Abstract
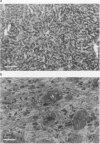
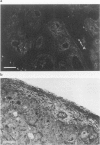
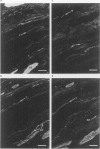
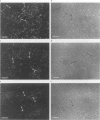
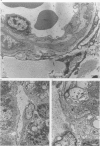
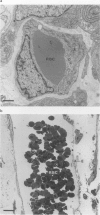
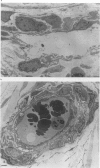
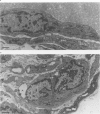
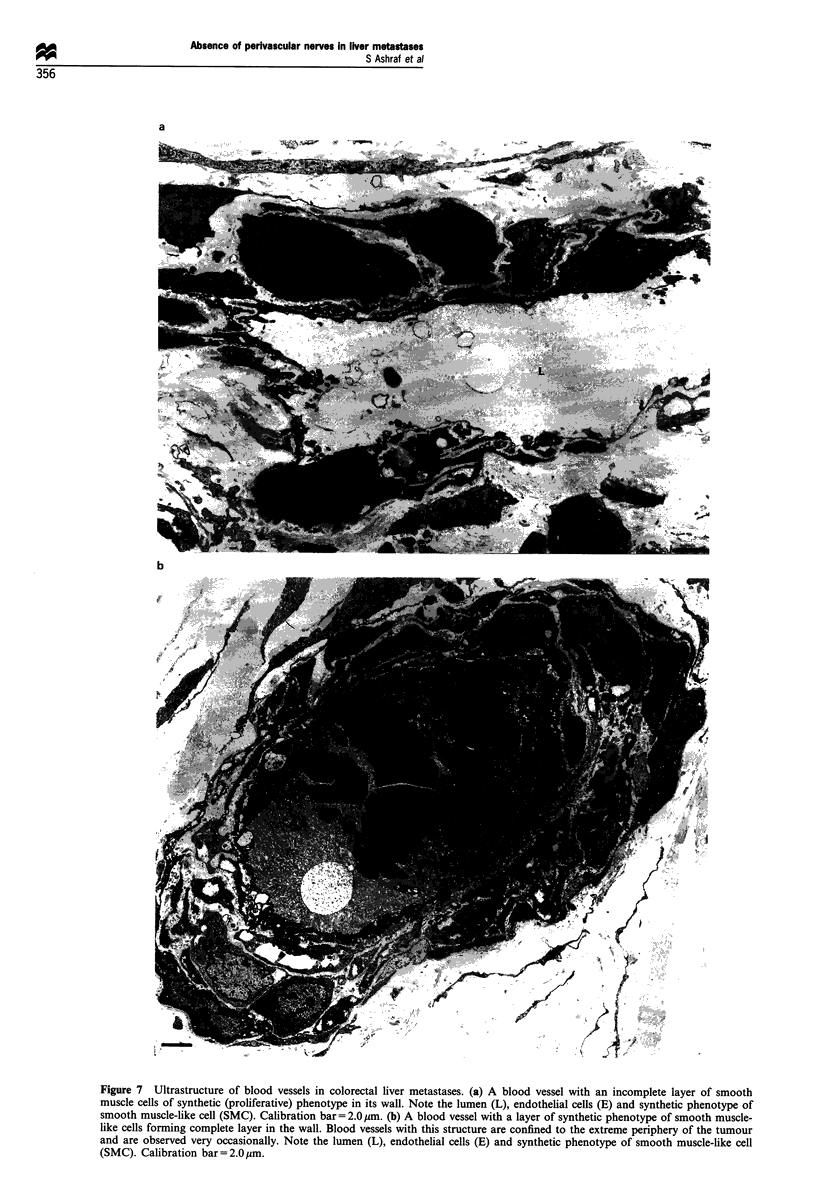
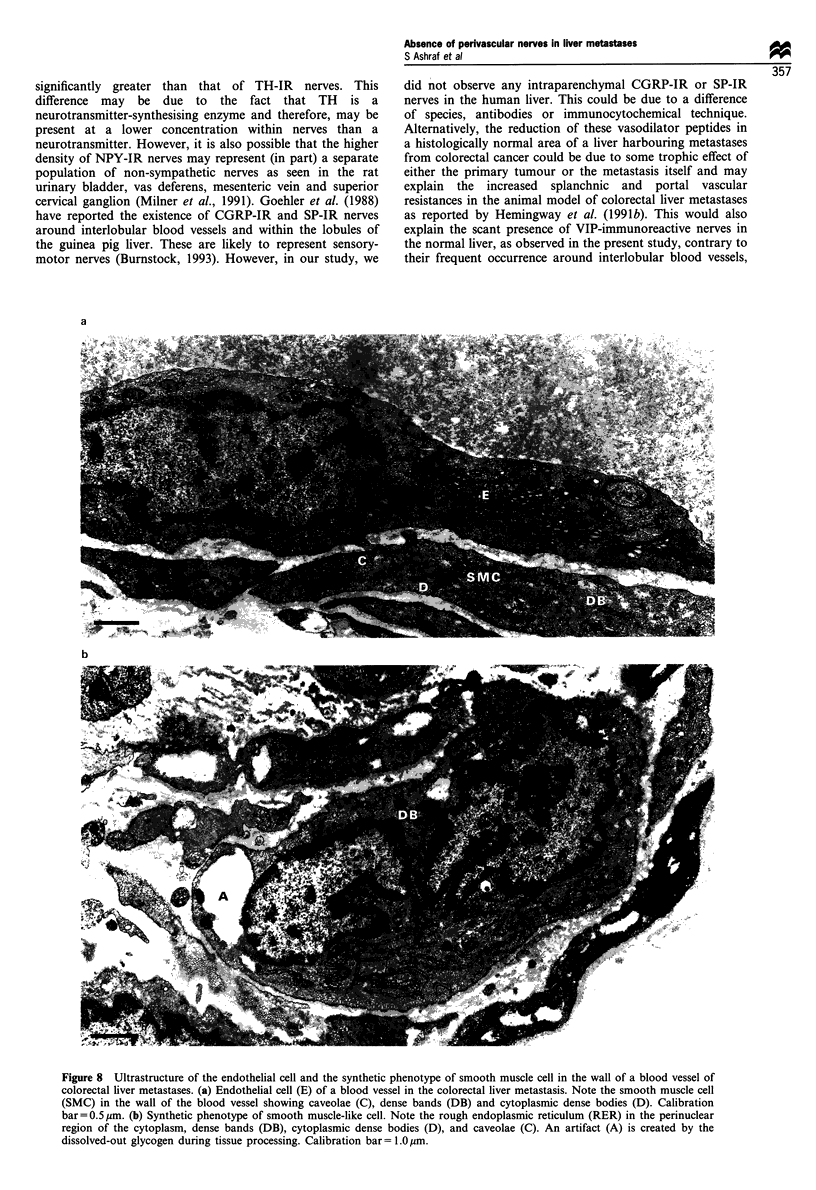
The peptidergic/aminergic innervation of normal liver and tumour blood vessels was investigated in order to determine vascular control with a view to improving the efficacy of hepatic arterial cytotoxic infusion in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases. Selected areas of liver metastases and macroscopically normal liver from resection specimens (n = 13) were studied using light microscope immunohistochemistry for the presence of protein gene product 9.5 (PGP), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), neuropeptide Y (NPY), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), substance P (SP) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). The ultrastructure of blood vessels supplying liver metastases and their perivascular innervation were also examined by transmission electron microscopy. In the normal liver, perivascular immunoreactive nerve fibres containing PGP, NPY and TH were observed around the interlobular blood vessels and along the sinusoids and the central vein of the hepatic lobule. The greatest density of immunoreactive nerve fibres was seen for PGP, followed (in decreasing order) by NPY and TH. VIP, SP and CGRP immunoreactivity was observed only in nerve bundles associated with the large interlobular blood vessels. In contrast, no perivascular immunoreactive nerves were observed in colorectal liver metastases. Electron microscopy confirmed the absence of perivascular nerves in liver metastases. In addition, it showed that the walls of these blood vessels were composed of a layer of endothelial cells surrounded by an incomplete or, very rarely in the periphery of the tumour, a complete, layer of synthetic phenotype of smooth muscle-like cells. These results imply that the blood vessels supplying liver metastases are bereft of normal neuronal regulation; whether there is a role for endothelial cell control of blood flow in these vessels is not yet known.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman N. B., Jacobs R., Bloom N. D., Poon T. T. Increased capillary flow in intrahepatic tumors due to alpha-adrenergic effects of catecholamines. Cancer. 1988 Apr 15;61(8):1550–1554. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880415)61:8<1550::aid-cncr2820610811>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Integration of factors controlling vascular tone. Overview. Anesthesiology. 1993 Dec;79(6):1368–1380. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199312000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt A. D., Tiniakos D., MacSween R. N., Griffiths M. R., Wisse E., Polak J. M. Localization of adrenergic and neuropeptide tyrosine-containing nerves in the mammalian liver. Hepatology. 1989 Jun;9(6):839–845. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder R., Withrington P. G. The actions of neuropeptide Y and peptide YY on the hepatic arterial and portal vascular beds of the anaesthetized dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1149–1156. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding W. G., Fujimura M., Mori A., Tooyama I., Kimura H. Light and electron microscopy of neuropeptide Y-containing nerves in human liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 1991 Oct;101(4):1054–1059. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90733-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehér E., Fodor M., Fehér J. Ultrastructural localization of somatostatin- and substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the feline liver. