Abstract
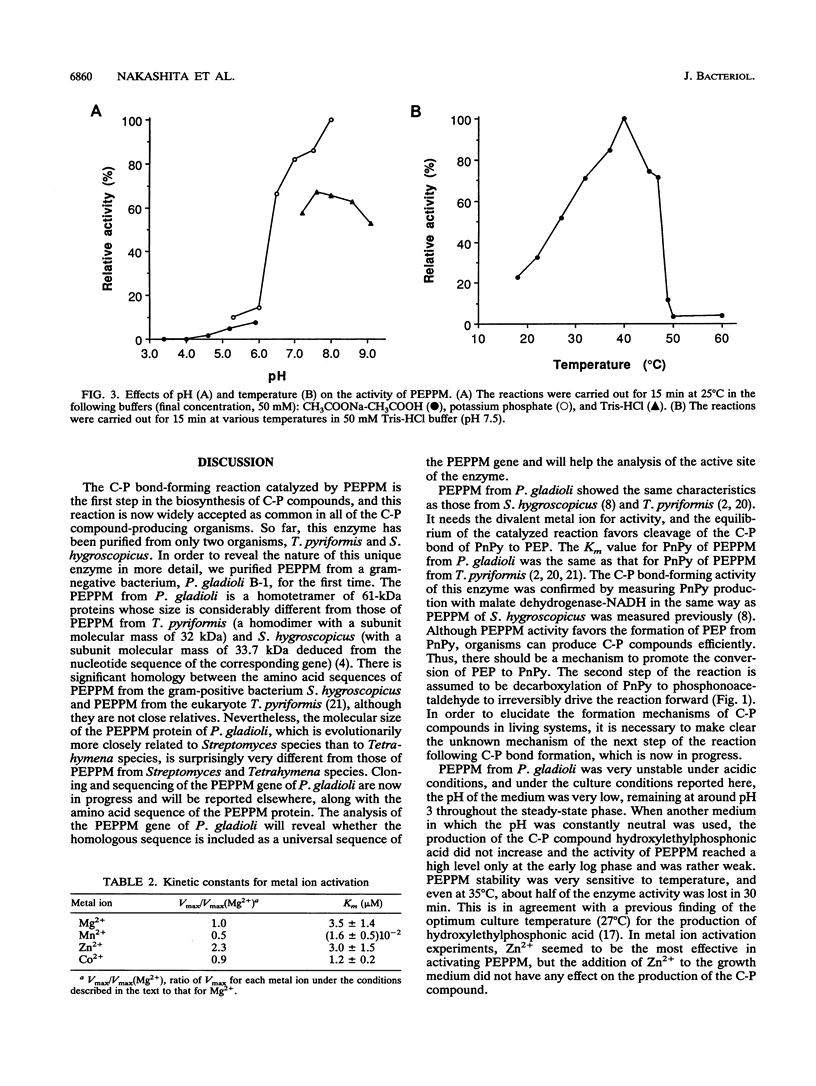
Phosphoenolpyruvate phosphomutase (PEPPM) catalyzes C-P bond formation by intramolecular rearrangement of phosphoenolpyruvate to phosphonopyruvate (PnPy). We purified PEPPM from a gram-negative bacterium, Pseudomonas gladioli B-1 isolated as a C-P compound producer. The equilibrium of this reaction favors the formation of the phosphate ester by cleaving the C-P bond of PnPy, but the C-P bond-forming reaction is physiologically significant. The C-P bond-forming activity of PEPPM was confirmed with a purified protein. The molecular mass of the native enzyme was estimated to be 263 and 220 kDa by gel filtration and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, respectively. A subunit molecular mass of 61 kDa was determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, indicating that the native protein was a tetramer. The optimum pH and temperature were 7.5 to 8.0 and 40 degrees C, respectively. The Km value for PnPy was 19 +/- 3.5 microM, and the maximum initial velocity of the conversion of PnPy to phosphoenolpyruvate was 200 microM/s/mg. PEPPM was activated by the presence of the divalent metal ion, and the Km values were 3.5 +/- 1.4 microM for Mg2+, 16 +/- 5 nM for Mn2+, 3.0 +/- 1.5 microM for Zn2+, and 1.2 +/- 0.2 microM for Co2+.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowman E. D., McQueney M. S., Scholten J. D., Dunaway-Mariano D. Purification and characterization of the Tetrahymena pyriformis P-C bond forming enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate phosphomutase. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7059–7063. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassaigne A., Lacoste A. M., Neuzil E. Transamination non enzymatique des acides aminés phosphoniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 21;252(3):506–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIGUCHI M., KANDATSU M. Isolation of 2-aminoethane phosphonic acid from rumen protozoa. Nature. 1959 Sep 19;184(Suppl 12):901–902. doi: 10.1038/184901b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendlin D., Stapley E. O., Jackson M., Wallick H., Miller A. K., Wolf F. J., Miller T. W., Chaiet L., Kahan F. M., Foltz E. L. Phosphonomycin, a new antibiotic produced by strains of streptomyces. Science. 1969 Oct 3;166(3901):122–123. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3901.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka T., Imai S., Hara O., Anzai H., Murakami T., Nagaoka K., Seto H. Carboxyphosphonoenolpyruvate phosphonomutase, a novel enzyme catalyzing C-P bond formation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3066–3072. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3066-3072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka T., Mori M., Imai S., Hara O., Nagaoka K., Seto H. Studies on the biosynthesis of bialaphos (SF-1293). 9. Biochemical mechanism of C-P bond formation in bialaphos: discovery of phosphoenolpyruvate phosphomutase which catalyzes the formation of phosphonopyruvate from phosphoenolpyruvate. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Mar;42(3):491–494. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai S., Seto H., Sasaki T., Tsuruoka T., Ogawa H., Satoh A., Inouye S., Niida T., Otake N. Studies on the biosynthesis of bialaphos (SF-1293). 6. Production of N-acetyl-demethylphosphinothricin and N-acetylbialaphos by blocked mutants of Streptomyces hygroscopicus SF-1293 and their roles in the biosynthesis of bialaphos. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 May;38(5):687–690. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itasaka O., Hori T., Sugita M. Biochemistry of shellfish lipids. XI. Incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate into ceramide ciliatine (2-aminoethylphosphonic acid) of the fresh-water mussel, Hyriopsis schlegelii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 10;176(4):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama N., Tsubotani S., Nozaki Y., Harada S., Ono H. Fosfadecin and fosfocytocin, new nucleotide antibiotics produced by bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1990 Mar;43(3):238–246. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.43.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. O., Birnbaum J. Biosynthesis of fosfomycin by Streptomyces fradiae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):121–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel H. M., Freeman S., Seto H., Knowles J. R. Phosphonate biosynthesis: isolation of the enzyme responsible for the formation of a carbon-phosphorus bond. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):457–458. doi: 10.1038/335457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel H. M., Pompliano D. L., Knowles J. R. Phosphonate biosynthesis: molecular cloning of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate mutase from Tetrahymena pyriformis and overexpression of the gene product in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2598–2608. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji J., Kato T., Hinoo H., Hattori T., Hirooka K., Matsumoto K., Tanimoto T., Kondo E. Production of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin) by Pseudomonas syringae. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Jul;39(7):1011–1012. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. A. Biosynthesis of phosphonic acids in Tetrahymena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 11;156(2):340–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]