Abstract
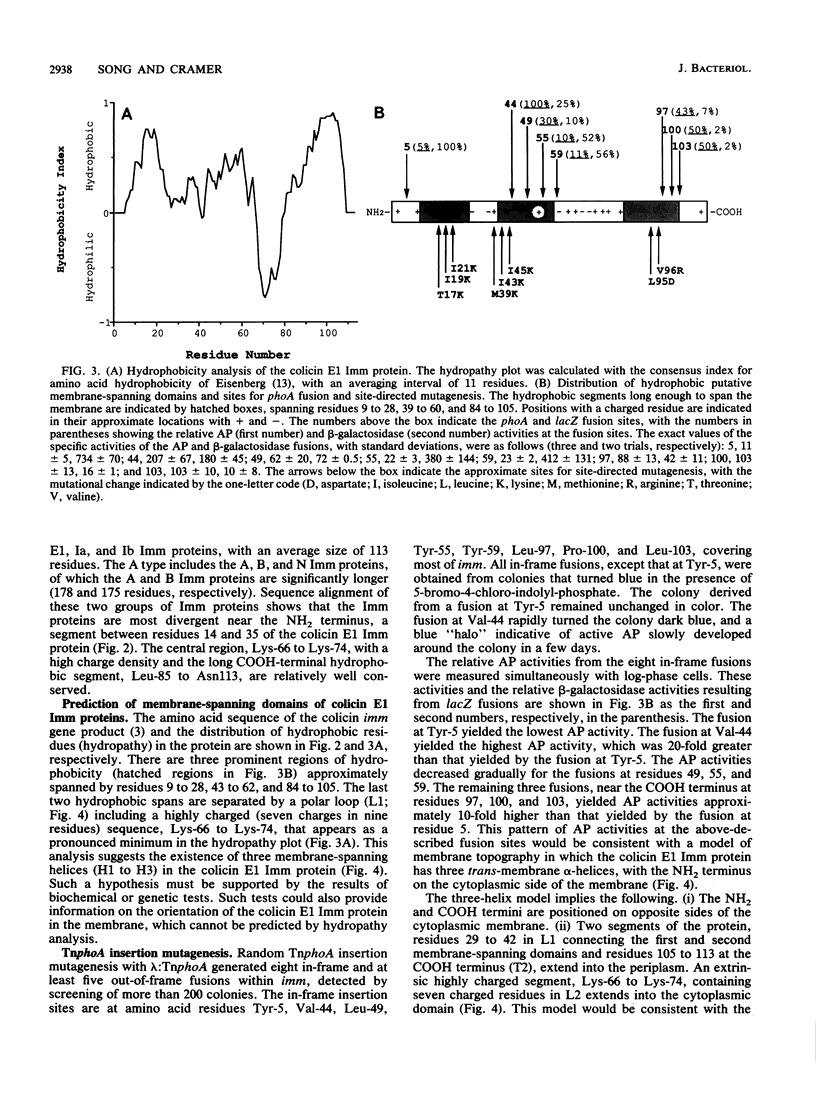
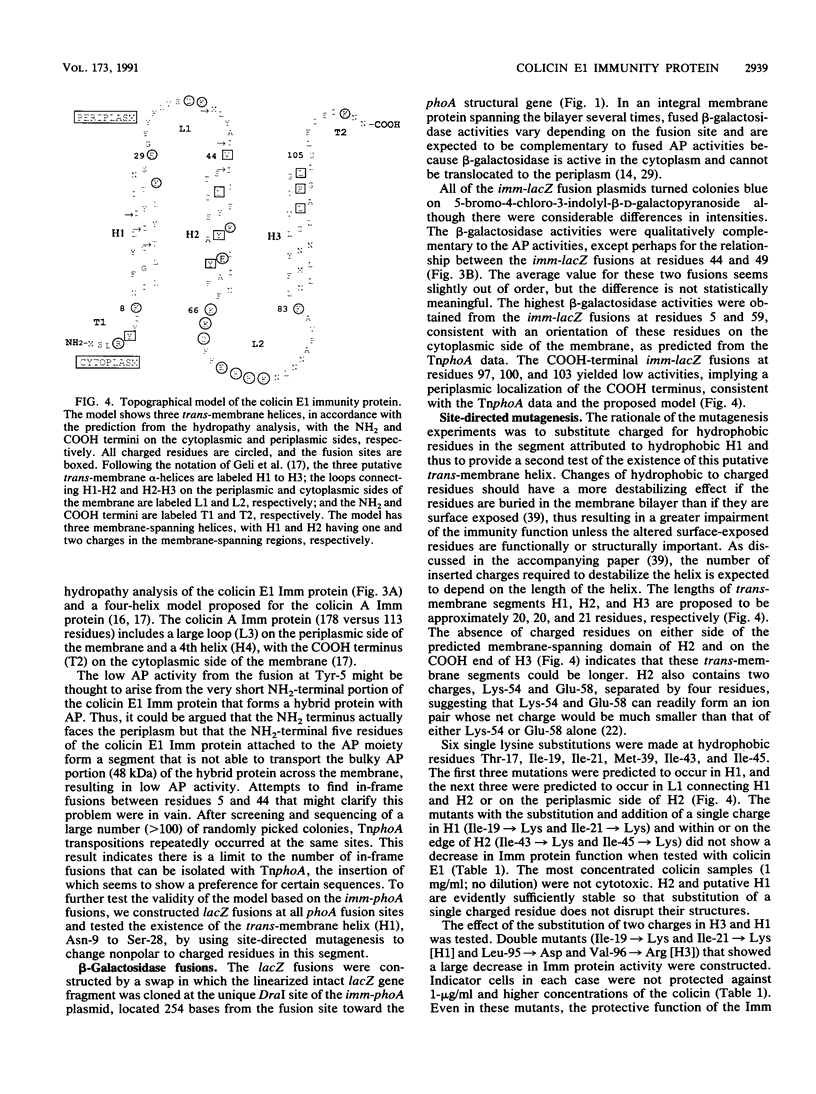
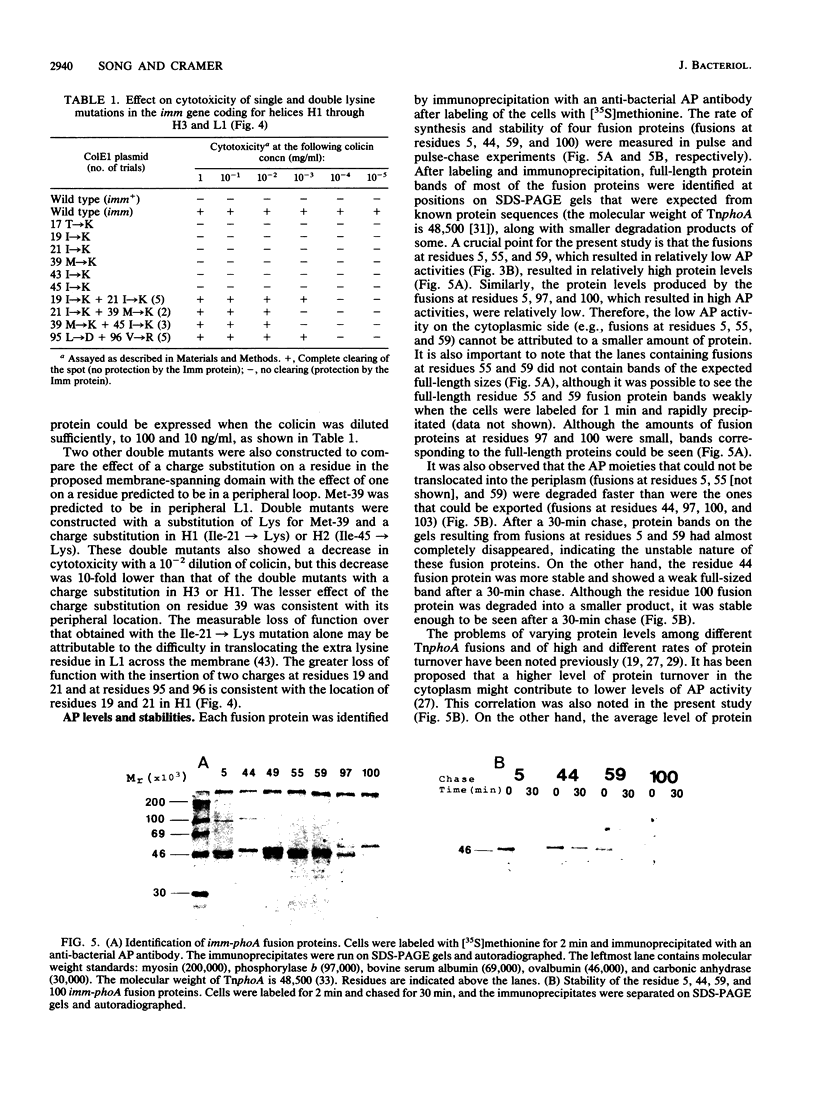
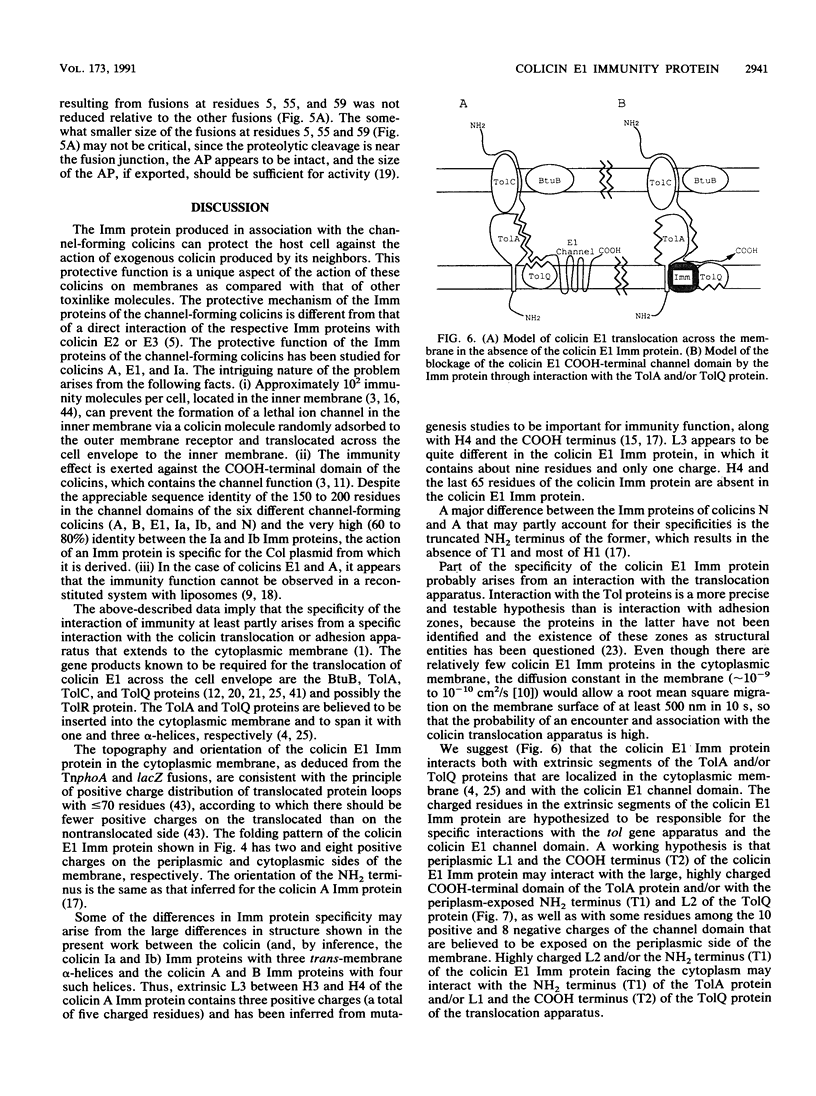
The topography of the colicin E1 immunity (Imm) protein was determined from the positions of TnphoA and complementary lacZ fusions relative to the three long hydrophobic segments of the protein and site-directed substitution of charged for nonpolar residues in the proposed membrane-spanning segments. Inactivation of the Imm protein function required substitution and insertion of two such charges. It was concluded that the 113-residue colicin E1 Imm protein folds in the membrane as three trans-membrane alpha-helices, with the NH2 and COOH termini on the cytoplasmic and periplasmic sides of the membrane, respectively. The approximate spans of the three helices are Asn-9 to Ser-28, Ile-43 to Phe-62, and Leu-84 to Leu-104. An extrinsic highly charged segment, Lys-66 to Lys-74, containing seven charges in nine residues, extends into the cytoplasmic domain. The specificity of the colicin E1 Imm protein for interaction with the translocation apparatus and the colicin E1 ion channel is proposed to reside in its peripheral segments exposed on the surface of the inner membrane. These regions include the highly charged segment Lys-66 to Lys-83 (loop 2) and the short (approximately eight-residue) NH2 terminus on the cytoplasmic side, and Glu-29 to Val-44 (loop 1) and the COOH-terminal segment Gly-105 to Asn-113 on the periplasmic side.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baty D., Pattus F., Parker M., Benedetti H., Frenette M., Bourdineaud J. P., Cavard D., Knibiehler M., Lazdunski C. Uptake across the cell envelope and insertion into the inner membrane of ion channel-forming colicins in E coli. Biochimie. 1990 Feb-Mar;72(2-3):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop L. J., Bjes E. S., Davidson V. L., Cramer W. A. Localization of the immunity protein-reactive domain in unmodified and chemically modified COOH-terminal peptides of colicin E1. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):237–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.237-244.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdineaud J. P., Howard S. P., Lazdunski C. Localization and assembly into the Escherichia coli envelope of a protein required for entry of colicin A. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2458–2465. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2458-2465.