Abstract
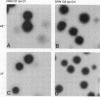
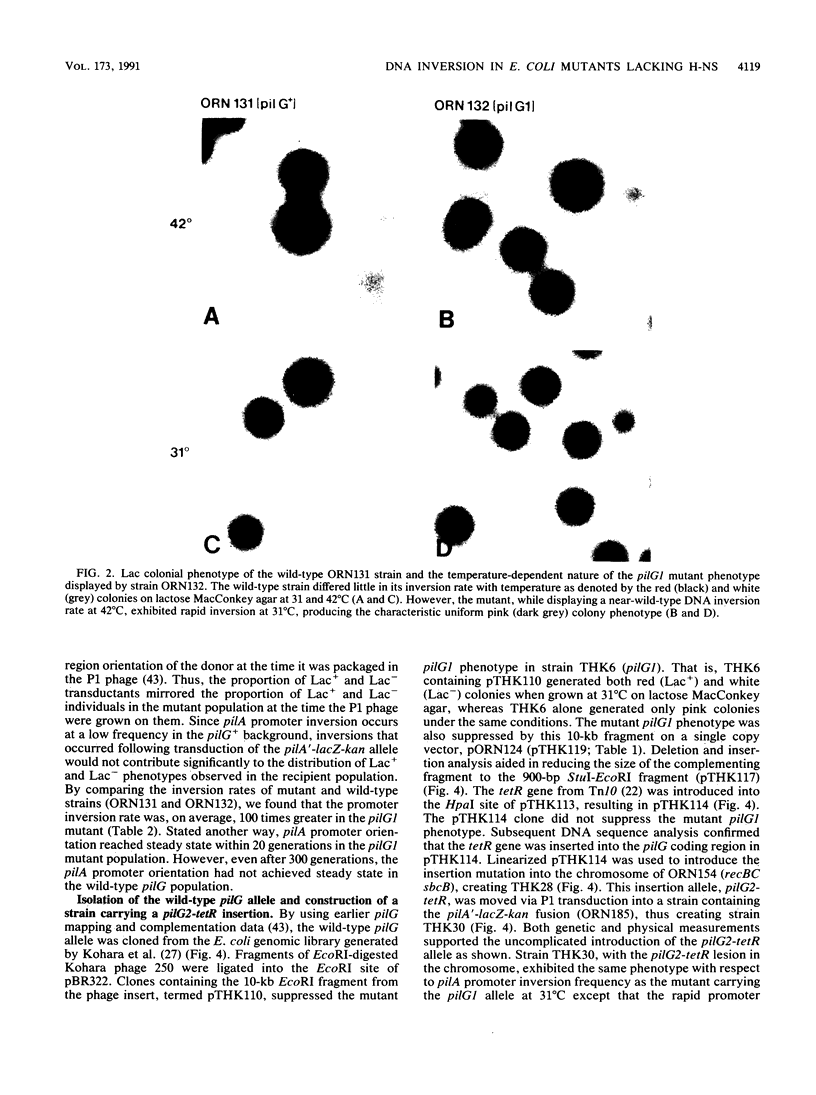
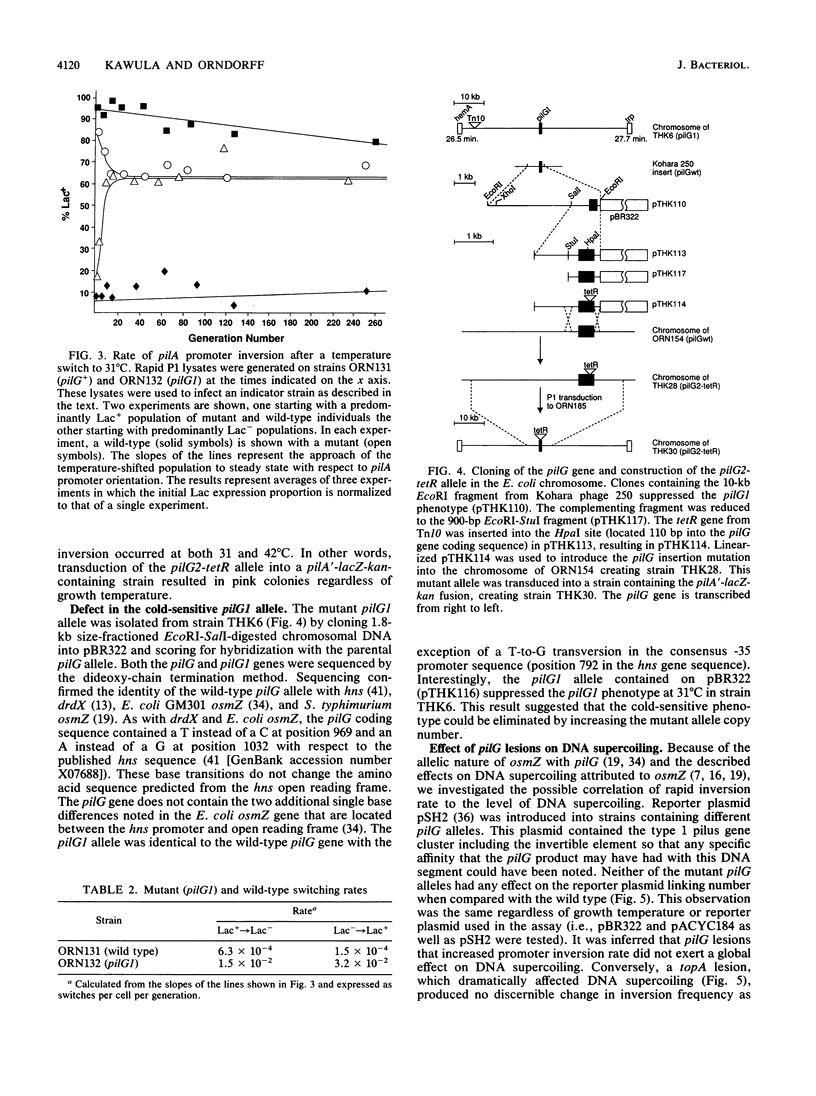
Escherichia coli pilG mutants are thought to have a dramatically higher DNA inversion rate as measured by the site-specific DNA inversion of the type 1 pili pilA promoter. DNA sequence of the pilG gene confirmed its identity to the gene encoding the bacterial histonelike protein H-NS. Unlike other histonelike protein complexes that enhance site-specific DNA recombination, the H-NS protein inhibited this process. This inhibition was indicated by the increased inversion rate of the pilA promoter region effected by two different mutant pilG alleles. One of these alleles, pilG1, conferred a mutant phenotype only at low temperature attributable to a T-to-G transversion in the -35 sequence of the pilG promoter. The other allele, pilG2-tetR, was an insertion mutation in the pilG coding region that conferred the mutant phenotype independent of temperature. We measured an approximately 100-fold-increased pilA promoter inversion rate in the mutant by exploiting the temperature-dependent expression of pilG1 and using a novel rapid-population-sampling method. Contrary to one current view on how the H-NS protein might act to increase DNA inversion rate, we found no evidence to support the hypothesis that DNA supercoiling affected pilA promoter inversion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Freitag C. S., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. An invertible element of DNA controls phase variation of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5724–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defez R., De Felice M. Cryptic operon for beta-glucoside metabolism in Escherichia coli K12: genetic evidence for a regulatory protein. Genetics. 1981 Jan;97(1):11–25. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Higgins C. F. Fimbrial phase variation in Escherichia coli: dependence on integration host factor and homologies with other site-specific recombinases. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3840–3843. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3840-3843.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Ni Bhriain N., Higgins C. F. DNA supercoiling and environmental regulation of virulence gene expression in Shigella flexneri. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):789–792. doi: 10.1038/344789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Sweet D. S., Vaughn V., Friedman D. I. Integration host factor is required for the DNA inversion that controls phase variation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6506–6510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconi M., Gualtieri M. T., La Teana A., Losso M. A., Pon C. L. Proteins from the prokaryotic nucleoid: primary and quaternary structure of the 15-kD Escherichia coli DNA binding protein H-NS. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):323–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitag C. S., Abraham J. M., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. Genetic analysis of the phase variation control of expression of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):668–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.668-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Sondén B., Nilsson P., Dagberg B., Forsman K., Emanuelsson K., Uhlin B. E. Transcriptional silencing and thermoregulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):682–685. doi: 10.1038/344682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffter P., Bickle T. A. Purification and DNA-binding properties of FIS and Cin, two proteins required for the bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination system, cin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Z., Clark A. J. Genetic analysis of the recF pathway to genetic recombination in Escherichia coli K12: isolation and characterization of mutants. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):327–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M. The invertible G segment of phage mu. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):605–606. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Seirafi A., Hinton J. C., Sidebotham J. M., Waddell L., Pavitt G. D., Owen-Hughes T., Spassky A., Buc H., Higgins C. F. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90458-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Kennedy K. E., Arber W. A site-specific, conservative recombination system carried by bacteriophage P1. Mapping the recombinase gene cin and the cross-over sites cix for the inversion of the C segment. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1445–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bruist M. F., Simon M. I. Host protein requirements for in vitro site-specific DNA inversion. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90878-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Berg D. E., Allet B., Reznikoff W. S. Restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn10, a transposon which encodes tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):681–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.681-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R. The relationship of two invertible segments in bacteriophage Mu and Salmonella typhimurium DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):564–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00352543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P., Christiansen G. Three fim genes required for the regulation of length and mediation of adhesion of Escherichia coli type 1 fimbriae. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00328136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Two regulatory fim genes, fimB and fimE, control the phase variation of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Kahmann R. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli host factor required for inversion of the G segment in bacteriophage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15673–15678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune P., Danchin A. Mutations in the bglY gene increase the frequency of spontaneous deletions in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):360–363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki S., Kuribayashi M., Miki T., Horiuchi T. An amber replication mutant of F plasmid mapped in the minimal replication region. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(2):231–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00334819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of a chromosomal gene controlling temperature-regulated expression of Shigella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Dersch P., Haardt M., Middendorf A., Bremer E. The osmZ (bglY) gene encodes the DNA-binding protein H-NS (H1a), a component of the Escherichia coli K12 nucleoid. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00259454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of a gene product that regulates type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):61–66. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.61-66.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Organization and expression of genes responsible for type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):736–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.736-744.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Spears P. A., Schauer D., Falkow S. Two modes of control of pilA, the gene encoding type 1 pilin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):321–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.321-330.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen L., Madsen O., Klemm P. Regulation of the phase switch controlling expression of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):925–931. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon C. L., Calogero R. A., Gualerzi C. O. Identification, cloning, nucleotide sequence and chromosomal map location of hns, the structural gene for Escherichia coli DNA-binding protein H-NS. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):199–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00334684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Phase variation: genetic analysis of switching mutants. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):845–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears P. A., Schauer D., Orndorff P. E. Metastable regulation of type 1 piliation in Escherichia coli and isolation and characterization of a phenotypically stable mutant. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):179–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.179-185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternglanz R., DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y., Becherer K., Zumstein L., Wang J. C. Mutations in the gene coding for Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I affect transcription and transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Kutsukake K., Komano T., Imamoto F., Kano Y. Participation of the hup gene product in site-specific DNA inversion in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1989;76(2):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]