Abstract
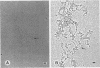
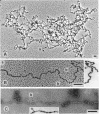
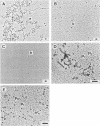
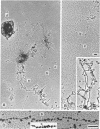
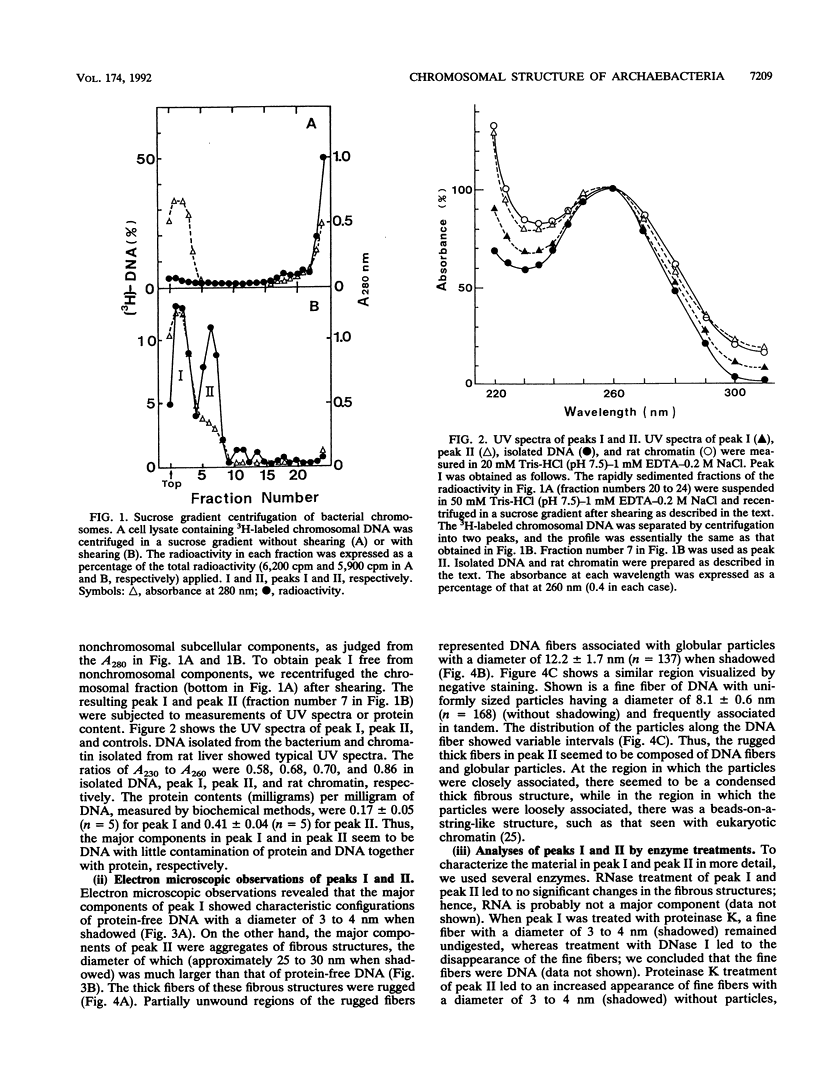
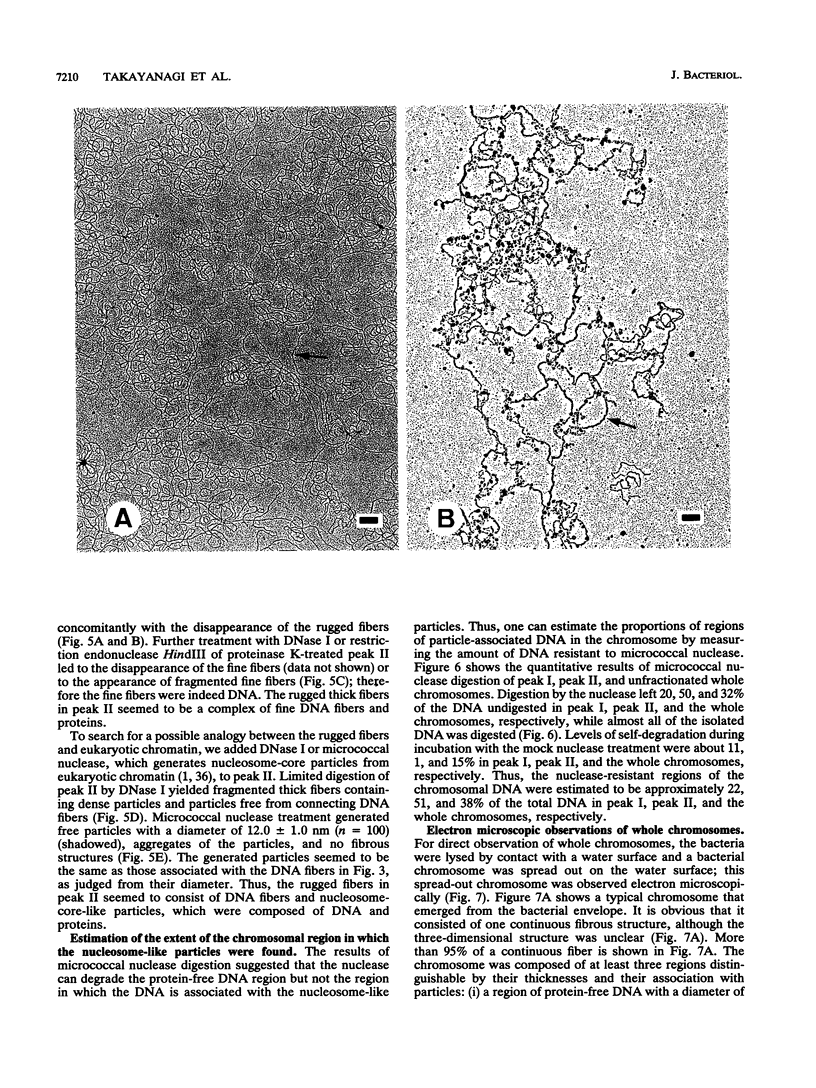
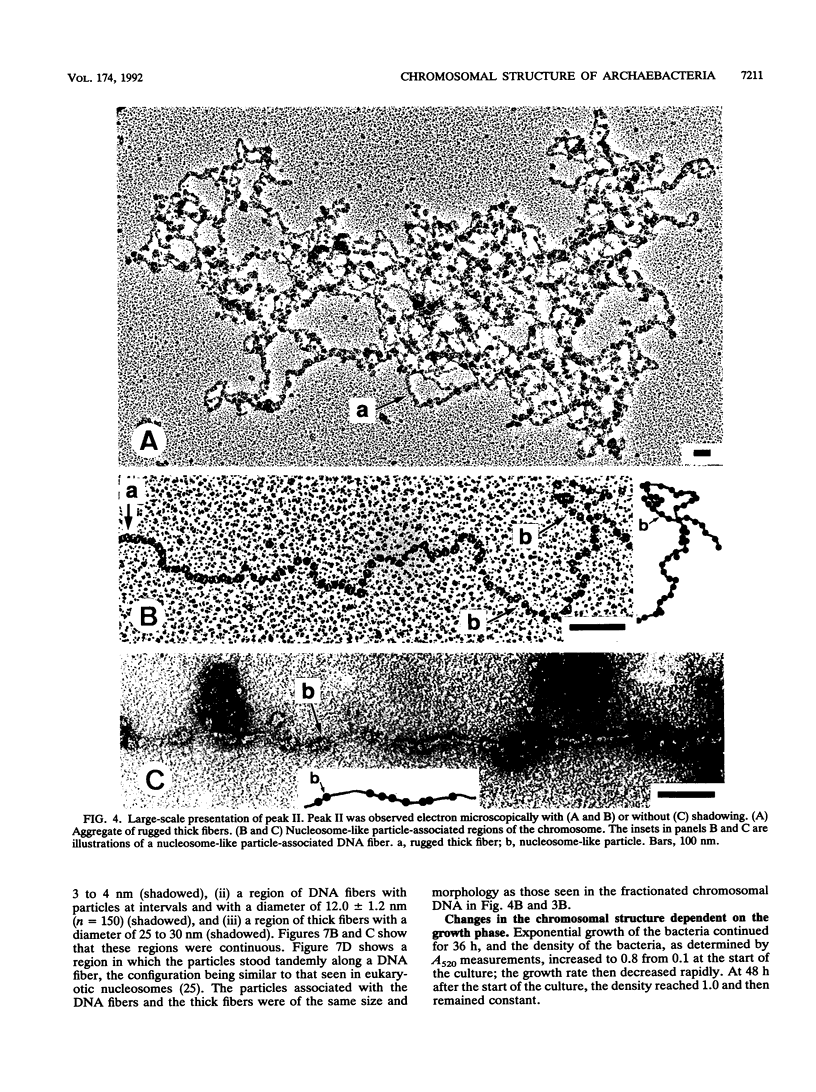
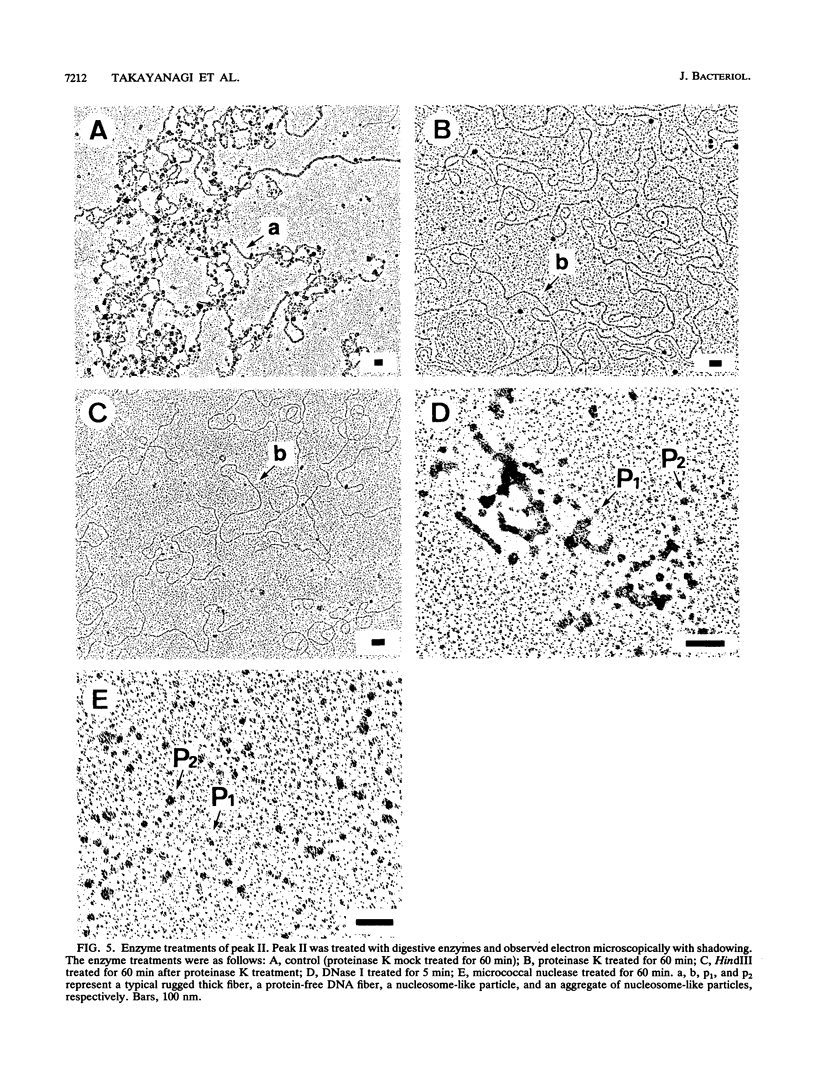
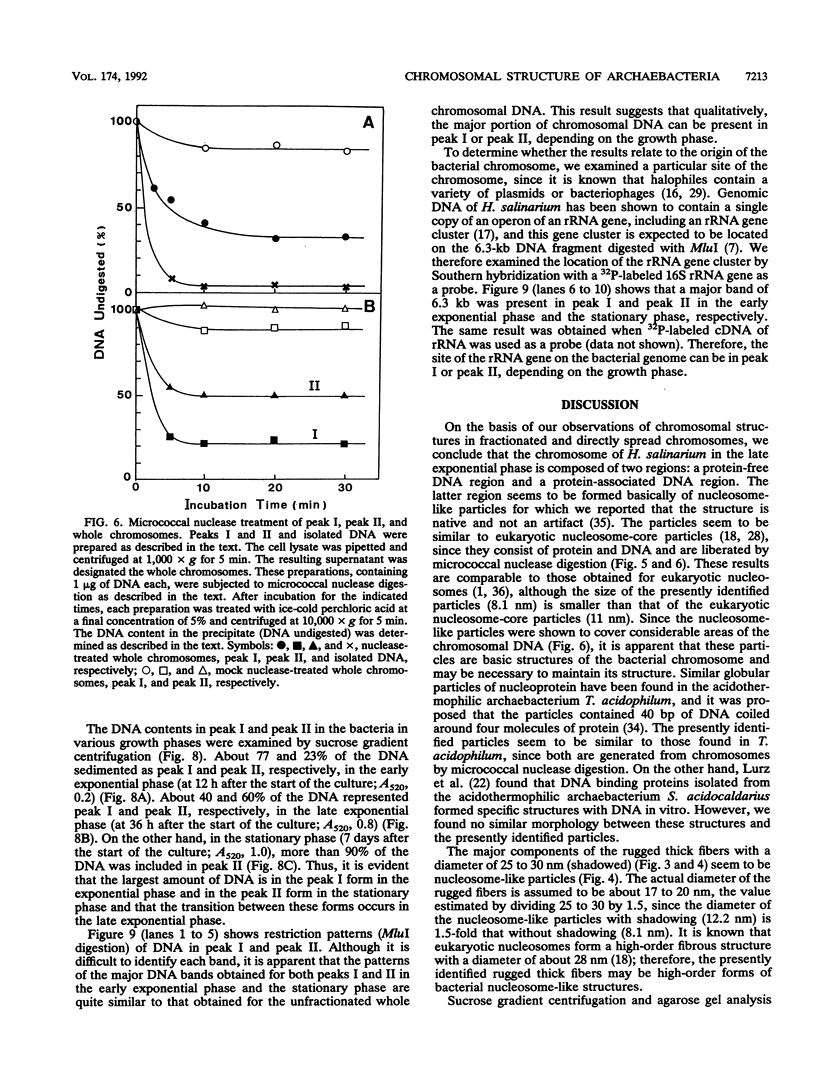
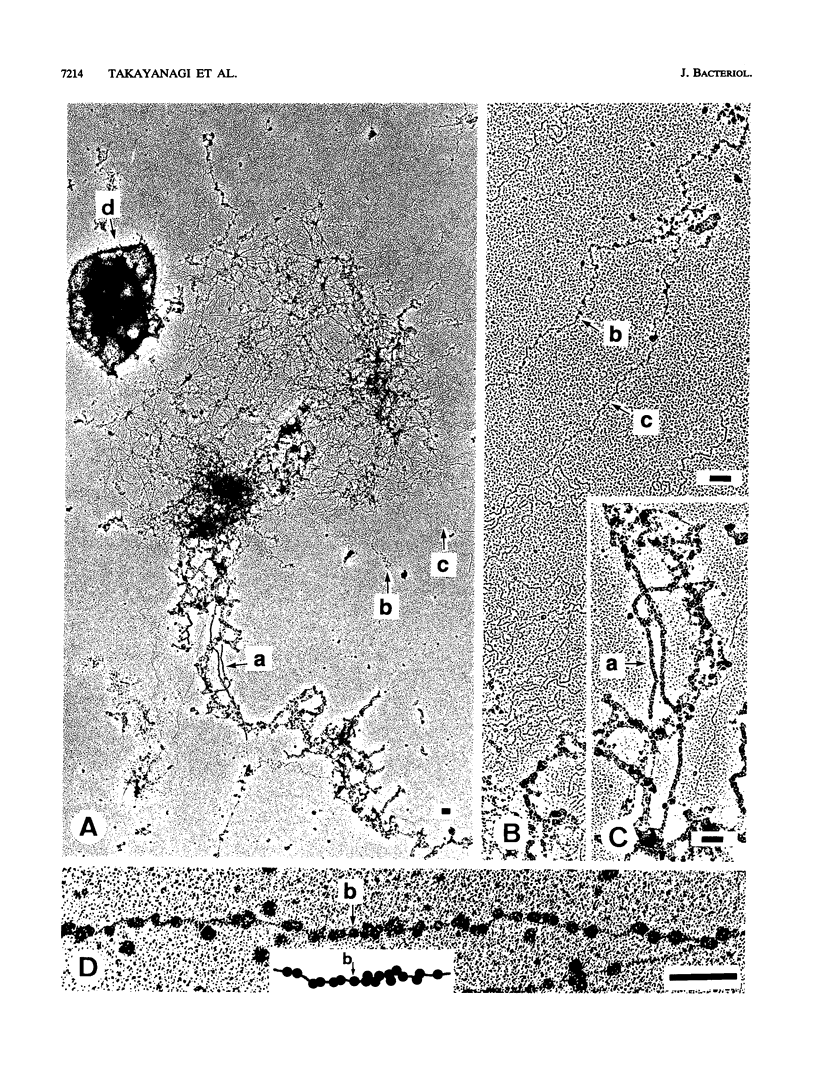
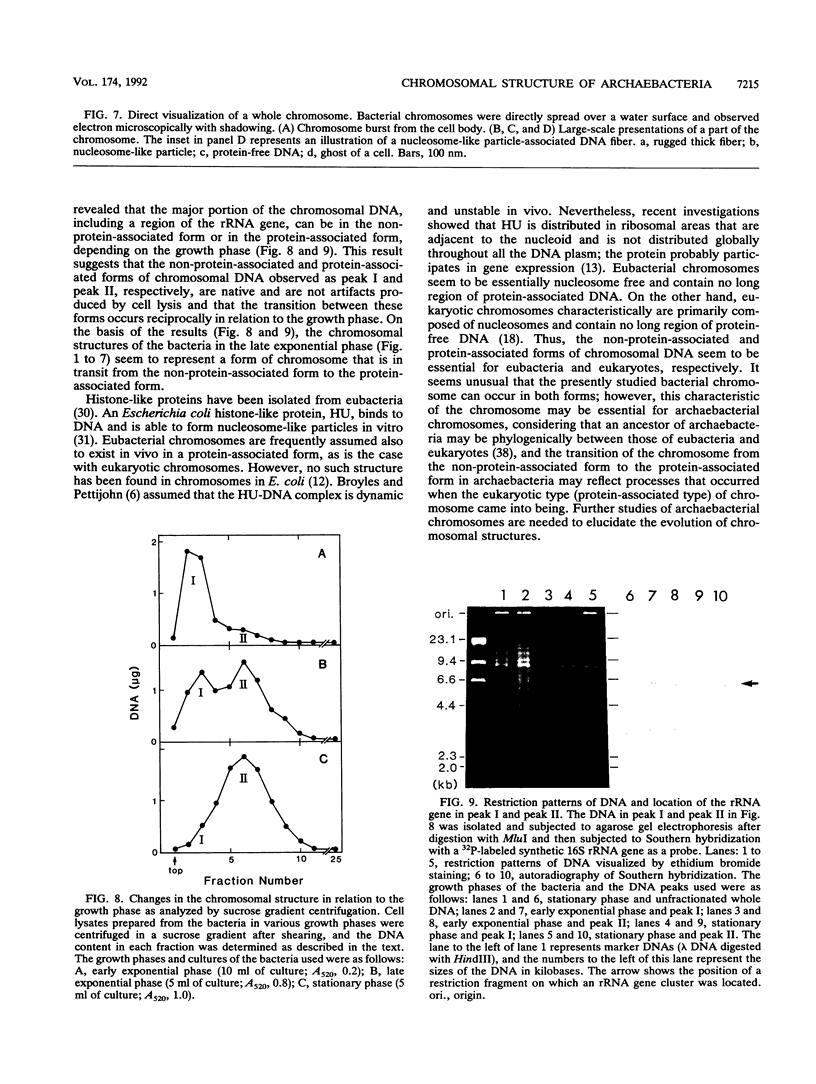
The chromosomal structure of the extremely halophilic archaebacterium Halobacterium salinarium was examined. Sheared chromosomes prepared from the bacteria in the late exponential phase were separated into two peaks (peaks I and II) by sucrose gradient centrifugation, suggesting that the chromosomes consist of two parts differing in quality. The UV spectra of peaks I and II resembled those of DNA and eukaryotic chromatin, respectively. Electron microscopic observations revealed that the major component of peak I was protein-free DNA, while the major components of peak II were rugged thick fibers with a diameter of 17 to 20 nm. The rugged fibers basically consisted of bacterial nucleosome-like