Abstract
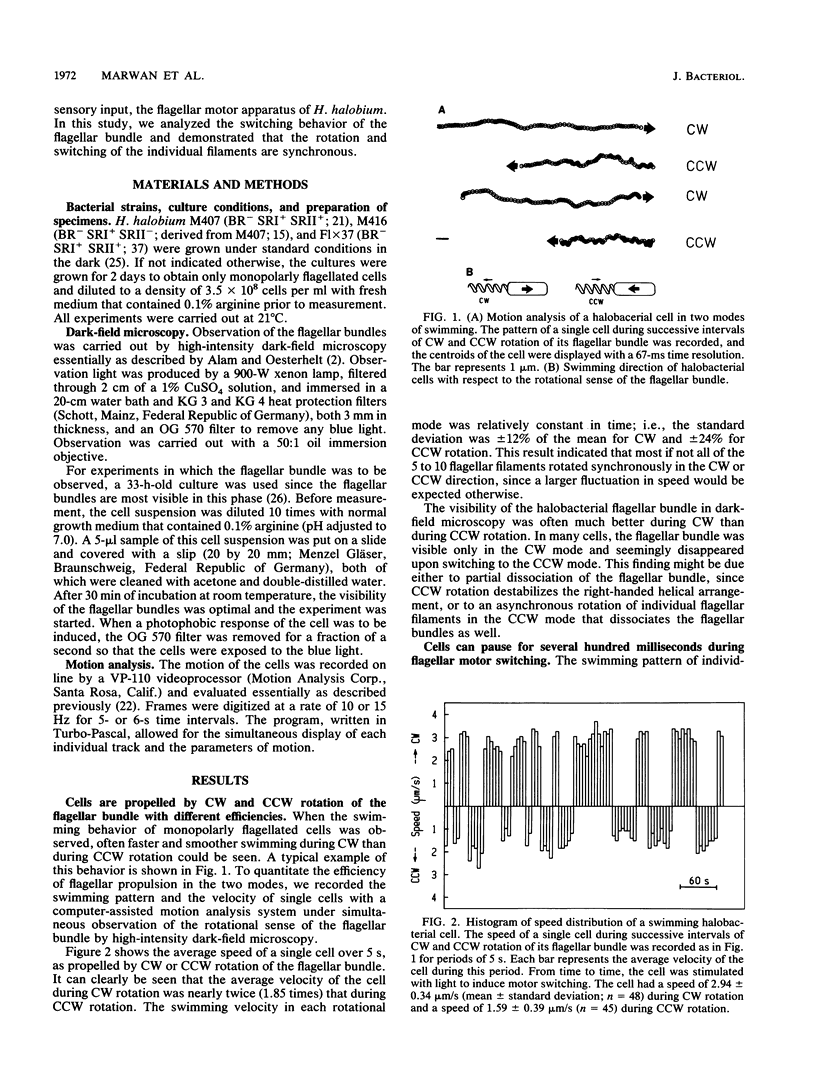
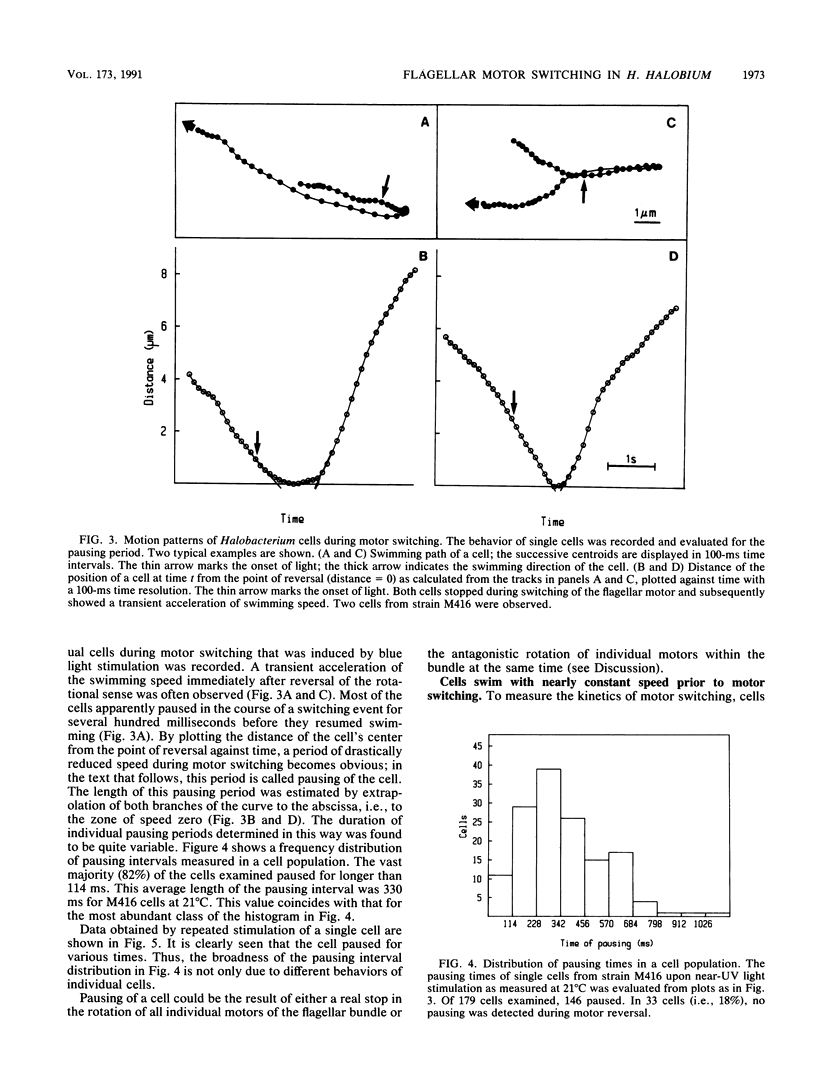
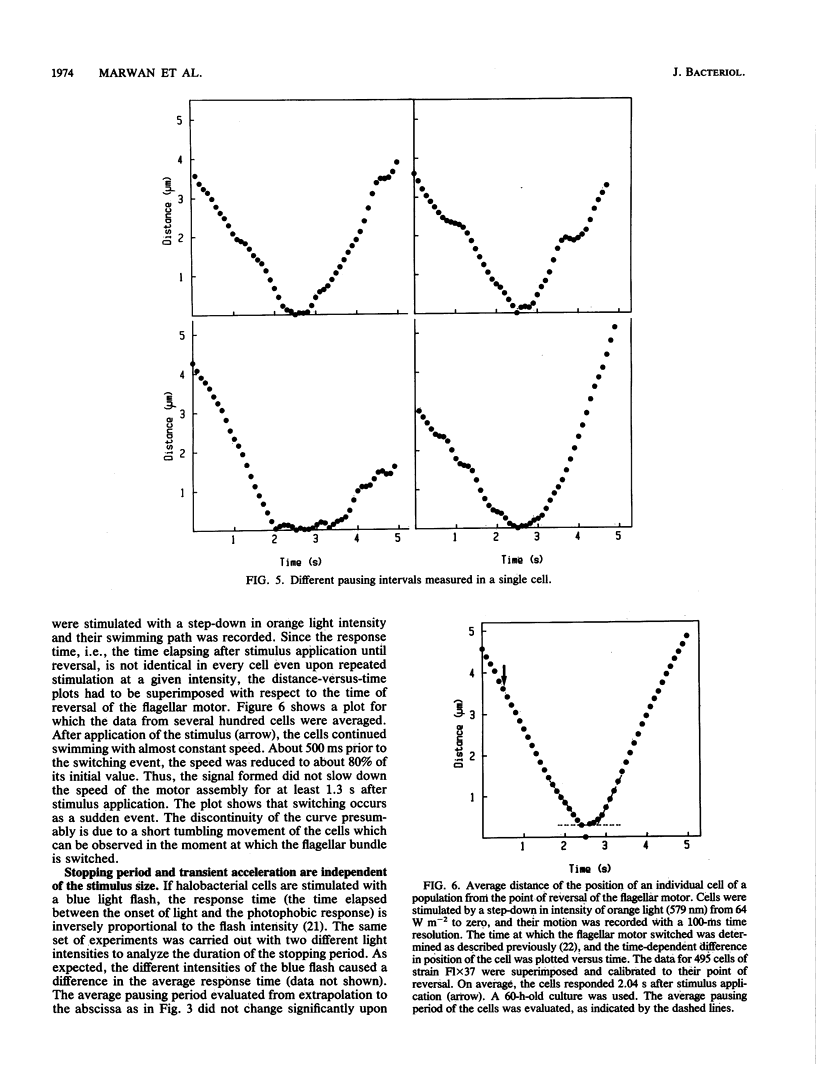
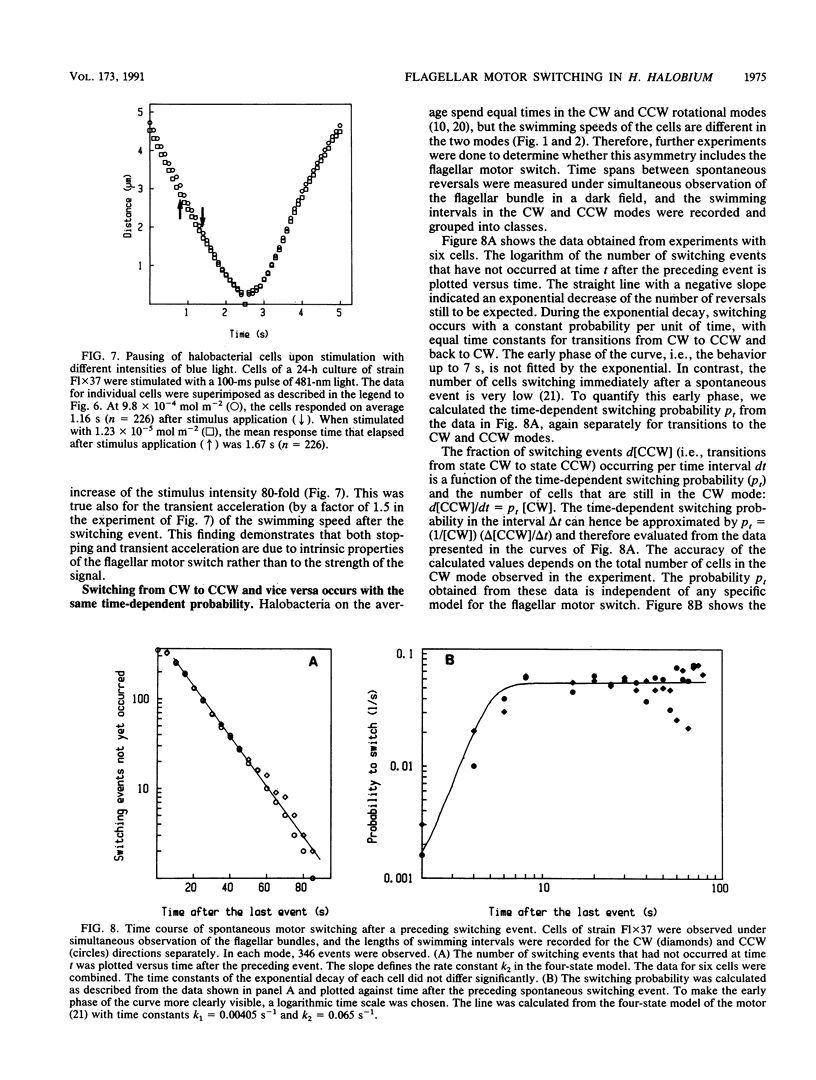
Halobacterium halobium swims with a polarly inserted motor-driven flagellar bundle. The swimming direction of the cell can be reserved by switching the rotational sense of the bundle. The switch is under the control of photoreceptor and chemoreceptor proteins that act through a branched signal chain. The swimming behavior of the cells and the switching process of the flagellar bundle were investigated with a computer-assisted motion analysis system. The cells were shown to swim faster by clockwise than by counterclockwise rotation of the flagellar bundle. From the small magnitude of speed fluctuations, it is concluded that the majority, if not all, of the individual flagellar motors of a cell rotate in the same direction at any given time. After stimulation with light (blue light pulse or orange light step-down), the cells continued swimming with almost constant speed but then slowed before they reversed direction. The cells passed through a pausing state during the change of the rotational sense of the flagellar bundle and then exhibited a transient acceleration. Both the average length of the pausing period and the transient acceleration were independent of the stimulus size and thus represent intrinsic properties of the flagellar motor assembly. The average length of the pausing period of individual cells, however, was not constant. The time course of the probability for spontaneous motor switching was calculated from frequency distribution and shown to be independent of the rotational sense. The time course further characterizes spontaneous switching as a stochastic rather than an oscillator-triggered event.