Abstract
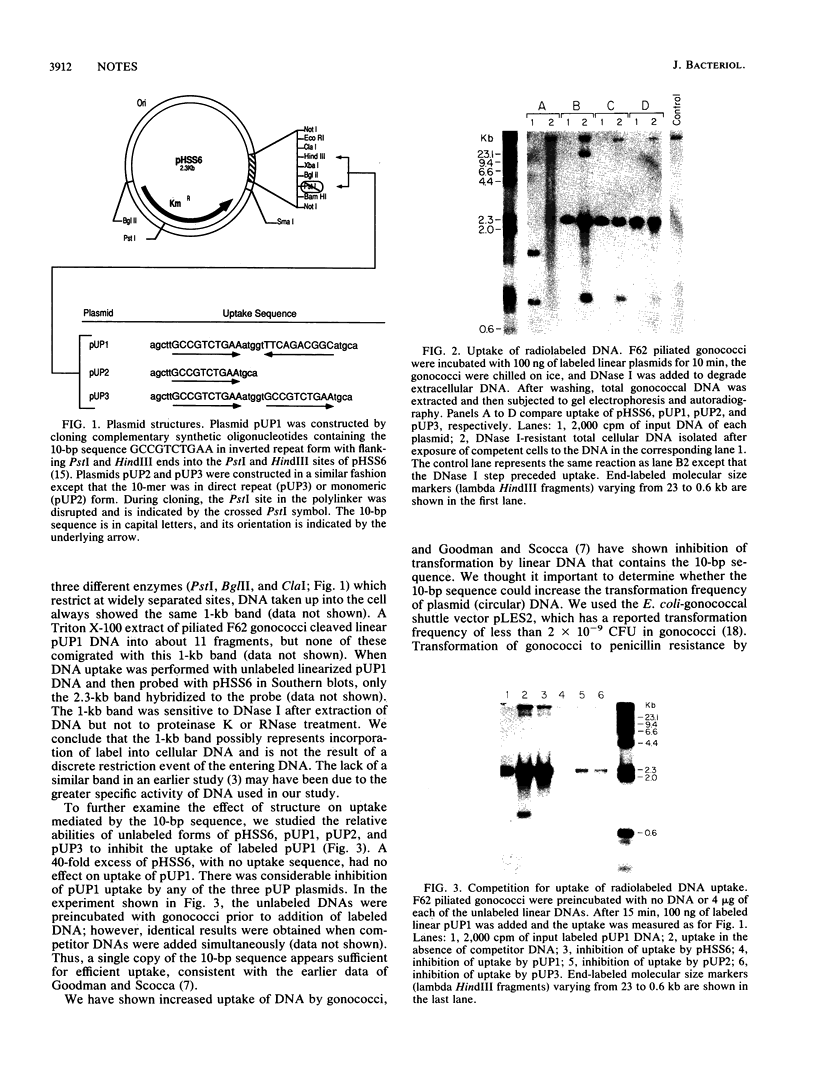
Piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae are known to be transformed less readily if transforming DNA competes with DNA containing the 10-bp sequence GCCGTCTGAA. It has been postulated that the 10-bp sequence is a recognition sequence which is required for efficient DNA uptake. We show that the presence of various forms of this 10-bp sequence results in increased uptake of double-stranded DNA into a DNase-resistant state and allows genetic transformation by an otherwise nontransformable plasmid.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biswas G. D., Lacks S. A., Sparling P. F. Transformation-deficient mutants of piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.657-664.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas G. D., Thompson S. A., Sparling P. F. Gene transfer in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S24–S28. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstein K. L., Dyer D. W., Sparling P. F. Preferential uptake of restriction fragments from a gonococcal cryptic plasmid by competent Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):547–557. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Sparling P. F. The genetics of the gonococcus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:111–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorward D. W., Garon C. F. DNA-binding proteins in cells and membrane blebs of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4196–4201. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4196-4201.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Asmus A., Tomasz A. Specificity of DNA uptake in genetic transformation of gonococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 15;86(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Scocca J. J. Identification and arrangement of the DNA sequence recognized in specific transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6982–6986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. E., Barany F., Smith H. O. Transformasomes: specialized membranous structures that protect DNA during Haemophilus transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6927–6931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis L. S., Scocca J. J. On the role of pili in transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Dec;130(12):3165–3173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-12-3165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., Kutter E., Nakanishi M. A restriction map of the bacteriophage T4 genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):421–435. doi: 10.1007/BF00425473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlner J., Halter R., Beyreuther K., Meyer T. F. Gene structure and extracellular secretion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae IgA protease. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):458–462. doi: 10.1038/325458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H. S., Chen E. Y., So M., Heffron F. Shuttle mutagenesis: a method of transposon mutagenesis for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):735–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. C., Silver L. E., Clark V. L., Young F. E. Construction and characterization of a new shuttle vector, pLES2, capable of functioning in Escherichia coli and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Brown M., Nickel P., Meyer T. F. Opacity genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: control of phase and antigenic variation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]