structures composed of DNA and protein, as demonstrated in experiments with proteinase and nuclease digestion. Whole-mount electron microscopic observations of the chromosomes directly spread onto a water surface revealed a configuration in which the above-described regions were localized on a continuous DNA fiber. From these results it is concluded that the H. salinarium chromosome is composed of regions of protein-free DNA and DNA associated with nucleosome-like structures. Peaks I and II were predominant in the early exponential phase and stationary phase, respectively; therefore, the transition of the chromosome structure between non-protein-associated and protein-associated forms seems to be related to the bacterial growth phase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2921–2925. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J., Dahmus M. E., Fambrough D., Huang R. C., Marushige K., Tuan D. Y. The Biology of Isolated Chromatin: Chromosomes, biologically active in the test tube, provide a powerful tool for the study of gene action. Science. 1968 Jan 5;159(3810):47–56. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3810.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Pettijohn D. E. Interaction of the Escherichia coli HU protein with DNA. Evidence for formation of nucleosome-like structures with altered DNA helical pitch. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlebois R. L., Hofman J. D., Schalkwyk L. C., Lam W. L., Doolittle W. F. Genome mapping in halobacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):21–29. doi: 10.1139/m89-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier F., Laine B., Bélaïche D., Sautière P. Primary structure of the chromosomal proteins MC1a, MC1b, and MC1c from the archaebacterium Methanothrix soehngenii. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17006–17015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choli T., Wittmann-Liebold B., Reinhardt R. Microsequence analysis of DNA-binding proteins 7a, 7b, and 7e from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7087–7093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Green G. R., Searcy D. G. A histone-like protein (HTa) from Thermoplasma acidophilum. