Abstract
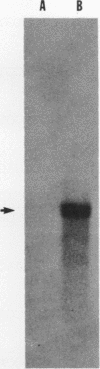
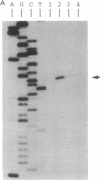
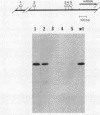
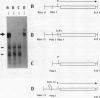
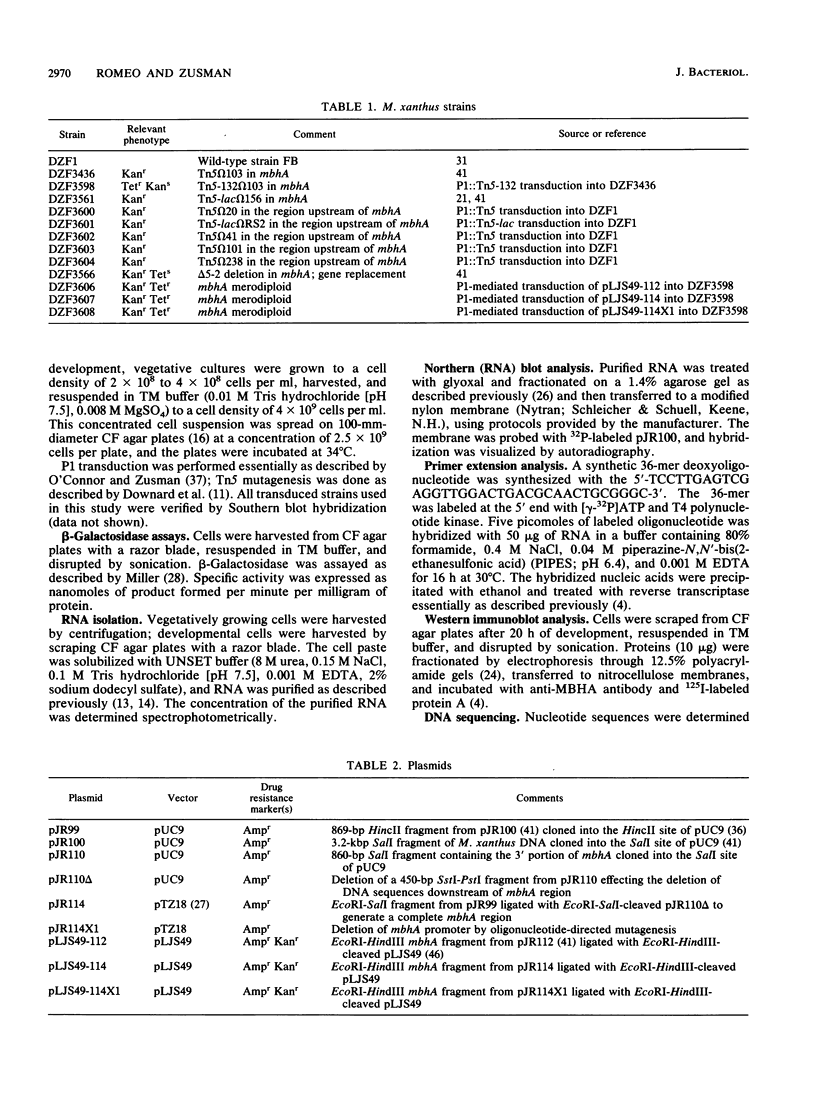
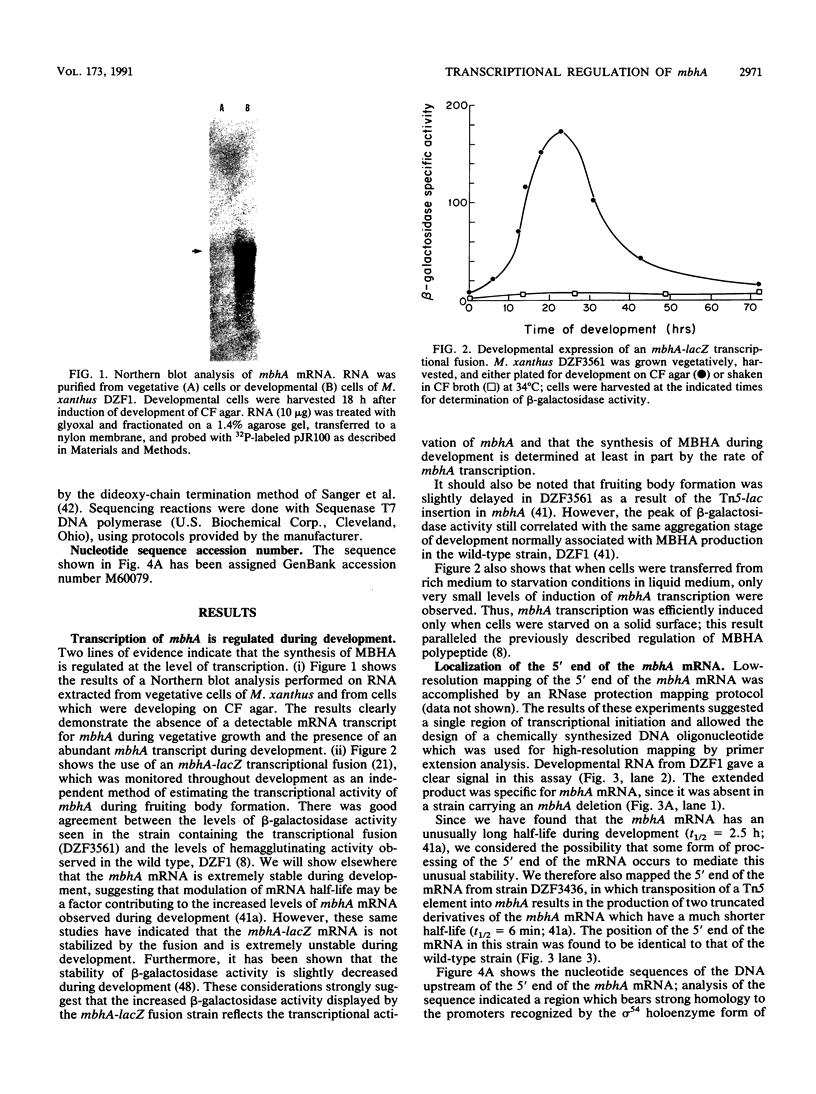
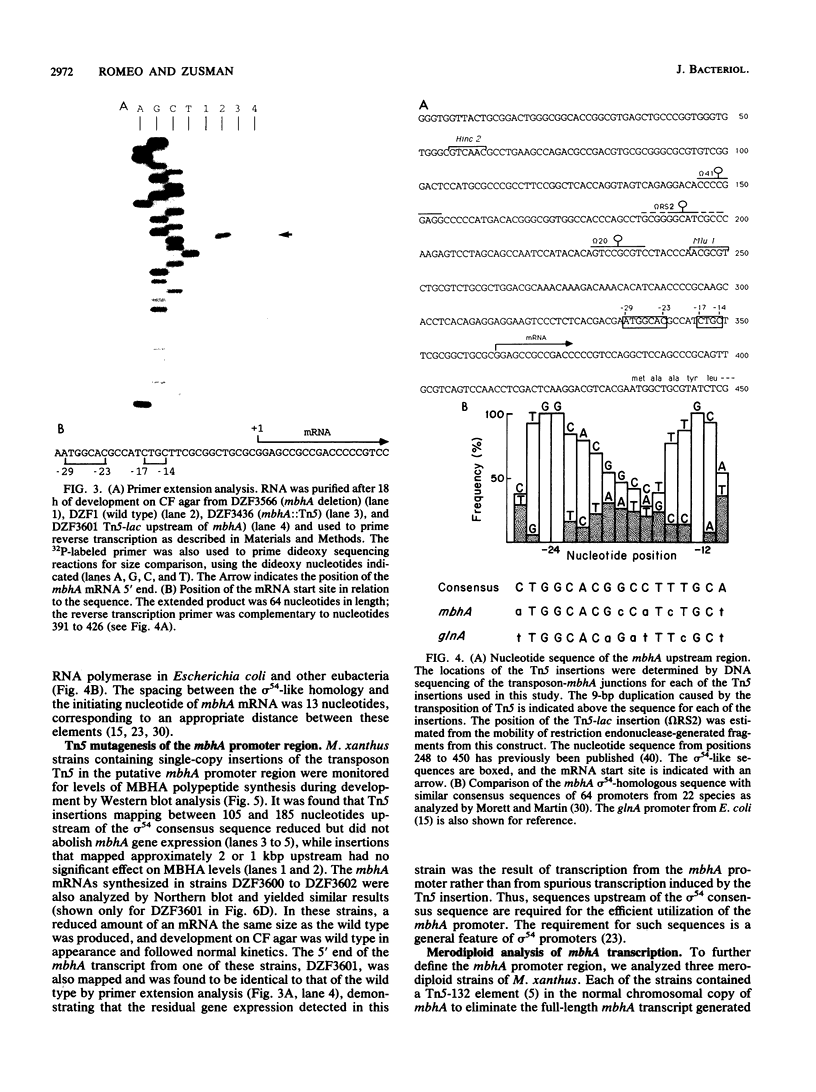
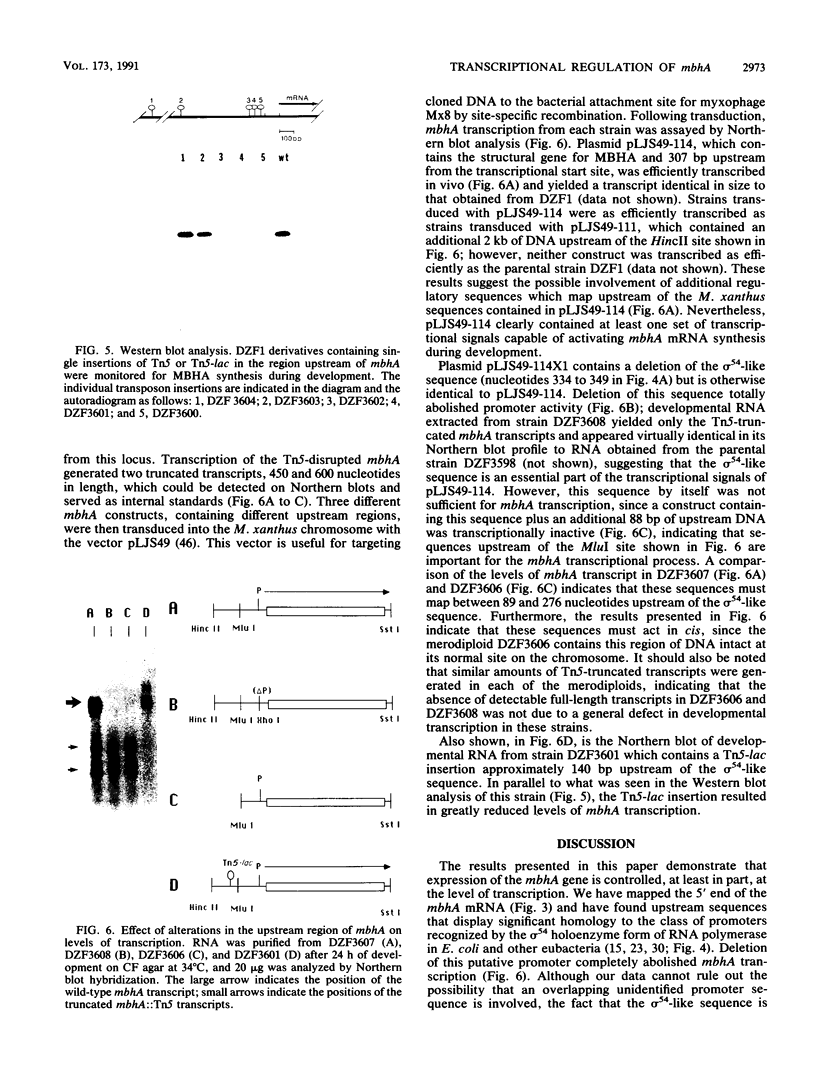
Myxobacterial hemagglutinin (MBHA) is a major developmentally induced protein that accumulates during the period of cellular aggregation of the fruiting bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. In this study, DNA sequences mediating the transcriptional regulation of mbhA have been identified. Examination of nucleotide sequences upstream of the start site for mbhA transcription has indicated a region of DNA that bears strong homology to the consensus sequence for promoters recognized by the sigma 54 holoenzyme form of RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli and other eubacteria. Deletion of this sequence completely abolished mbhA transcription. Additionally, a cis-acting DNA element, affecting the efficiency of mbhA transcription, has been mapped within a region of DNA 89 to 276 nucleotides upstream of the sigma 54-like sequence. Transposon insertions, mapping within the cis element, drastically reduced mbhA transcriptional activity. These observations suggest that transcription of mbhA requires a productive interaction between a form of RNA polymerase that recognizes a sigma 54-like sequence and a transcriptional activator that binds to DNA sequences upstream of the mbhA promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apelian D., Inouye S. Development-specific sigma-factor essential for late-stage differentiation of Myxococcus xanthus. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1396–1403. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Weiss A., Crossland L. Polarity of Tn5 insertion mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.439-446.