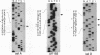Abstract
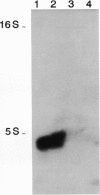
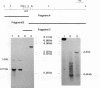
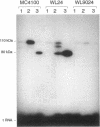
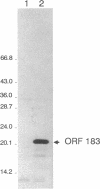
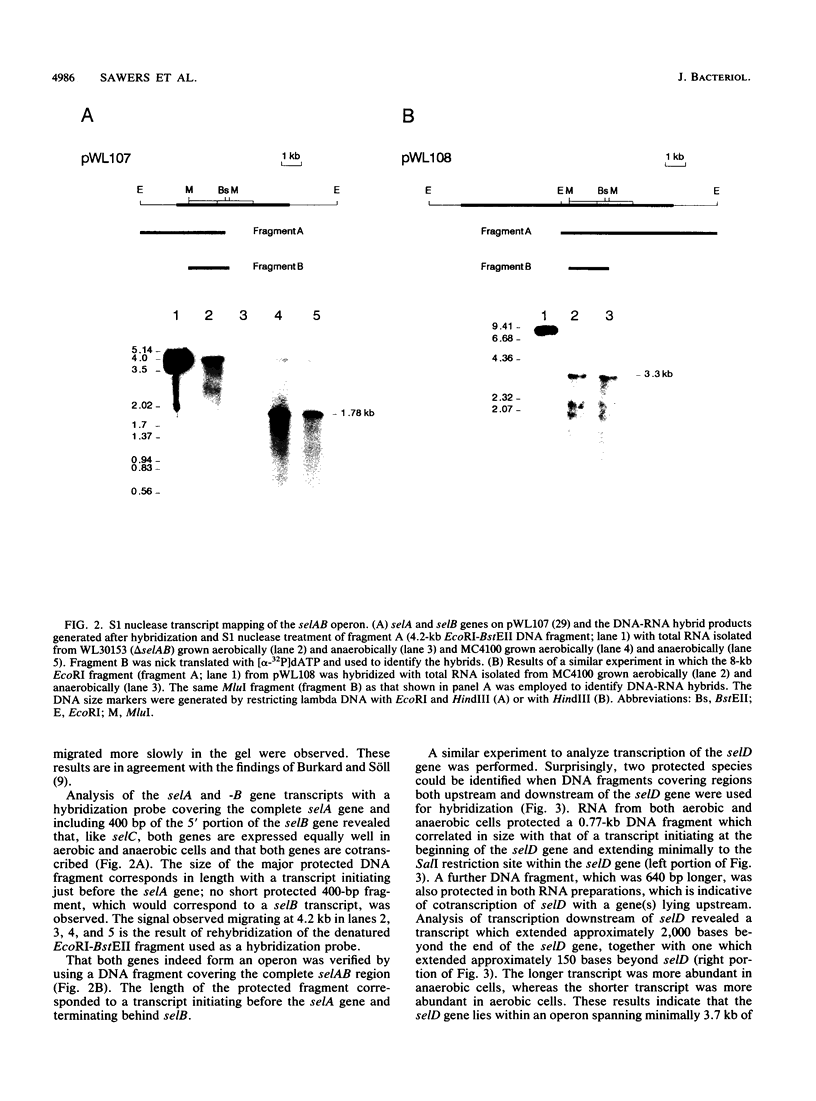
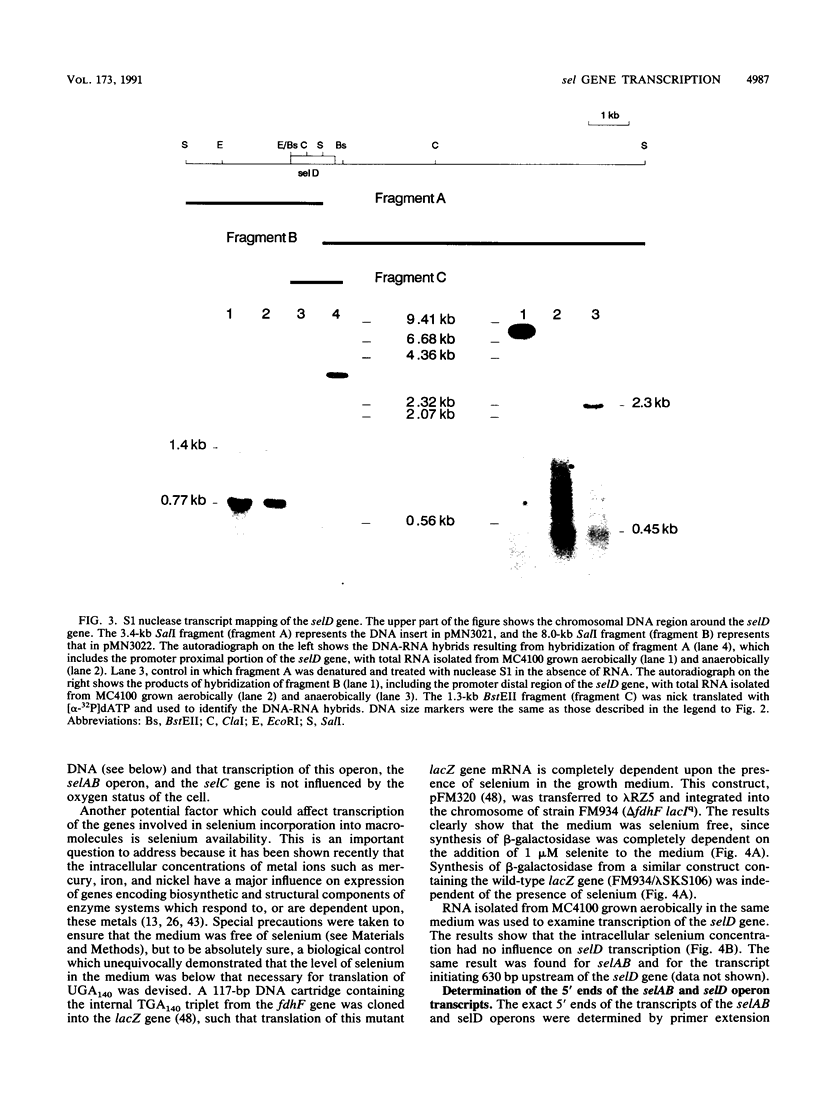
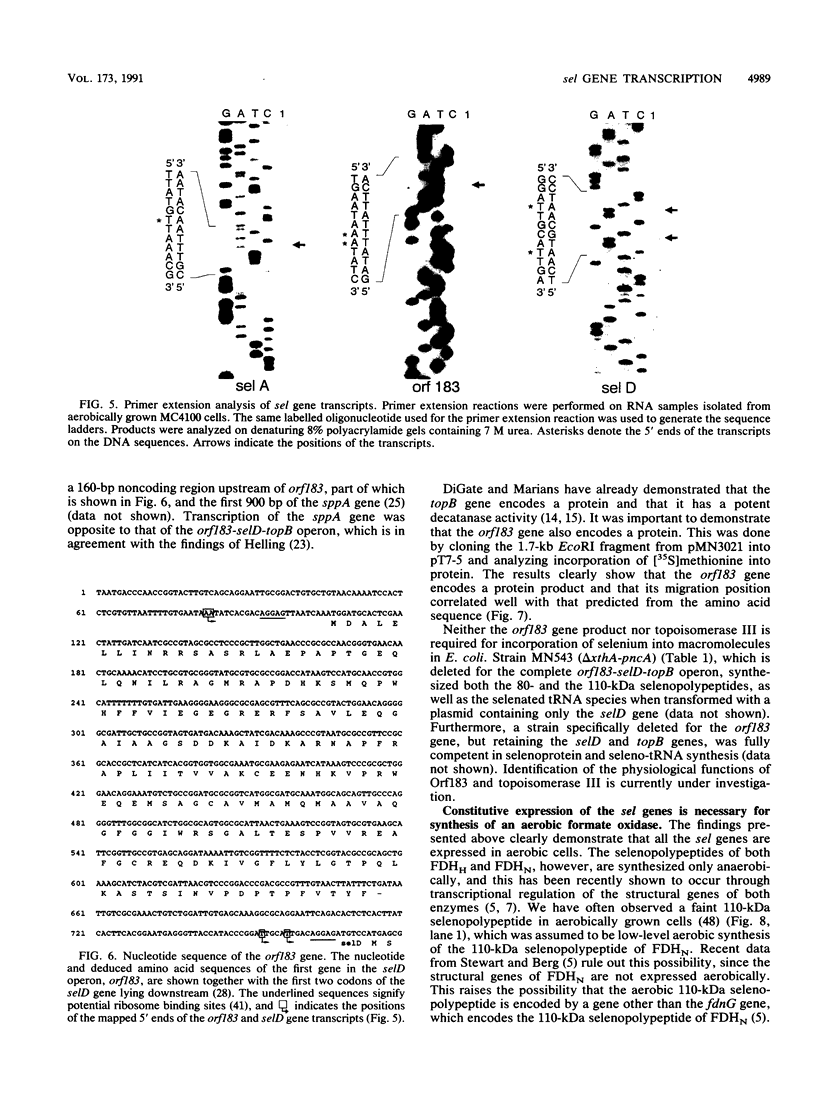
A detailed analysis of the expression of the sel genes, the products of which are necessary for the specific incorporation of selenium into macromolecules in Escherichia coli, showed that transcription was constitutive, being influenced neither by aerobiosis or anaerobiosis nor by the intracellular selenium concentration. The gene encoding the tRNA molecule which is specifically aminoacylated with selenocysteine (selC) proved to be monocistronic. In contrast, the other three sel genes (selA, -B, and -D) were shown to be constituents of two unlinked operons. The selA and selB genes formed one transcriptional unit (sel vector AB), while selD was shown to be the central gene in an operon including two other genes, the promoter distal of which (topB) encodes topoisomerase III. The promoter proximal gene (orf183) was sequenced and shown to encode a protein consisting of 183 amino acids (Mr, 20,059), the amino acid sequence of which revealed no similarity to any currently known protein. The products of the orf183 and topB genes were required neither for selenoprotein biosynthesis nor for selenation of tRNAs. selAB transcription was driven by a single, weak promoter; however, two major selD operon transcripts were identified. The longer initiated just upstream of the orf183 gene, whereas the 5' end of the other mapped in a 116-bp nontranslated region between orf183 and selD. Aerobic synthesis of all four sel gene products incited a reexamination of a weak 110-kDa selenopolypeptide which is produced under these conditions. The aerobic appearance of this 110-kDa selenopolypeptide was not a consequence of residual expression of the gene encoding the 110-kDa selenopolypeptide of the anaerobically inducible formate dehydrogenase N (FDHN) enzyme, as previously surmised, but rather resulted from the expression of a gene encoding a third, distinct selenopolypeptide in E. coli. A mutant strain no longer capable of synthesizing the 80- and 110-kDa selenopolypeptides of FDHH and FDHN, respectively, still synthesized this alternative 110-kDa selenopolypeptide which was present at equivalent levels in cells grown aerobically and anaerobically with nitrate. Furthermore, this strain exhibited a formate- and sel gene-dependent respiratory activity, indicating that it is probable that this selenopolypeptide constitutes a major component of the formate oxidase, an enzyme activity initially discovered in aerobically grown E. coli more than 30 years ago.