Abstract
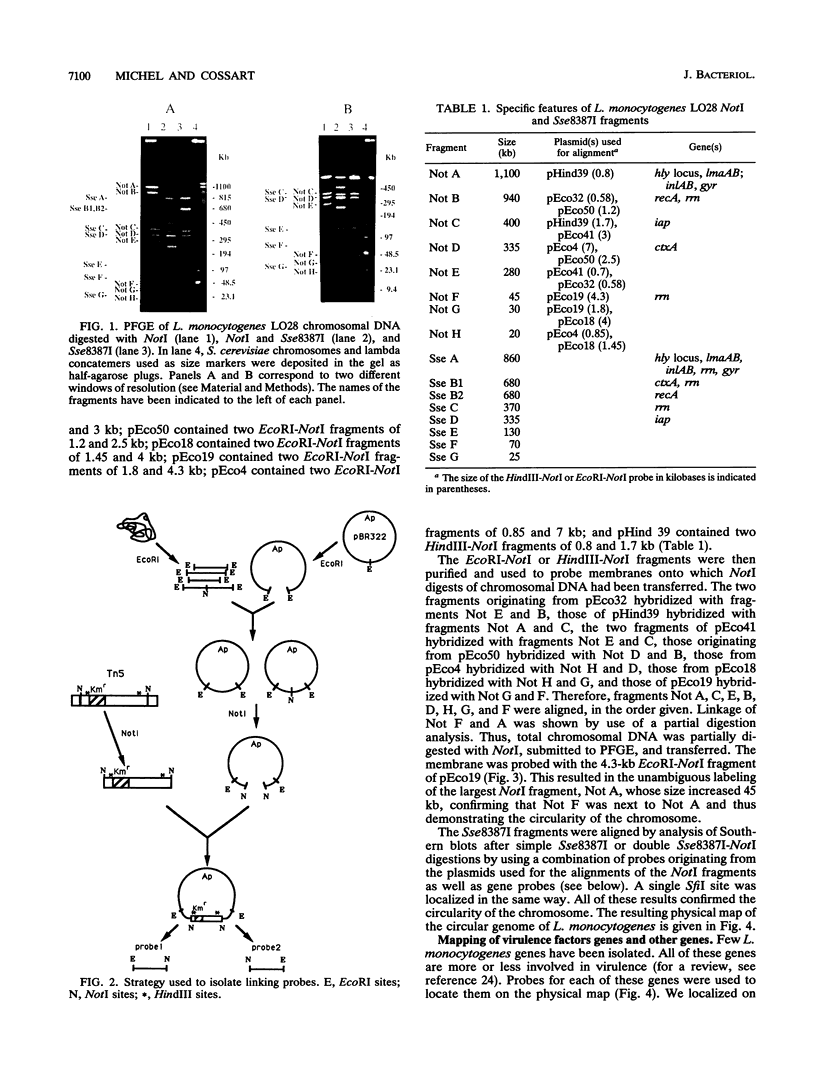
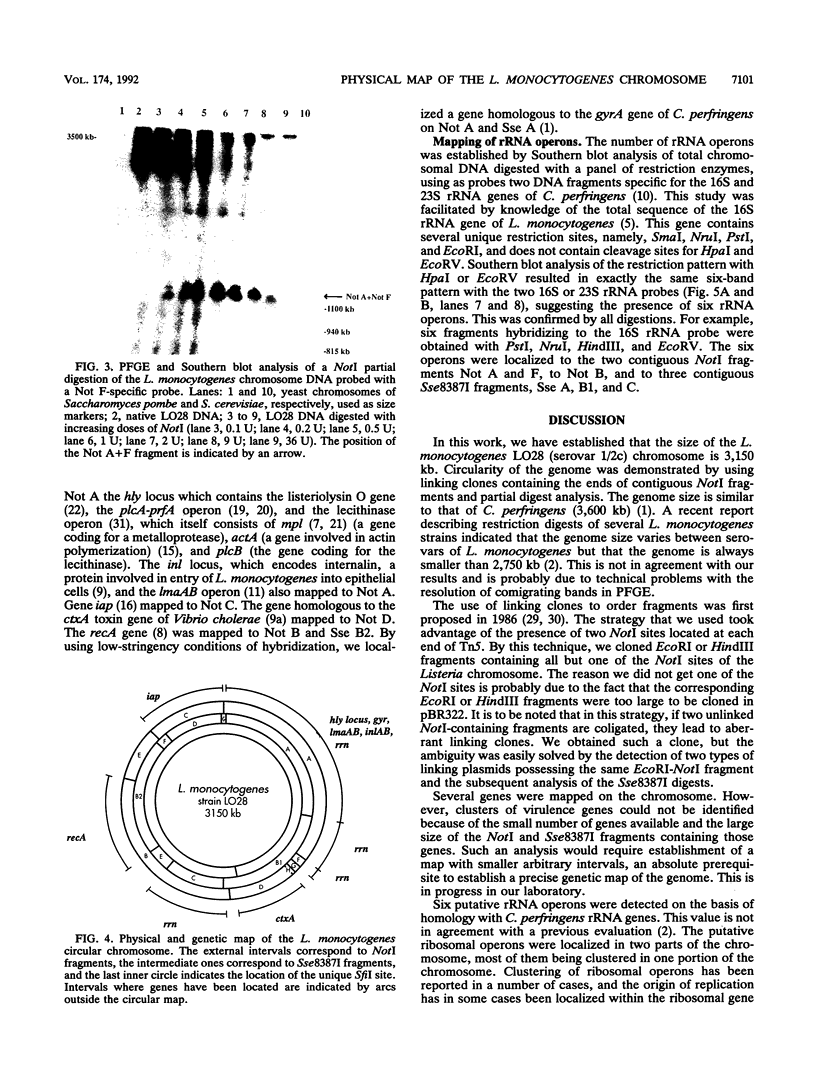
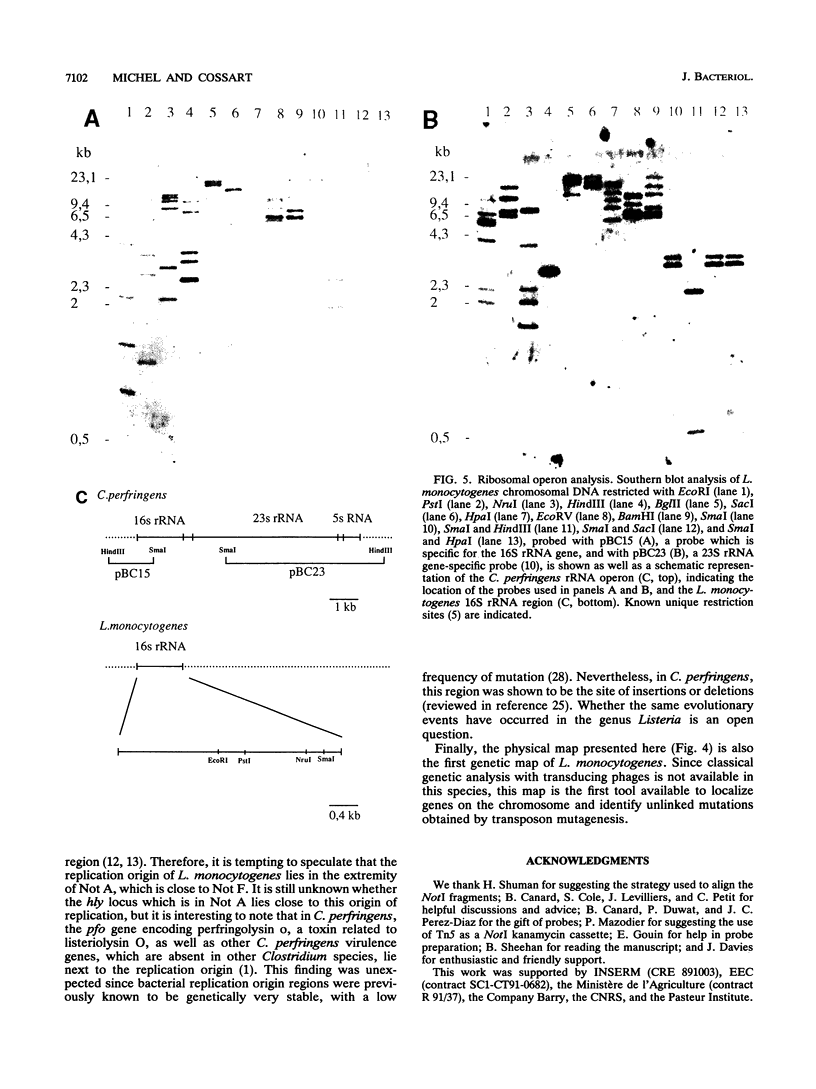
The circular physical map of the pathogenic bacterium Listeria monocytogenes LO28 (serovar 1/2c) was established by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. The L. monocytogenes chromosome contains eight NotI fragments of 1,100, 940, 400, 335, 280, 45, 30, and 20 kb in size and eight Sse8387I fragments of 860, 680, 680, 370, 335, 130, 70, and 25 kb. Therefore, the total length of the genome is 3,150 kb. To order the NotI fragments on the chromosome, we used a strategy which can be of general use. We first cloned chromosomal HindIII or EcoRI fragments in pBR322. DNA extracted from the total libraries was digested by NotI and ligated to a NotI-kanamycin resistance cassette obtained by cutting Tn5 with NotI. After transformation in Escherichia coli, kanamycin-resistant clones originating from NotI-containing EcoRI or HindIII fragments were isolated. The two EcoRI-NotI or HindIII-NotI fragments of each recombinant plasmid were isolated and used as probes on Southern blot hybridizations to identify and link the corresponding NotI fragments. Seven NotI fragments were ordered in this way. The last junction was demonstrated by partial digest analysis. All L. monocytogenes genes identified so far as well as the six rRNA operons were localized on the NotI map. Regions homologous to genes from closely related bacteria were also detected and localized. Southern blot analysis of simple Sse8387I digests or double Sse8387I-NotI digests probed with the various NotI probes allowed us to align the Sse8387I fragments and localize the single SfiI site, resulting in the establishment of the first genetic and physical map of the L. monocytogenes chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canard B., Cole S. T. Genome organization of the anaerobic pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6676–6680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carriere C., Allardet-Servent A., Bourg G., Audurier A., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphism in strains of Listeria monocytogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1351–1355. