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(91)90055-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losberger C., Ernst J. F. Sequence of the Candida albicans gene encoding actin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9488–9488. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra P. K., Lobo Z. A kinetic study of glycolytic enzyme synthesis in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):475–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. B., Brandt M. E., Buckley H. R. Enolase activity associated with a C. albicans cytoplasmic antigen. Yeast. 1989 Apr;5(Spec No):S231–S239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R., Burnie J. Cloning of a DNA sequence encoding a major fragment of the 47 kilodalton stress protein homologue of Candida albicans. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 1;51(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleese S. M., Dunbar B., Fothergill J. E., Hinks L. J., Day I. N. Complete amino acid sequence of the neurone-specific gamma isozyme of enolase (NSE) from human brain and comparison with the non-neuronal alpha form (NNE). Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):413–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Holland M. J. Targeted deletion of a yeast enolase structural gene. Identification and isolation of yeast enolase isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7181–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Mitsui H., Takayama Y., Kushiya E., Sakimura K., Takahashi Y. cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence of rat muscle-specific enolase (beta beta enolase). FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva D., Barba G., Barbieri G., Giallongo A., Feo S. Cloning, expression and sequence homologies of cDNA for human gamma enolase. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90217-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Cole M. D., White A. T., Huang R. C. Sequence organization of cloned intracisternal A particle genes. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranjape V., Datta A. Overexpression of the actin gene is associated with the morphogenesis of Candida albicans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):423–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91387-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peshavaria M., Hinks L. J., Day I. N. Structure of human muscle (beta) enolase mRNA and protein deduced from a genomic clone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8862–8862. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. A., Dunbar B., Fothergill-Gilmore L. A. The complete amino acid sequence of chicken skeletal-muscle enolase. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):115–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2360115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Obinata M., Odani S., Takahashi Y. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of cDNA for neuron-specific enolase messenger RNA of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Obinata M., Takahashi Y. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of cDNA to mRNA for non-neuronal enolase (alpha alpha enolase) of rat brain and liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4365–4378. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Takahashi Y., Suzuki Y. The structure and expression of neuron-specific enolase gene. Gene. 1987;60(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saporito S. M., Sypherd P. S. The isolation and characterization of a calmodulin-encoding gene (CMD1) from the dimorphic fungus Candida albicans. Gene. 1991 Sep 30;106(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90564-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segil N., Shrutkowski A., Dworkin M. B., Dworkin-Rastl E. Enolase isoenzymes in adult and developing Xenopus laevis and characterization of a cloned enolase sequence. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):31–39. doi: 10.1042/bj2510031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. A., Allaudeen H. S., Whitman M. H., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Isolation and characterization of a beta-tubulin gene from Candida albicans. Gene. 1988;63(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec B., Lebioda L. Refined structure of yeast apo-enolase at 2.25 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90023-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Largen M. T., Zweibel S. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and molecular weight characterization of antigens from Candida albicans that are recognized by human sera. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):715–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.715-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
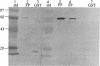
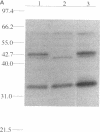
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Characterization of antigens specific to the surface of germ tubes of Candida albicans by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):850–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.850-855.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Enzymatic release of germ tube-specific antigens from cell walls of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.609-614.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Antigenic differences between mannoproteins of germ tubes and blastospores of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):616–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.616-620.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P., Smith D., Sypherd P. S. Sequence analysis and expression of the two genes for elongation factor 1 alpha from the dimorphic yeast Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2036–2045. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2036-2045.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Straeten D., Rodrigues-Pousada R. A., Goodman H. M., Van Montagu M. Plant enolase: gene structure, expression, and evolution. Plant Cell. 1991 Jul;3(7):719–735. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.7.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Hathorn J. W., Sobel J. D., Merz W. G., Sanchez V., Maret S. M., Buckley H. R., Pfaller M. A., Schaufele R., Sliva C. Detection of circulating candida enolase by immunoassay in patients with cancer and invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 11;324(15):1026–1031. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104113241504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng M., Makaroff C. A., Zalkin H. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli pyrG encoding CTP synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5568–5574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wey S. B., Mori M., Pfaller M. A., Woolson R. F., Wenzel R. P. Hospital-acquired candidemia. The attributable mortality and excess length of stay. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Dec;148(12):2642–2645. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.12.2642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G. J., Lietman T., Williams L. A., Stapel S. O., de Jong W. W., Horwitz J., Piatigorsky J. Tau-crystallin/alpha-enolase: one gene encodes both an enzyme and a lens structural protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2729–2736. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]