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Sidikaro J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3 in vitro and mechanism of immunity in colicinogenic cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):133–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio234133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Determinants of membrane protein topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E., Beckwith J. Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and phi80 transducing phages. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Cohen F. S., Merrill A. R., Song H. Y. Structure and dynamics of the colicin E1 channel. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):519–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J. R., Uratani Y., Grabau C., Cramer W. A., Hermodson M. On a domain structure of colicin E1. A COOH-terminal peptide fragment active in membrane depolarization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3857–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Green G. N., Boyd D., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of the membrane insertion and topology of MalF, a cytoplasmic membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90539-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Baty D., Crozel V., Morlon J., Lloubes R., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. A molecular genetic approach to the functioning of the immunity protein to colicin A. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Mar;202(3):455–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00333276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Baty D., Lazdunski C. Use of a foreign epitope as a "tag" for the localization of minor proteins within a cell: the case of the immunity protein to colicin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Baty D., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. Topology and function of the integral membrane protein conferring immunity to colicin A. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):679–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Knibiehler M., Bernadac A., Lazdunski C. Purification and reconstitution into liposomes of an integral membrane protein conferring immunity to colicin A. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gött P., Boos W. The transmembrane topology of the sn-glycerol-3-phosphate permease of Escherichia coli analysed by phoA and lacZ protein fusions. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):655–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the vitamin B12 receptor protein in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):904–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.904-908.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K., Mann B. J., Kadner R. J. Cloning and expression of the gene for the vitamin B12 receptor protein in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):896–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.896-903.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B. H., Hubbell W. L. Stability of "salt bridges" in membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5412–5416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E. The 'Bayer bridges' confronted with results from improved electron microscopy methods. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):697–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levengood S. K., Webster R. E. Nucleotide sequences of the tolA and tolB genes and localization of their products, components of a multistep translocation system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6600–6609. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6600-6609.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloubes R. P., Chartier M. J., Journet A. M., Varenne S. G., Lazdunski C. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the immunity protein to colicin A. Analysis of codon usage of immunity proteins as compared to colicins. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. D., Kadner R. J. Topology of the Escherichia coli uhpT sugar-phosphate transporter analyzed by using TnphoA fusions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1688–1693. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1688-1693.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankovich J. A., Hsu C. H., Konisky J. DNA and amino acid sequence analysis of structural and immunity genes of colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.228-236.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C. Analysis of protein localization by use of gene fusions with complementary properties. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1035–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1035-1042.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Hunt J. F., Beckwith J. Effects of signal sequence mutations on the kinetics of alkaline phosphatase export to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):160–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.160-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Nomura N., Morita M., Sugisaki H., Sugimoto K., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of small ColE1 derivatives: structure of the regions essential for autonomous replication and colicin E1 immunity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 4;172(2):151–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00268276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The immunity and lysis genes of ColN plasmid pCHAP4. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Feb;211(2):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00330613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm E., Olschläger T., Tröger W., Braun V. Sequence, expression and localization of the immunity protein for colicin B. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):176–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00338410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song H. Y., Cohen F. S., Cramer W. A. Membrane topography of ColE1 gene products: the hydrophobic anchor of the colicin E1 channel is a helical hairpin. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2927–2934. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2927-2934.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suit J. L., Fan M. L., Kayalar C., Luria S. E. Genetic study of the functional organization of the colicin E1 molecule. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):944–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.944-948.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. P., Webster R. E. Nucleotide sequence of a gene cluster involved in entry of E colicins and single-stranded DNA of infecting filamentous bacteriophages into Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2667–2674. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2667-2674.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. A., Redborg A. H., Konisky J. Plasmid-determined immunity of Escherichia coli K-12 to colicin Ia Is mediated by a plasmid-encoded membrane protein. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):817–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.817-828.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Gavel Y. Topogenic signals in integral membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):671–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]