Abstract
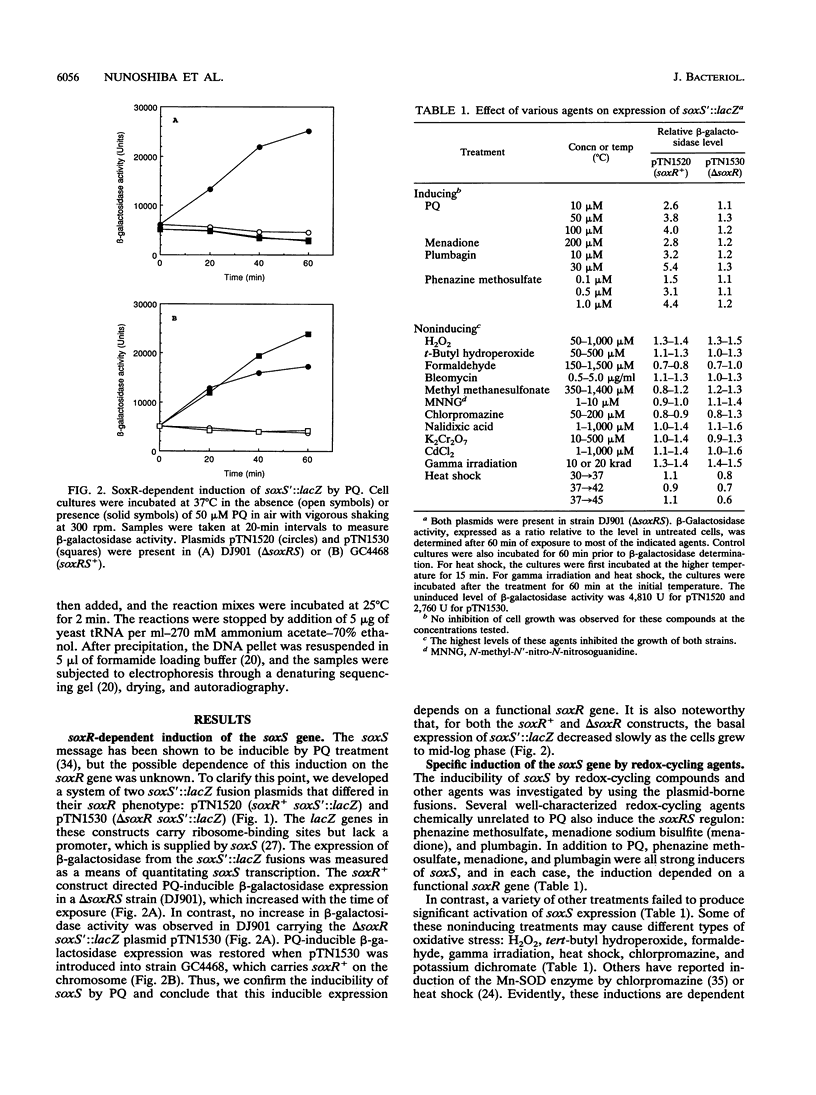
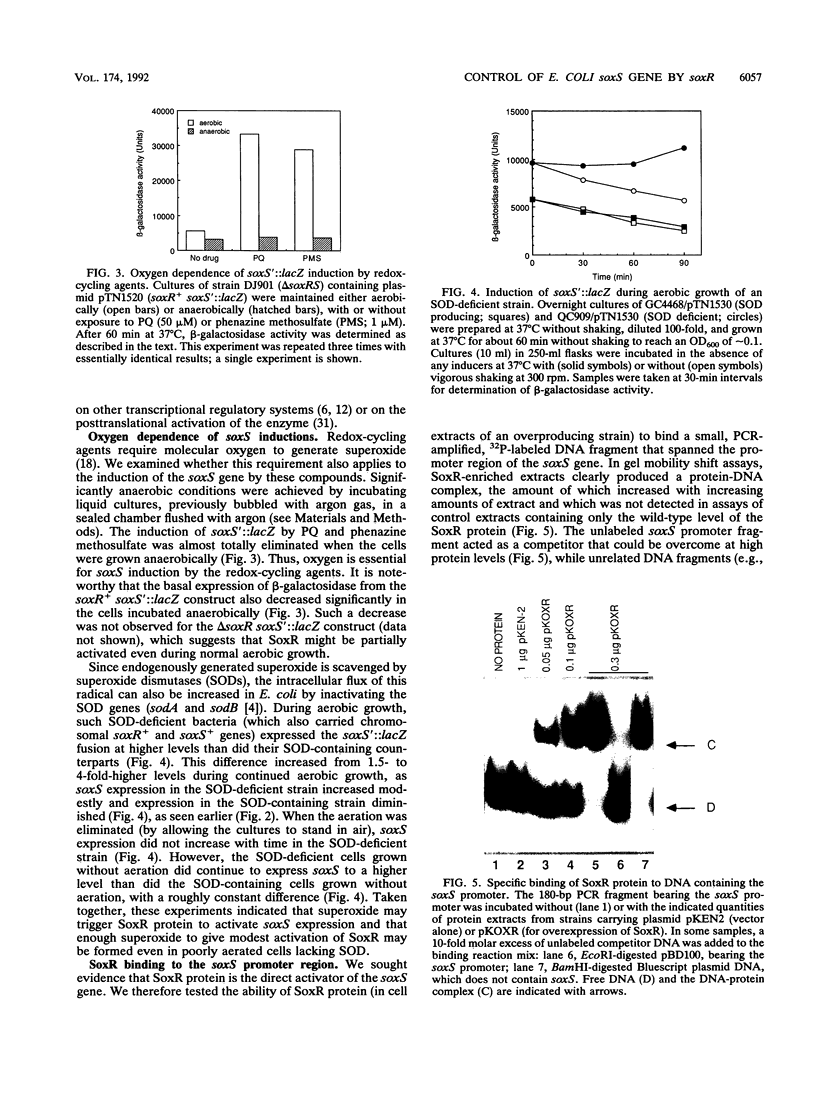
Escherichia coli responds to the redox stress imposed by superoxide-generating agents such as paraquat by activating the synthesis of as many as 80 polypeptides. Expression of a key group of these inducible proteins is controlled at the transcriptional level by the soxRS locus (the soxRS regulon). A two-stage control system was hypothesized for soxRS, in which an intracellular redox signal would trigger the SoxR protein as a transcriptional activator of the soxS gene and the resulting increased levels of SoxS protein would activate transcription of the various soxRS regulon genes (B. Demple and C.F. Amábile Cuevas, Cell 67:837-839, 1990). We have constructed operon fusions of the E. coli lac genes to the soxS promoter to monitor soxS transcription. Expression from the soxS promoter is strongly inducible by paraquat in a manner strictly dependent on a functional soxR gene. Several other superoxide-generating agents also trigger soxR(+)-dependent soxS expression, and the inductions by paraquat and phenazine methosulfate were dependent on the presence of oxygen. Numerous other oxidative stress agents (H2O2, gamma rays, heat shock, etc.) failed to induce soxS, while aerobic growth of superoxide dismutase-deficient bacteria triggered soxR-dependent soxS expression. These results indicate a specific redox signal for soxS induction. A direct role for SoxR protein in the activation of the soxS gene is indicated by band-shift and DNase I footprinting experiments that demonstrate specific binding of the SoxR protein in cell extracts to the soxS promoter. The mode of SoxR binding to DNA appears to be similar to that of its homolog MerR in that the SoxR footprint spans the -10 to -35 region of the soxS promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amábile-Cuevas C. F., Demple B. Molecular characterization of the soxRS genes of Escherichia coli: two genes control a superoxide stress regulon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4479–4484. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A. Z., Chael M. L., O'Halloran T. V. Allosteric underwinding of DNA is a critical step in positive control of transcription by Hg-MerR. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):87–89. doi: 10.1038/355087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlioz A., Touati D. Isolation of superoxide dismutase mutants in Escherichia coli: is superoxide dismutase necessary for aerobic life? EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E., Weiss B. Endonuclease IV of Escherichia coli is induced by paraquat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3189–3193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Amábile-Cuevas C. F. Redox redux: the control of oxidative stress responses. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):837–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B. Regulation of bacterial oxidative stress genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:315–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr S. B., D'Ari R., Touati D. Oxygen-dependent mutagenesis in Escherichia coli lacking superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8268–8272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A. Regulation of sod genes in Escherichia coli: relevance to superoxide dismutase function. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2599–2610. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz B., O'Halloran T. V. DNA distortion accompanies transcriptional activation by the metal-responsive gene-regulatory protein MerR. Biochemistry. 1990 May 22;29(20):4747–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00472a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide radical: an endogenous toxicant. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:239–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Chou J. H., Monach P. A., Demple B. Activation of oxidative stress genes by mutations at the soxQ/cfxB/marA locus of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4433–4439. