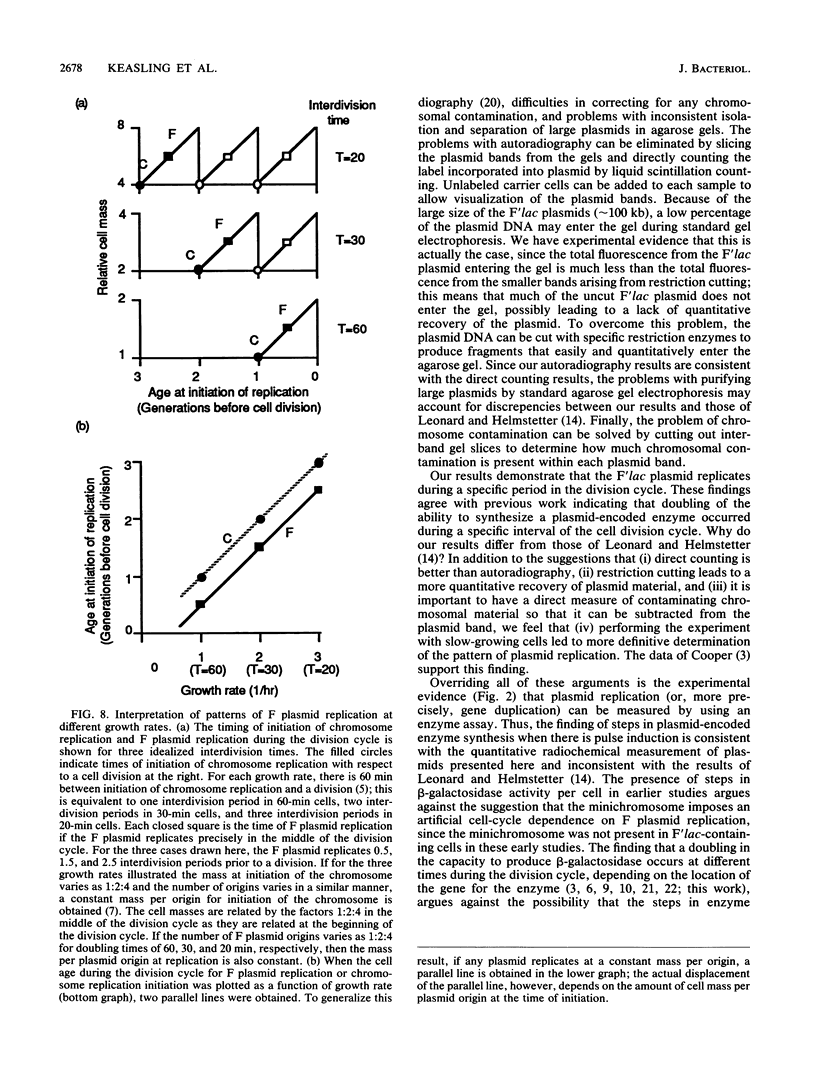
Abstract
F plasmid replication during the Escherichia coli division cycle was investigated by using the membrane-elution technique to produce cells labeled at different times during the division cycle and scintillation counting for quantitative analysis of radioactive plasmid DNA. The F plasmid replicated, like the minichromosome, during a restricted portion of the bacterial division cycle; i.e., F plasmid replication is cell-cycle specific. The F plasmid replicated at a different time during the division cycle than a minichromosome present in the same cell. F plasmid replication coincided with doubling in the rate of enzyme synthesis from a plasmid-encoded gene. When the cell cycle age of replication of the F plasmid was determined over a range of growth rates, the cell size at which the F plasmid replicated followed the same rules as did replication of the bacterial chromosome--initiation occurred when a constant mass per origin was achieved--except that the initiation mass per origin for the F plasmid was different from that for the chromosome origin. In contrast, the high-copy mini-R6K plasmid replicated throughout the division cycle.