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1351-1355.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Mengaud J. Listeria monocytogenes. A model system for the molecular study of intracellular parasitism. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):463–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Chakraborty T. Nucleotide sequence of the listeriolysin gene from a Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a strain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6406–6406. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duwat P., Ehrlich S. D., Gruss A. A general method for cloning recA genes of gram-positive bacteria by polymerase chain reaction. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5171–5175. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5171-5175.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier T., Canard B., Cole S. T. Cloning, mapping, and molecular characterization of the rRNA operons of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5431–5438. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5431-5438.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göhmann S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Schiltz E., Goebel W., Chakraborty T. Characterization of a Listeria monocytogenes-specific protein capable of inducing delayed hypersensitivity in Listeria-immune mice. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1091–1099. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henckes G., Vannier F., Seiki M., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H., Seror-Laurent S. J. Ribosomal RNA genes in the replication origin region of Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):268–271. doi: 10.1038/299268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvenberg J. E. Outbreaks of listeriosis/Listeria-contaminated foods. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Dec;5(12):355–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. The gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes and its use as a specific probe for Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1943-1950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Braun-Breton C., Cossart P. Identification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Listeria monocytogenes: a novel type of virulence factor? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Dramsi S., Gouin E., Vazquez-Boland J. A., Milon G., Cossart P. Pleiotropic control of Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by a gene that is autoregulated. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2273–2283. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Geoffroy C., Cossart P. Identification of a new operon involved in Listeria monocytogenes virulence: its first gene encodes a protein homologous to bacterial metalloproteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1043–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1043-1049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel E., Reich K. A., Favier R., Berche P., Cossart P. Attenuated mutants of the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes obtained by single amino acid substitutions in listeriolysin O. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2167–2178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood J. I., Cole S. T. Molecular genetics and pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Dec;55(4):621–648. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.4.621-648.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Shields D. C., Wolfe K. H., Li W. H. Chromosomal location and evolutionary rate variation in enterobacterial genes. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):808–810. doi: 10.1126/science.2683084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Approaches to physical mapping of the human genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):115–122. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente M. F., Pérez-Diaz J. C., Amils R., Baquero F., Marin I. Towards a physical map of the Listeria chromosome: the pulsed field electrophoresis approach. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1989;36(2-3):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]