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:289–292. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura S., Eguchi G., Iino T. Salmonella flagella: in vitro reconstruction and over-all shapes of flagellar filaments. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):302–316. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Segall J. E., Berg H. C. Adaptation kinetics in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):312–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.312-323.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton J. W., Murray R. G. Cell envelope associations of Aquaspirillum serpens flagella. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1037–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1037-1049.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M. Functions of the flagellar modes of rotation in bacterial motility and chemotaxis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):161–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M., Wolf A., Welch M., Caplan S. R., Lapidus I. R., Macnab R. M., Aloni H., Asher O. Pausing, switching and speed fluctuation of the bacterial flagellar motor and their relation to motility and chemotaxis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 5;211(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90265-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L. Flagella, gas vacuoles and cell-wall structure in Halobacterium halobium; an electron microscope study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):146–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Dencher N. Two photosystems controlling behavioural responses of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):46–48. doi: 10.1038/257046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Multiple kinetic states for the flagellar motor switch. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6279–6287. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6279-6287.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus I. R., Welch M., Eisenbach M. Pausing of flagellar rotation is a component of bacterial motility and chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3627–3632. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3627-3632.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Bacterial flagella rotating in bundles: a study in helical geometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):221–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Examination of bacterial flagellation by dark-field microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):258–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.258-265.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Han D. P. Asynchronous switching of flagellar motors on a single bacterial cell. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Oesterhelt D. Quantitation of photochromism of sensory rhodopsin-I by computerized tracking of Halobacterium halobium cells. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Oesterhelt D. Signal formation in the halobacterial photophobic response mediated by a fourth retinal protein (P480). J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90654-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Schäfer W., Oesterhelt D. Signal transduction in Halobacterium depends on fumarate. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):355–362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCain D. A., Amici L. A., Spudich J. L. Kinetically resolved states of the Halobacterium halobium flagellar motor switch and modulation of the switch by sensory rhodopsin I. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4750–4758. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4750-4758.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Krippahl G. Phototrophic growth of halobacteria and its use for isolation of photosynthetically-deficient mutants. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jul-Aug;134B(1):137–150. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(83)80101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Marwan W. Change of membrane potential is not a component of the photophobic transduction chain in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3515–3520. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3515-3520.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Tittor J. Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otomo J., Marwan W., Oesterhelt D., Desel H., Uhl R. Biosynthesis of the two halobacterial light sensors P480 and sensory rhodopsin and variation in gain of their signal transduction chains. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2155–2159. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2155-2159.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Waterbury J. B., Trüper H. G. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2374–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2374-2392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Control of transmembrane ion fluxes to select halorhodopsin-deficient and other energy-transduction mutants of Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4308–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Sensory rhodopsins of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:193–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