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4433-4439.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. A global response induced in Escherichia coli by redox-cycling agents overlaps with that induced by peroxide stress. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3933–3939. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3933-3939.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. Overproduction of peroxide-scavenging enzymes in Escherichia coli suppresses spontaneous mutagenesis and sensitivity to redox-cycling agents in oxyR-mutants. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2611–2617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Monach P., Chou J. H., Josephy P. D., Demple B. Positive control of a global antioxidant defense regulon activated by superoxide-generating agents in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Ballard B. T., Walsh C. T. The MerR metalloregulatory protein binds mercuric ion as a tricoordinate, metal-bridged dimer. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):946–948. doi: 10.1126/science.2305262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Fridovich I. Assay of metabolic superoxide production in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6957–6965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappus H., Sies H. Toxic drug effects associated with oxygen metabolism: redox cycling and lipid peroxidation. Experientia. 1981 Dec 15;37(12):1233–1241. doi: 10.1007/BF01948335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liochev S. I., Fridovich I. Fumarase C, the stable fumarase of Escherichia coli, is controlled by the soxRS regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5892–5896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettleton C. J., Bull C., Baldwin T. O., Fee J. A. Isolation of the Escherichia coli iron superoxide dismutase gene: evidence that intracellular superoxide concentration does not regulate oxygen-dependent synthesis of the manganese superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4970–4973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalle C. T., Fridovich I. Induction of superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli by heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2723–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Park S. J., Summers A. O. Genetic analysis of transcriptional activation and repression in the Tn21 mer operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4009–4018. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4009-4018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Christman M. F., Sies H., Ames B. N. Spontaneous mutagenesis and oxidative damage to DNA in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardat B., Touati D. Two global regulators repress the anaerobic expression of MnSOD in Escherichia coli::Fur (ferric uptake regulation) and Arc (aerobic respiration control). Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):455–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase biosynthesis in Escherichia coli, studied with operon and protein fusions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2511–2520. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2511-2520.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaneva I. R., Weiss B. soxR, a locus governing a superoxide response regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4197–4205. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4197-4205.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Weiss B. Two divergently transcribed genes, soxR and soxS, control a superoxide response regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2864–2871. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2864-2871.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q. M., Yonei S. Induction of manganese-superoxide dismutase by membrane-binding drugs in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3488–3491. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3488-3491.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]