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Kaiser D. dsg, a gene required for cell-cell interaction early in Myxococcus development. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3719–3726. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3719-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Purification and characterization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin, a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12581–12588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Kim S. H., Kil K. S. Localization of the cis-acting regulatory DNA sequences of the Myxococcus xanthus tps and ops genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4931–4938. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4931-4938.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Kupfer D., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus. Analysis of the genes for protein S. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):469–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Zusman D. R. Differential expression of protein S genes during Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1146–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1146-1155.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Bertrand H., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in Neurospora mitochondria: nuclear mutants defective in both splicing and 3' end synthesis of the large rRNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Ike Y., Inouye M. Tandem repeat of the genes for protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Control of multicellular development: Dictyostelium and Myxococcus. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:539–566. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kil K. S., Brown G. L., Downard J. S. A segment of Myxococcus xanthus ops DNA functions as an upstream activation site for tps gene transcription. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3081–3088. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3081-3088.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R., Kuner J., Hagen D., Manoil C., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions of Myxococcus xanthus: analysis of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1394–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1394-1404.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. In vivo studies on the interaction of RNA polymerase-sigma 54 with the Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti nifH promoters. The role of NifA in the formation of an open promoter complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin D., Minnich S., Chen L. S., Newton A. A set of positively regulated flagellar gene promoters in Caulobacter crescentus with sequence homology to the nif gene promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):939–943. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Localization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin in the periplasmic space and on the cell surface of Myxococcus xanthus during developmental aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12589–12595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Initiation of transcription at the bacterial glnAp2 promoter by purified E. coli components is facilitated by enhancers. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon B. T., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Two-component regulatory systems responsive to environmental stimuli share strongly conserved domains with the nitrogen assimilation regulatory genes ntrB and ntrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Coliphage P1-mediated transduction of cloned DNA from Escherichia coli to Myxococcus xanthus: use for complementation and recombinational analyses. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):317–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.317-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Esmon B., Zusman D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the myxobacterial hemagglutinin gene contains four homologous domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Zusman D. R. Cloning of the gene for myxobacterial hemagglutinin and isolation and analysis of structural gene mutations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3801–3808. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3801-3808.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Probing the Escherichia coli glnALG upstream activation mechanism in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8934–8938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Asher S. J. Use of recombination techniques to examine the structure of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00338394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Control of morphogenesis in myxobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(3):195–227. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teintze M., Thomas R., Furuichi T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Two homologous genes coding for spore-specific proteins are expressed at different times during development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):121–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.121-125.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. Evidence that the Myxococcus xanthus frz genes are developmentally regulated. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6174–6186. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6174-6186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]