Abstract
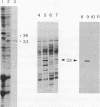
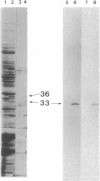
During sulfur-limited growth, the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 loses most of its photosynthetic pigments and develops an increased capacity to acquire sulfate. Sulfur deprivation also triggers the synthesis of several soluble polypeptides. We have isolated a prominent polypeptide of 33 kDa that accumulates specifically under sulfur-limiting conditions. This polypeptide was localized to the periplasmic space. The gene for this protein (designated rhdA) was isolated and discovered to lie within a region of the Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 genome that encodes components of the sulfate permease system. The mRNA for the 33-kDa protein accumulates to high levels within an hour after the cells are deprived of sulfur and drops rapidly when sulfur is added back to the cultures. The amino acid sequence of the protein has similarity to bovine liver rhodanese, an enzyme that transfers the thiol group of thiosulfate to a thiophilic acceptor molecule, and a rhodaneselike protein of Saccharopolyspora erythraea. A strain in which rhdA was interrupted by a drug resistance marker exhibited marginally lower levels of rhodanese activity but was still capable of efficiently utilizing a variety of inorganic sulfur sources. The possible role of this protein in the transport of specific sulfur compounds is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. M. Cyanobacterial cell inclusions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Joshi A. K. Energy coupling in bacterial periplasmic permeases. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4133–4137. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4133-4137.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Beatty J. T., Adams C. W., von Gabain A., Cohen S. N. Differential expression of photosynthesis genes in R. capsulata results from segmental differences in stability within the polycistronic rxcA transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop L., Agbayani R., Jr, Ambudkar S. V., Maloney P. C., Ames G. F. Reconstitution of a bacterial periplasmic permease in proteoliposomes and demonstration of ATP hydrolysis concomitant with transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6953–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. A., Grossman A. R. Identification and Purification of a Derepressible Alkaline Phosphatase from Anacystis nidulans R2. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1179–1184. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Belasco J. G. Degradation of pufLMX mRNA in Rhodobacter capsulatus is initiated by nonrandom endonucleolytic cleavage. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4578–4586. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4578-4586.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blomberg F. Immunochemical studies of thylakoid membrane polypeptides from spinach and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. A modified procedure for crossed immunoelectrophoresis of dodecyl sulfate.protein complexes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley P. B., Lemaux P. G., Grossman A. R. Cyanobacterial light-harvesting complex subunits encoded in two red light-induced transcripts. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):550–553. doi: 10.1126/science.3931221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donadio S., Shafiee A., Hutchinson C. R. Disruption of a rhodaneselike gene results in cysteine auxotrophy in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):350–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.350-360.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. S., Grossman A. R. Changes in sulfate transport characteristics and protein composition of Anacystis nidulans R2 during sulfur deprivation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):583–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.583-587.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. S., Laudenbach D. E., Grossman A. R. A region of a cyanobacterial genome required for sulfate transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1949–1953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryniewicz M., Sirko A., Pałucha A., Böck A., Hulanicka D. Sulfate and thiosulfate transport in Escherichia coli K-12: identification of a gene encoding a novel protein involved in thiosulfate binding. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3358–3366. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3358-3366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanjean R., Broda E. Dependence of sulphate uptake by Anacystis nidulans on energy, on osmotic shock and on sulphate stravation. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):19–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00429625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A. Enzymic reduction of thiosulphate in preparations from beef liver. Acta Biochim Pol. 1968;15(2):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau R. H., Blakeley S. D., Alvarado-Urbina G., Bailly J. E., Condie J. A., Lau P. C. Duplication of the phycocyanin operon in the unicellular cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans R2. Gene. 1989 Aug 15;80(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudenbach D. E., Grossman A. R. Characterization and mutagenesis of sulfur-regulated genes in a cyanobacterium: evidence for function in sulfate transport. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2739–2750. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2739-2750.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegman J. H., Drent G., Kalk K. H., Hol W. G. Structure of bovine liver rhodanese. I. Structure determination at 2.5 A resolution and a comparison of the conformation and sequence of its two domains. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):557–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J., Weng L., Keim P. S., Heinrikson R. L. The covalent structure of bovine liver rhodanese. Isolation and partial structural analysis of cyanogen bromide fragements and the complete sequence of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8102–8108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirko A., Hryniewicz M., Hulanicka D., Böck A. Sulfate and thiosulfate transport in Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence and expression of the cysTWAM gene cluster. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3351–3357. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3351-3357.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Lascelles J. Thiosulphate metabolism and rhodanese in Chromatium sp. strain D. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Mar;42(3):357–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression: 3' inverted repeats act as mRNA processing and stabilizing elements, but do not terminate transcription. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1145–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandeau de Marsac N., Borrias W. E., Kuhlemeier C. J., Castets A. M., van Arkel G. A., van den Hondel C. A. A new approach for molecular cloning in cyanobacteria: cloning of an Anacystis nidulans met gene using a Tn901-induced mutant. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Plas J., Bovy A., Kruyt F., de Vrieze G., Dassen E., Klein B., Weisbeek P. The gene for the precursor of plastocyanin from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7937: isolation, sequence and regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Mar;3(3):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng L., Heinrikson R. L., Westley J. Active site cysteinyl and arginyl residues of rhodanese. A novel formation of disulfide bonds in the active site promoted by phenylglyoxal. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8109–8119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley J. Rhodanese. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;39:327–368. doi: 10.1002/9780470122846.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]