Abstract
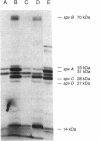
The spv region of the Salmonella virulence plasmids consists of five genes located on an 8-kb fragment previously shown to be essential for virulence in mice. Four structural genes, spvABCD, form an operon that is transcriptionally activated by the spvR gene product in the stationary phase of growth. The role of the individual spv genes in the virulence phenotype was tested by isolating translation termination linker insertions in each gene. Analysis of proteins synthesized in minicells identified each of the spvABCD gene products and confirmed the dependence of spv structural gene expression on the SpvR regulatory protein. The oligonucleotide insertions in spvA, -B, and -C were shown to be nonpolar. Virulence testing indicated that the SpvB protein, regulated by SpvR, is essential for Salmonella dublin to cause lethal disease in mice. Inserts in spvC and spvD were unstable in vivo for unknown reasons, but these mutants still killed mice at slightly higher inocula. Abolition of spvA had no effect on virulence in this system.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird G. D., Manning E. J., Jones P. W. Evidence for related virulence sequences in plasmids of Salmonella dublin and Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1815–1823. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow P. A., Lovell M. A. Functional homology of virulence plasmids in Salmonella gallinarum, S. pullorum, and S. typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3136–3141. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3136-3141.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beninger P. R., Chikami G., Tanabe K., Roudier C., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Physical and genetic mapping of the Salmonella dublin virulence plasmid pSDL2. Relationship to plasmids from other Salmonella strains. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1341–1347. doi: 10.1172/JCI113461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell A. L., Gulig P. A. The Salmonella typhimurium virulence plasmid encodes a positive regulator of a plasmid-encoded virulence gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7176–7185. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7176-7185.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikami G. K., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Plasmid-mediated virulence in Salmonella dublin demonstrated by use of a Tn5-oriT construct. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):420–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.420-424.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F. C., Krause M., Roudier C., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Growth regulation of a Salmonella plasmid gene essential for virulence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6783–6789. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6783-6789.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Chiodo V. A. Genetic and DNA sequence analysis of the Salmonella typhimurium virulence plasmid gene encoding the 28,000-molecular-weight protein. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2651–2658. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2651-2658.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and transposon insertion mutagenesis of virulence genes of the 100-kilobase plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3262–3271. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3262-3271.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2891–2901. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2891-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulig P. A. Virulence plasmids of Salmonella typhimurium and other salmonellae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan E. J., Fierer J., Chikami G., Guiney D. Natural history of oral Salmonella dublin infection in BALB/c mice: effect of an 80-kilobase-pair plasmid on virulence. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1254–1259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., So M., McCarthy B. J. In vitro mutagenesis of a circular DNA molecule by using synthetic restriction sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi M., Sukupolvi S., Edwards M. F., Rhen M. Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella enteritidis. Microb Pathog. 1988 May;4(5):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rabert D. K., Svinarich D. M., Whitfield H. J. Association of adhesive, invasive, and virulent phenotypes of Salmonella typhimurium with autonomous 60-megadalton plasmids. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.476-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Haraguchi Y., Tsuchimoto M., Terakado N., Danbara H. Evidence of correlation between 50-kilobase plasmid of Salmonella choleraesuis and its virulence. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Tsuchimoto M., Sudo K., Terakado N., Danbara H. Identification and mapping of mba regions of the Salmonella choleraesuis virulence plasmid pKDSC50 responsible for mouse bacteremia. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90004-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Fang F. C., Guiney D. G. Regulation of plasmid virulence gene expression in Salmonella dublin involves an unusual operon structure. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4482–4489. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4482-4489.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Guiney D. G. Identification of a multimer resolution system involved in stabilization of the Salmonella dublin virulence plasmid pSDL2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5754–5762. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5754-5762.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Roudier C., Fierer J., Harwood J., Guiney D. Molecular analysis of the virulence locus of the Salmonella dublin plasmid pSDL2. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):307–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax A. J., Pullinger G. D., Baird G. D., Williamson C. M. The virulence plasmid of Salmonella dublin: detailed restriction map and analysis by transposon mutagenesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1117–1123. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-6-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Kawahara K., Terakado N., Danbara H. Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding a 29 kDa polypeptide in mba region of the virulence plasmid, pKDSC50, of Salmonella choleraesuis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1055–1055. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Kawahara K., Terakado N., Danbara H. Nucleotide sequences of genes encoding 32 kDa and 70 kDa polypeptides in mba region of the virulence plasmid, pKDSc50, of Salmonella choleraesuis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2181–2182. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Popoff M. Y., Durviaux S., Coynault C., Cornelis G. A new method for the physical and genetic mapping of large plasmids: application to the localisation of the virulence determinants on the 90 kb plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Microb Pathog. 1987 Aug;3(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norel F., Coynault C., Miras I., Hermant D., Popoff M. Y. Cloning and expression of plasmid DNA sequences involved in Salmonella serotype typhimurium virulence. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):733–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norel F., Pisano M. R., Nicoli J., Popoff M. Y. A plasmid-borne virulence region (2.8 kb) from Salmonella typhimurium contains two open reading frames. Res Microbiol. 1989 Nov-Dec;140(9):627–630. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norel F., Pisano M. R., Nicoli J., Popoff M. Y. Nucleotide sequence of the plasmid-borne virulence gene mkfA encoding a 28 kDa polypeptide from Salmonella typhimurium. Res Microbiol. 1989 Mar-Apr;140(3):263–265. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norel F., Pisano M. R., Nicoli J., Popoff M. Y. Nucleotide sequence of the plasmid-borne virulence gene mkfB from Salmonella typhimurium. Res Microbiol. 1989 Sep;140(7):455–457. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. The MURFI linker for multiple reading frame insertion of a sense or nonsense codon into DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2139–2155. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann L. S., Stauffer G. V. Nucleotide sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium metR gene and the metR-metE control region. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3932–3937. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3932-3937.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppe C., Curtiss R., 3rd, Gulig P. A., Gyles C. L. Hybridization studies with a DNA probe derived from the virulence region of the 60 Mdal plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Vet Res. 1989 Oct;53(4):378–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullinger G. D., Baird G. D., Williamson C. M., Lax A. J. Nucleotide sequence of a plasmid gene involved in the virulence of salmonellas. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7983–7983. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhen M., Virtanen M., Mäkelä P. H. Localization by insertion mutagenesis of a virulence-associated region on the Salmonella typhimurium 96 kilobase pair plasmid. Microb Pathog. 1989 Feb;6(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roudier C., Krause M., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Correlation between the presence of sequences homologous to the vir region of Salmonella dublin plasmid pSDL2 and the virulence of twenty-two Salmonella serotypes in mice. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1180-1185.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira S., Baumann M., Riikonen P., Sukupolvi S., Rhen M. Amino-terminal sequence analysis of four plasmid-encoded virulence-associated proteins of Salmonella typhimurium. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90573-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira S., Rhen M. Identification and genetic analysis of mkaA--a gene of the Salmonella typhimurium virulence plasmid necessary for intracellular growth. Microb Pathog. 1989 Sep;7(3):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira S., Rhen M. Molecular organization of genes constituting the virulence determinant on the Salmonella typhimurium 96 kilobase pair plasmid. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81551-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira S., Rhen M. Nucleotide sequence of mkaD, a virulence-associated gene of Salmonella typhimurium containing variable and constant regions. Gene. 1990 Sep 1;93(1):147–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90150-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira S., Riikonen P., Saarilahti H., Sukupolvi S., Rhen M. The mkaC virulence gene of the Salmonella serovar typhimurium 96 kb plasmid encodes a transcriptional activator. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Sep;228(3):381–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00260630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terakado N., Sekizaki T., Hashimoto K., Naitoh S. Correlation between the presence of a fifty-megadalton plasmid in Salmonella dublin and virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):443–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.443-444.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone S. E., Chikami G. K. Characterization of three proteins expressed from the virulence region of plasmid pSDL2 in Salmonella dublin. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3511–3517. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3511-3517.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson C. M., Baird G. D., Manning E. J. A common virulence region on plasmids from eleven serotypes of Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):975–982. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson C. M., Pullinger G. D., Lax A. J. Identification of an essential virulence region on Salmonella plasmids. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):469–473. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]