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):900–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Worcel A. Letter: Electron microscopic visualization of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;82(1):107–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90577-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger M., Bjornsti M. A., Uetz T., Hobot J. A., Kellenberger E. Intracellular location of the histonelike protein HU in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4757–4768. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4757-4768.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. R., Searcy D. G., DeLange R. J. Histone-like protein in the Archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 17;741(2):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp F., Palm P., Zillig W. Expression and regulation of Halobacterium halobium phage phi H genes. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):182–188. doi: 10.1139/m89-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui I., Dennis P. P. Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene clusters in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSANE J. M., ROBINS E. The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Kimura J., Davie P., Reinhardt R., Dijk J. The amino acid sequence of a small DNA binding protein from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):176–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80935-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Origin of the eukaryotic nucleus determined by rate-invariant analysis of rRNA sequences. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):184–186. doi: 10.1038/331184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurz R., Grote M., Dijk J., Reinhardt R., Dobrinski B. Electron microscopic study of DNA complexes with proteins from the Archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3715–3721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04705.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Rhodopsin-like protein from the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):149–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio233149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Mevarech M. Isolation and partial characterization of plasmids found in three Halobacterium volcanii isolates. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):92–95. doi: 10.1139/m89-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Gros F. Characterization of a novel, low-molecular-weight DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Yaniv M., Germond J. E. E. coli DNA binding protein HU forms nucleosomelike structure with circular double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searcy D. G. Histone-like protein in the prokaryote Thermoplasma acidophilum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 23;395(4):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searcy D. G., Stein D. B. Nucleoprotein subunit structure in an unusual prokaryotic organism: Thermoplasma acidophilum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 26;609(1):180–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda M., Sugimori K., Shiroya T., Takayanagi S. Nucleosomelike structures associated with chromosomes of the archaebacterium Halobacterium salinarium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4514–4517. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4514-4517.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]