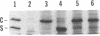Abstract
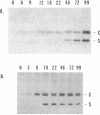
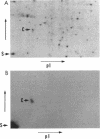
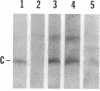
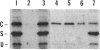
Fruiting body formation in Myxococcus xanthus involves the aggregation of cells to form mounds and the differentiation of rod-shaped cells into spherical myxospores. The surface of the myxospore is composed of several sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-soluble proteins, the best characterized of which is protein S (Mr, 19,000). We have identified a new major spore surface protein called protein C (Mr, 30,000). Protein C is not present in extracts of vegetative cells but appears in extracts of developing cells by 6 h. Protein C, like protein S, is produced during starvation in liquid medium but is not made during glycerol-induced sporulation. Its synthesis is blocked in certain developmental mutants but not others. When examined by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, two forms of protein C are observed. Protein C is quantitatively released from spores by treatment with 0.1 N NaOH or by boiling in 1% SDS. It is slowly washed from the spore surface in water but is stabilized by the presence of magnesium. Protein C binds to the surface of spores depleted of protein C and protein S. Protein C is a useful new marker for development in M. xanthus because it is developmentally regulated, spore associated, abundant, and easily purified.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., GIBSON S. M. A SYSTEM FOR STUDYING MICROBIAL MORPHOGENESIS: RAPID FORMATION OF MICROCYSTS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):243–244. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Kupfer D., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus. Analysis of the genes for protein S. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):469–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Zusman D. R. Differential expression of protein S genes during Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1146–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1146-1155.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Kaiser D. Cell interactions in myxobacterial growth and development. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):18–24. doi: 10.1126/science.3929384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Komano T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Functional complementation between the two homologous genes, ops and tps, during differentiation of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):434–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00330755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. E., Cull M. G. Control of developmental gene expression by cell-to-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R. C., Dahmus M. E. Rapid visualization of protein bands in preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Franceschini T., Inouye M. Structural similarities between the development-specific protein S from a gram-negative bacterium, Myxococcus xanthus, and calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6829–6833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Ike Y., Inouye M. Tandem repeat of the genes for protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Furuichi T., Teintze M., Inouye M., Inouye S. Effects of deletion of the gene for the development-specific protein S on differentiation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1195–1197. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1195-1197.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Multiple immunoreplica Technique: screening for specific proteins with a series of different antibodies using one polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90577-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Localization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin in the periplasmic space and on the cell surface of Myxococcus xanthus during developmental aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12589–12595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Patterns of cellular interactions during fruiting-body formation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6013–6024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6013-6024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Esmon B., Zusman D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the myxobacterial hemagglutinin gene contains four homologous domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Zusman D. R. Cloning of the gene for myxobacterial hemagglutinin and isolation and analysis of structural gene mutations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3801–3808. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3801-3808.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teintze M., Thomas R., Furuichi T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Two homologous genes coding for spore-specific proteins are expressed at different times during development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):121–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.121-125.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. Alkaline, acid, and neutral phosphatase activities are induced during development in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2294–2302. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2294-2302.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]