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91812-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Felten S. Y., Perry K. W., Snoddy H. D., Felten D. L. Sympathetic noradrenergic innervation of guinea-pig liver: histofluorescence and pharmacological studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jul;218(1):282–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goehler L. E., Sternini C., Brecha N. C. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the biliary pathway and liver of the guinea-pig: distribution and colocalization with substance P. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Jul;253(1):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00221749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. A., Thomson J. A., Bradnam M. S., Fenner J., Bessent R. G., McKillop J. H., Kerr D. J., McArdle C. S. Angiotensin II as a potential method of targeting cytotoxic-loaded microspheres in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jul;64(1):114–119. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbenkian S., Wharton J., Hacker G. W., Varndell I. M., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Co-localization of neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY) and its C-terminal flanking peptide (C-PON). Peptides. 1985 Nov-Dec;6(6):1237–1243. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90456-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafström L., Nobin A., Persson B., Sundqvist K. Effects of catecholamines on cardiovascular response and blood flow distribution to normal tissue and liver tumors in rats. Cancer Res. 1980 Feb;40(2):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemingway D. M., Cooke T. G., Chang D., Grime S. J., Jenkins S. A. The effects of intra-arterial vasoconstrictors on the distribution of a radiolabelled low molecular weight marker in an experimental model of liver tumour. Br J Cancer. 1991 Apr;63(4):495–498. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemingway D. M., Cooke T. G., Grime S. J., Nott D. M., Jenkins S. A. Changes in hepatic haemodynamics and hepatic perfusion index during the growth and development of hypovascular HSN sarcoma in rats. Br J Surg. 1991 Mar;78(3):326–330. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. M., Flowerdew A. D., Birch S. J., Williams J. D., Mullee M. A., Taylor I. Prospective randomized controlled trial of hepatic arterial embolization or infusion chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and degradable starch microspheres for colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg. 1990 Jul;77(7):779–782. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue N., Magari S., Ito Y., Sakanaka M. Distribution, possible origins and fine structure of neuropeptide Y-containing nerve fibers in the rat liver. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 24;493(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katusic Z. S., Vanhoutte P. M. Superoxide anion is an endothelium-derived contracting factor. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):H33–H37. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.1.H33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemeny N., Daly J., Reichman B., Geller N., Botet J., Oderman P. Intrahepatic or systemic infusion of fluorodeoxyuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):459–465. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylova N. V. Characteristics of microcirculation in experimental tumours. Bibl Anat. 1969;10:301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyösola K., Penttilä O., Ihamäki T., Varis K., Salaspuro M. Adrenergic innervation of the human liver. A fluorescence histochemical analysis of clinical liver biopsy specimens. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Mar;20(2):254–256. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M. Evidence for coexistence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) and acetylcholine in neurons of cat exocrine glands. Morphological, biochemical and functional studies. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1981;496:1–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. High levels of neuropeptide Y in peripheral noradrenergic neurons in various mammals including man. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson J., Lilja J., Peterson H. I. Influence of vasoactive drugs on local tumor blood flow. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1982 Jul;18(7):677–684. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(82)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel C., Gatta A., Caregaro L., Sacerdoti D., Rondana M., Ruol A. Effect of somatostatin on liver blood flow and liver metabolic activity in patients with cirrhosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987 Nov;47(7):667–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz W., Forssmann W. G. Innervation of the liver in guinea pig and rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1980;160(3):239–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00305105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. M., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent contractions to arachidonic acid are mediated by products of cyclooxygenase. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 2):H432–H437. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.4.H432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner P., Lincoln J., Corr L. A., Aberdeen J. A., Burnstock G. Neuropeptide Y in non-sympathetic nerves of the rat: changes during maturation but not after guanethidine sympathectomy. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90324-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moghimzadeh E., Nobin A., Rosengren E. Adrenergic nerves and receptors in the liver. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jul-Dec;9(1-6):709–714. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESTANA C., REITEMEIER R. J., MOERTEL C. G., JUDD E. S., DOCKERTY M. B. THE NATURAL HISTORY OF CARCINOMA OF THE COLON AND RECTUM. Am J Surg. 1964 Dec;108:826–829. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(64)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. D., Withrington P. G. The role of beta-adrenoceptors in the responses of the hepatic arterial vascular bed of the dog to phenylephrine, isoprenaline, noradrenaline and adrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;60(2):239–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Imaoka S., Hasegawa Y., Nakano S., Ishikawa O., Ohigashi H., Taniguchi K., Koyama H., Iwanaga T., Terasawa T. Changes in distribution of hepatic blood flow induced by intra-arterial infusion of angiotensin II in human hepatic cancer. Cancer. 1985 Jan 15;55(2):311–316. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850115)55:2<311::aid-cncr2820550202>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitzmann J. V., Wu Y., Cameron J. L. Altered angiotensin-II receptors in human hepatocellular and hepatic metastatic colon cancers. Ann Surg. 1994 May;219(5):500–507. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199405000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soediono P., Belai A., Burnstock G. Prevention of neuropathy in the pyloric sphincter of streptozotocin-diabetic rats by gangliosides. Gastroenterology. 1993 Apr;104(4):1072–1082. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90276-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno T., Inuzuka S., Torimura T., Sakata R., Sakamoto M., Gondo K., Aoki T., Tanikawa K., Tsutsumi V. Distribution of substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide in the human liver: light and electron immunoperoxidase methods of observation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 Nov;86(11):1633–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Salhy M., Stenling R., Grimelius L. Peptidergic innervation and endocrine cells in the human liver. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Sep;28(9):809–815. doi: 10.3109/00365529309104014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]