Abstract
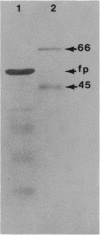
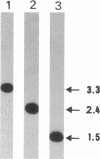
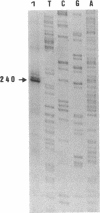
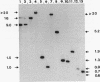
Electron microscopic observation of spiroplasmas lysed by detergent (sodium deoxycholate) revealed the release of bundles of fibrils from the cells. Individual fibrils are 4 nm in diameter and possess a 9-nm periodicity along their length. These fibrils are thought to function as cytoskeletal structures involved in the shape and motility of spiroplasmas. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of density gradient-purified fibrils showed a protein of approximately 55 kDa. Oligonucleotide probes were constructed from the N-terminal amino acid sequence of two peptides obtained after V8 protease hydrolysis of the fibril protein. The probes were used to identify the clones in a genomic DNA library of Spiroplasma citri that contained inserts carrying the probe sequence. Sequencing of a 3.3-kbp fragment yielded the full open reading frame of the fibril protein gene and the start of a second open reading frame of an unknown protein. The fibril protein is composed of 515 amino acids, which have a computed molecular mass of 59 kDa. Northern (RNA) blot hybridization and primer extension experiments showed that transcription of the fibril protein gene starts from a promoter located 100 nucleotides upstream of the initiation codon and stops at a rho-independent type terminator, leading to a 1.7-kbp transcript. Southern blot hybridization of genomic DNA using the fibril protein gene as the probe showed that a single copy of the gene is present in the chromosomes of both S. citri and Spiroplasma melliferum. The genotypic symbol fib is proposed for the spiroplasma fibril protein gene.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busetta B. Examination of folding patterns for predicting protein topologies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 28;870(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier C., Saillard C., Bove J. M. Spiralins of Spiroplasma citri and Spiroplasma melliferum: amino acid sequences and putative organization in the cell membrane. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6090–6097. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6090-6097.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier C., Saillard C., Bové J. M. Organization and nucleotide sequences of the Spiroplasma citri genes for ribosomal protein S2, elongation factor Ts, spiralin, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate kinase, and an unidentified protein. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2693–2703. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2693-2703.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geier G. E., Modrich P. Recognition sequence of the dam methylase of Escherichia coli K12 and mode of cleavage of Dpn I endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1408–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Morris N. R. Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid methylase mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1143–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1143-1150.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaudin J., Pascarel M. C., Bové J. M. Spiroplasma virus 4: nucleotide sequence of the viral DNA, regulatory signals, and proposed genome organization. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4950–4961. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4950-4961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallantin M., Huet J. C., Demarteau C., Pernollet J. C. Reassessment of commercially available molecular weight standards for peptide sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using electroblotting and microsequencing. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jan;11(1):34–36. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamburski C., Renaudin J., Bove J. M. Characterization of a promoter and a transcription terminator of Spiroplasma melliferum virus SpV4. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5586–5592. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5586-5592.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend R., Archer D. B., Plaskitt K. A. Purification and preliminary characterization of Spiroplasma fibrils. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):694–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.694-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. L. Unusual fibrils from the spirochete-like sex ratio organism. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):904–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.904-906.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski H., Johansson K. E., Hjérten S. Purification and characterization of spiralin, the main protein of the Spiroplasma citri membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]