Full text
PDF

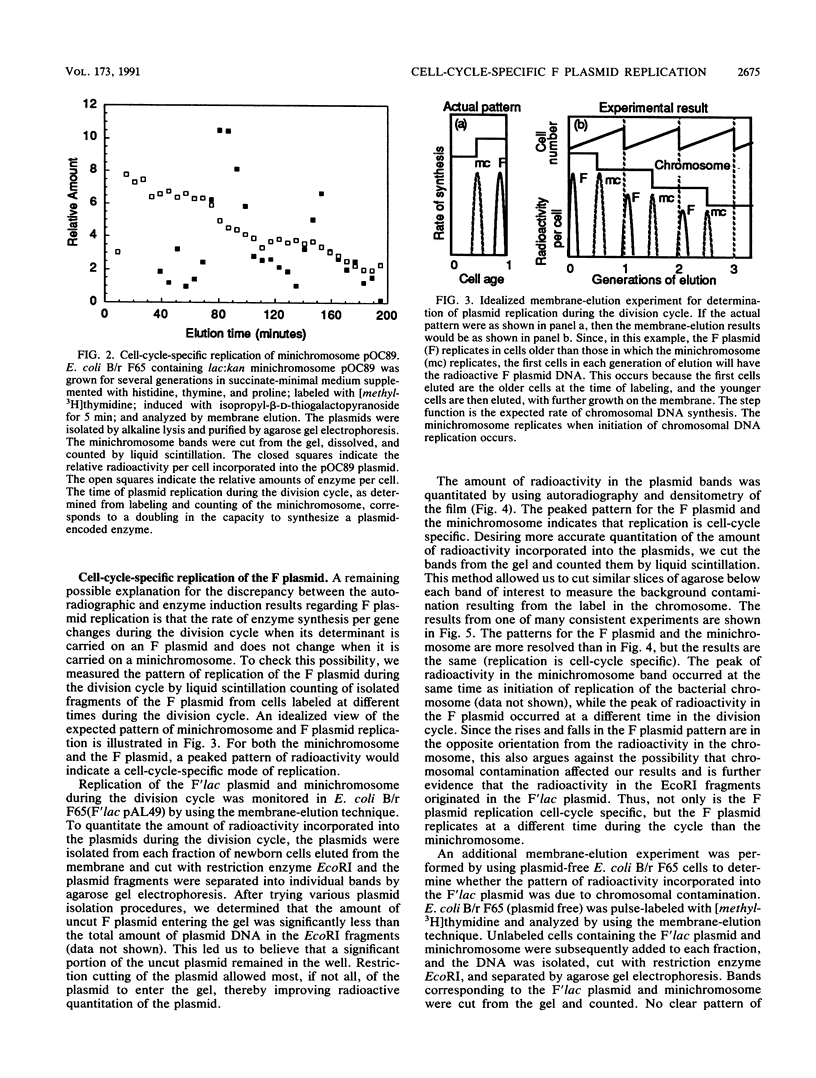
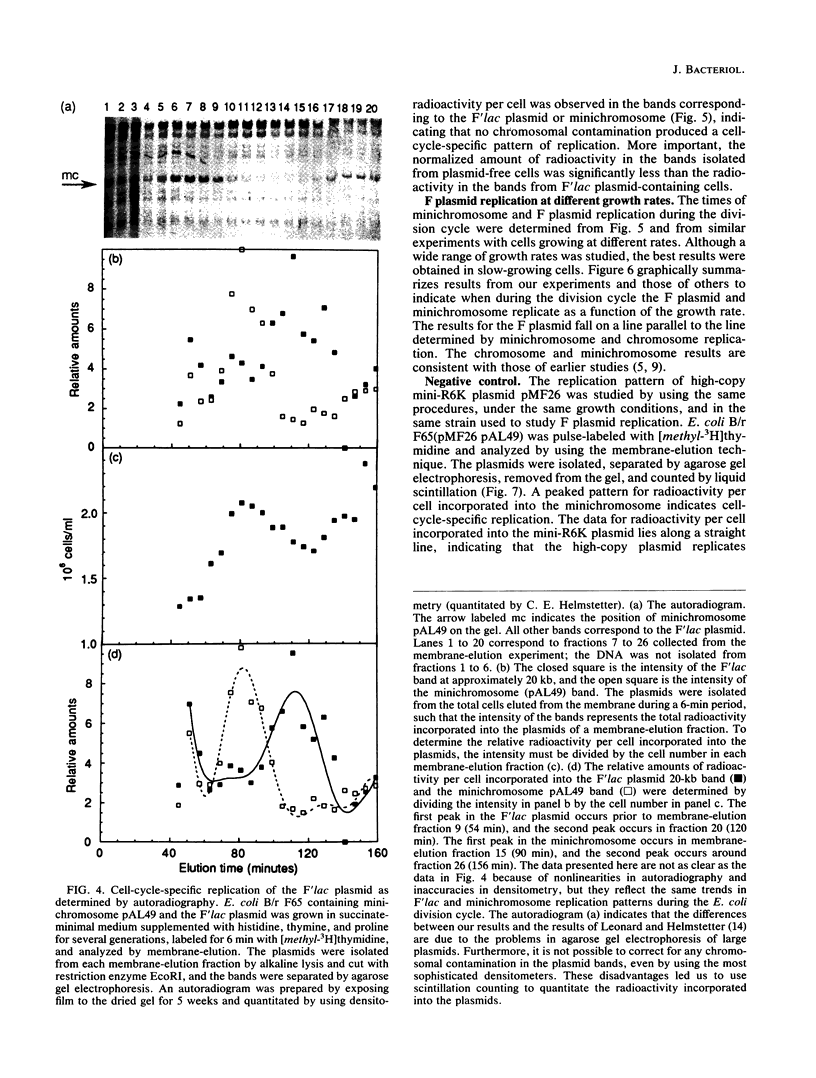
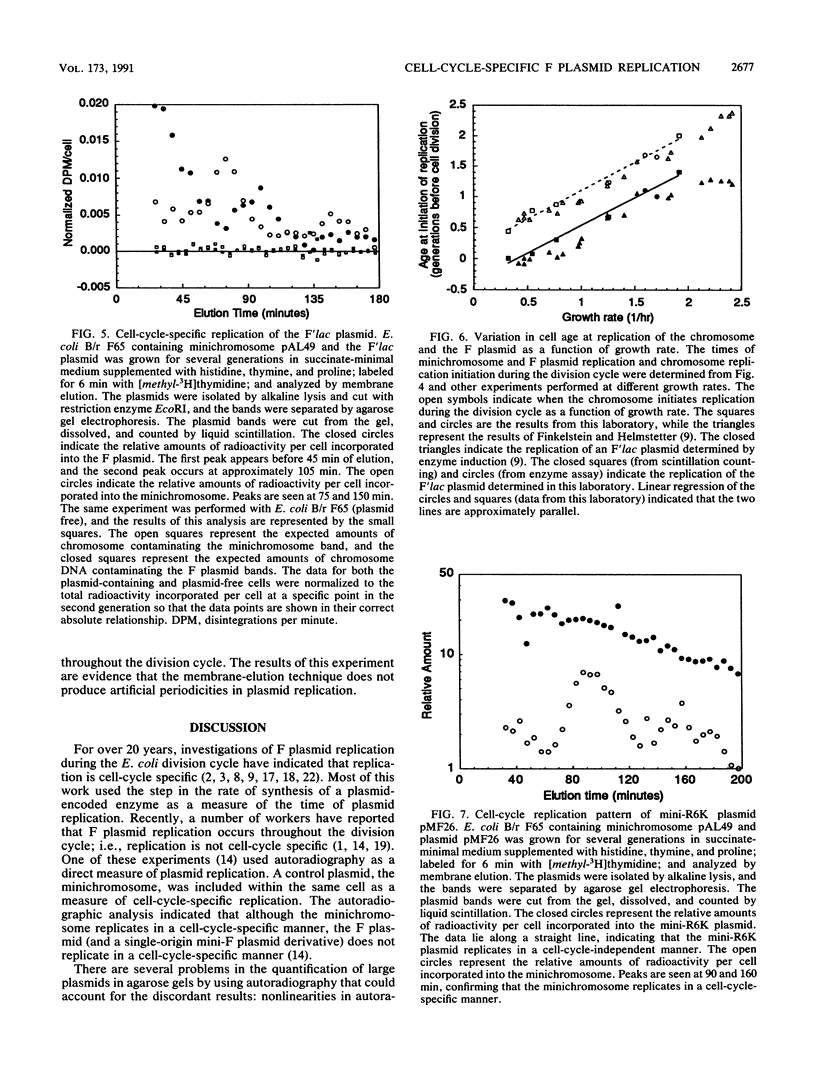


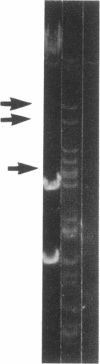
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andresdottir V., Masters M. Evidence that F' lac replicates asynchronously during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 11;163(2):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00267411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Pritchard R. H. Relationship between chromosome replication and F'lac episome replication in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;78(1):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. Leucine uptake and protein synthesis are exponential during the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):436–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.436-438.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. Relationship of Flac replication and chromosome replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2706–2710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. B., Helmstetter C. E. Control of F'lac replication in Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):294–299. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.294-299.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D., Masters M. Evidence for polarity of chromosome replication in F- strains of Escherichia coli. Genet Res. 1966 Aug;8(1):119–124. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D. Relationship between cell size and time of initiation of DNA replication. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1077–1079. doi: 10.1038/2191077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M., Helmstetter C. E. Cell cycle analysis of F'lac replication in Escherichia coli B/r. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):884–895. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.884-895.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C. E. DNA synthesis during the division cycle of rapidly growing Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):507–518. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstetter C. E. Origin and sequence of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1634–1641. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1634-1641.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard A. C., Helmstetter C. E. Cell cycle-specific replication of Escherichia coli minichromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5101–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard A. C., Helmstetter C. E. Replication patterns of multiple plasmids coexisting in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1380–1383. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1380-1383.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi A., Horiuchi T. Beta-galactosidase formation controlled by an episomal gene during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1966 Sep;60(3):338–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard R. H., Chandler M. G., Collins J. Independence of F replication and chromosome replication in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;138(2):143–155. doi: 10.1007/BF02428118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D. A., Helmstetter C. E. F plasmid replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. Plasmid. 1981 Nov;6(3):342–353. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Cochaux P., Lecocq R. A pitfall in the computer-aided quantitation of autoradiograms. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):440–441. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuthen J., Morozow E., Pato M. L. Pattern of replication of a colicin factor during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1425–1427. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1425-1427.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuthen J., Pato M. L. Replication of the F'lac sex factor in the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):242–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00433109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]