Abstract
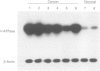
Recent studies have shown that bafilomycin A1-sensitive vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase (V-ATPase) plays important roles in cell growth and differentiation. However, there is no published study that has focused on the expression of V-ATPase in human tumour tissues. This study was designed to examine the mRNA and protein levels for the 16 kilodalton (kDa) proteolipid of V-ATPase in human pancreatic carcinoma tissues. We first investigated the mRNA level for V-ATPase in six cases of invasive pancreatic cancers and two normal pancreases, using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction technique. Then, we examined immunohistochemically the level of V-ATPase protein in 49 pancreatic cancers and ten benign cystic neoplasms of the pancreas, using antisera raised against the 16 kDa proteolipid. There was a notable difference in the level of V-ATPase mRNA between normal and pancreatic carcinoma tissues, with no evident difference in the expression of the beta-actin gene. Immunohistochemically, 42 out of 46 invasive ductal cancers (92%) displayed a mild to marked immunoreactivity for V-ATPase in the cytoplasm, whereas neither non-invasive ductal cancers nor benign cystic neoplasms expressed detectable immunoreactive proteins. These findings suggest that the overexpression of V-ATPase protein is characteristic of invasive pancreatic tumours. V-ATPase may play some crucial roles in tumour progression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi I., Arai H., Pimental R., Forgac M. Proteolysis and orientation on reconstitution of the coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):960–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akisaka T., Gay C. V. Ultracytochemical evidence for a proton-pump adenosine triphosphatase in chick osteoclasts. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;245(3):507–512. doi: 10.1007/BF00218550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Berne M., Forgac M. Inhibition of the coated vesicle proton pump and labeling of a 17,000-dalton polypeptide by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11006–11011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Berne M., Terres G., Terres H., Puopolo K., Forgac M. Subunit composition and ATP site labeling of the coated vesicle proton-translocating adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6632–6638. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Terres G., Pink S., Forgac M. Topography and subunit stoichiometry of the coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8796–8802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Shimaya A., Hiratani N., Ohkuma S. Purification and characterization of lysosomal H(+)-ATPase. An anion-sensitive v-type H(+)-ATPase from rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5649–5660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R., Neff L., Louvard D., Courtoy P. J. Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2210–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Gas N., Prats H., Baldin V., Tauber J. P., Teissié J., Amalric F. Basic fibroblast growth factor enters the nucleolus and stimulates the transcription of ribosomal genes in ABAE cells undergoing G0----G1 transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6770–6774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Dschida W. J., Harris T., Bowman E. J. The vacuolar ATPase of Neurospora crassa contains an F1-like structure. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15606–15612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J., Siebers A., Altendorf K. Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Maire P., Gautron S., Kahn A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissue. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):858–860. doi: 10.1038/333858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y., Forgac M. Cysteine 254 of the 73-kDa A subunit is responsible for inhibition of the coated vesicle (H+)-ATPase upon modification by sulfhydryl reagents. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5817–5822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., Goodwin S. F., Meagher L., Lane N. J., Keen J., Findlay J. B., Kaiser K. Evidence that the 16 kDa proteolipid (subunit c) of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase and ductin from gap junctions are the same polypeptide in Drosophila and Manduca: molecular cloning of the Vha16k gene from Drosophila. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jul;107(Pt 7):1817–1824. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.7.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., John S., Kam E., Apps D. K., Pitts J. D. Disposition and orientation of ductin (DCCD-reactive vacuolar H(+)-ATPase subunit) in mammalian membrane complexes. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Aug;207(2):261–270. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M. Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):765–796. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M. Structure, function and regulation of the coated vesicle V-ATPase. J Exp Biol. 1992 Nov;172:155–169. doi: 10.1242/jeb.172.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie G. A., Somlo S., Germino G. G., Weinstat-Saslow D., Reeders S. T. CpG island in the region of an autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease locus defines the 5' end of a gene encoding a putative proton channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4289–4293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Andresson T., Sparkowski J. J., Schlegel R. The BPV-1 E5 protein, the 16 kDa membrane pore-forming protein and the PDGF receptor exist in a complex that is dependent on hydrophobic transmembrane interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4851–4859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. E., Hall P. A. Immunolocalization of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 and its ligands in human tissues. Lab Invest. 1993 Aug;69(2):173–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Morel N., Lesbats B., Birman S., Manaranche R. Purification of a presynaptic membrane protein that mediates a calcium-dependent translocation of acetylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9226–9230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Randall S. K., Sze H. N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteolipid of the vacuolar H+-ATPase from oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1282–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern H. F., Röher H. D., von Bülow M., Klöppel G. Fine structure of three major grades of malignancy of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 1987;2(1):2–13. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198701000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobrin M. S., Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Lopez M. E., Korc M. Aberrant expression of type I fibroblast growth factor receptor in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4741–4744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manabe T., Yoshimori T., Henomatsu N., Tashiro Y. Inhibitors of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase suppresses proliferation of cultured cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Dec;157(3):445–452. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolson M. F., Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Identification of 3-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate- and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding subunits of a higher plant H+-translocating tonoplast ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12273–12279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Zaguilan R., Lynch R. M., Martinez G. M., Gillies R. J. Vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPases are functionally expressed in plasma membranes of human tumor cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 1):C1015–C1029. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.4.C1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Futai M. H(+)-ATPase, a primary pump for accumulation of neurotransmitters, is a major constituent of brain synaptic vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):443–448. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. Cold inactivation of vacuolar proton-ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3577–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Yamamoto A., Tashiro Y., Futai M. Chromaffin granule H(+)-ATPase has F1-like structure. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81111-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai H., Kuroda A., Morioka Y. Lymphatic and local spread of T1 and T2 pancreatic cancer. A study of autopsy material. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):65–71. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda A., Gukovskaya A., Tseng J., Grinstein S. Activation of vacuolar-type proton pumps by protein kinase C. Role in neutrophil pH regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22740–22746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Nelson N. Disruption of genes encoding subunits of yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase causes conditional lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3503–3507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure and pharmacology of the proton-ATPases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Feb;12(2):71–75. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90501-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure, molecular genetics, and evolution of vacuolar H+-ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Oct;21(5):553–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00808113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezu J., Motojima K., Tamura H., Ohkuma S. Molecular cloning of a rat liver cDNA encoding the 16 kDa subunit of vacuolar H(+)-ATPases: organellar and tissue distribution of 16 kDa proteolipids. J Biochem. 1992 Aug;112(2):212–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numata M., Ohkuma S., Iseki S. Expression and localization of mRNA for the 16 KD subunit of V-ATPase in the rat embryo. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995 Aug;43(8):761–769. doi: 10.1177/43.8.7622839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numata M., Ono T., Iseki S. Expression and localization of the mRNA for DNA (cytosine-5)- methyltransferase in mouse seminiferous tubules. J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Sep;42(9):1271–1276. doi: 10.1177/42.9.8064134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Shimizu S., Noto M., Sai Y., Kinoshita K., Tamura H. Inhibition of cell growth by bafilomycin A1, a selective inhibitor of vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1993 Nov;29A(11):862–866. doi: 10.1007/BF02631364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Nagakawa T., Ueno K., Kayahara M., Mori K., Kobayashi H., Takeda T., Miyazaki I. The mode of lymphatic and local spread of pancreatic carcinomas less than 4.0 cm in size. Int Surg. 1993 Jul-Sep;78(3):208–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Halban P., Perrelet A., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Anderson R. G. pH-independent and -dependent cleavage of proinsulin in the same secretory vesicle. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1149–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Storch M. J., Anderson R. G., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. Proteolytic maturation of insulin is a post-Golgi event which occurs in acidifying clathrin-coated secretory vesicles. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puopolo K., Forgac M. Functional reassembly of the coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14836–14841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. Z., Xie X. S., Stone D. K. Isolation and reconstitution of the dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive proton pore of the clathrin-coated vesicle proton translocating complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14790–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow C. J., Grinstein S., Rotstein O. D. A vacuolar type H(+)-ATPase regulates cytoplasmic pH in murine macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7645–7654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper H., Sundler R. Cytosolic pH regulation in mouse macrophages. Proton extrusion by plasma-membrane-localized H(+)-ATPase. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):245–250. doi: 10.1042/bj2810245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlander J. W., Madsen K. M., Tisher C. C. Structural and functional features of proton and bicarbonate transport in the rat collecting duct. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Jul;11(4):465–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen H. K., Karhukorpi E. K., Sundquist K., Wallmark B., Roininen I., Hentunen T., Tuukkanen J., Lakkakorpi P. Evidence for the presence of a proton pump of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase type in the ruffled borders of osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1305–1311. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X. S., Stone D. K. Partial resolution and reconstitution of the subunits of the clathrin-coated vesicle proton ATPase responsible for Ca2+-activated ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9859–9867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Buchler M., Beger H. G., Uchida E., Onda M., Kobrin M. S., Korc M. Overexpression of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors in human pancreatic cancer correlates with advanced tumor stage. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5289–5296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Myers M., Forgac M. Characterization of the V0 domain of the coated vesicle (H+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9773–9778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]