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Heider J., Böck A. Mutagenesis of selC, the gene for the selenocysteine-inserting tRNA-species in E. coli: effects on in vivo function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6761–6766. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. L., Stewart V. Structural genes for nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):691–702. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Zinoni F., Sawers G., Böck A. Factors affecting transcriptional regulation of the formate-hydrogen-lyase pathway of Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Jun;148(1):44–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00429646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkard U., Söll D. The unusually long amino acid acceptor stem of Escherichia coli selenocysteine tRNA results from abnormal cleavage by RNase P. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11617–11624. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Forchhammer K., Heider J., Leinfelder W., Sawers G., Veprek B., Zinoni F. Selenocysteine: the 21st amino acid. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):515–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. Genetics and molecular biology of siderophore-mediated iron transport in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):517–530. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.517-530.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGate R. J., Marians K. J. Identification of a potent decatenating enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13366–13373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGate R. J., Marians K. J. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of Escherichia coli topB, the gene encoding topoisomerase III. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17924–17930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg-Kulka H., Schoulaker-Schwarz R. A flexible genetic code, or why does selenocysteine have no unique codon? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):419–421. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Analysis of the reaction sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6324–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Boesmiller K., Veprek B., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of the gene (selA) and purification of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Identification of a novel translation factor necessary for the incorporation of selenocysteine into protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):453–456. doi: 10.1038/342453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Rücknagel K. P., Böck A. Purification and biochemical characterization of SELB, a translation factor involved in selenoprotein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9346–9350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider J., Forchhammer K., Sawers G., Böck A. Interspecies compatibility of selenoprotein biosynthesis in Enterobacteriaceae. Arch Microbiol. 1991;155(3):221–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00252204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B. The glutamate dehydrogenase structural gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(3):508–512. doi: 10.1007/BF00264460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara S., Suzuki T., Suzuki M., Mizushima S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the sppA gene and characterization of the encoded protease IV, a signal peptide peptidase, of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9405–9411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Maier R. J. Transcriptional regulation of hydrogenase synthesis by nickel in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18729–18732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Forchhammer K., Veprek B., Zehelein E., Böck A. In vitro synthesis of selenocysteinyl-tRNA(UCA) from seryl-tRNA(UCA): involvement and characterization of the selD gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):543–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Forchhammer K., Zinoni F., Sawers G., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Escherichia coli genes whose products are involved in selenium metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.540-546.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Zehelein E., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Gene for a novel tRNA species that accepts L-serine and cotranslationally inserts selenocysteine. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):723–725. doi: 10.1038/331723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons L. B., Zinder N. D. The genetic map of the filamentous bacteriophage f1. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):45–60. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSENT J. The need for selenite and molybdate in the formation of formic dehydrogenase by members of the coli-aerogenes group of bacteria. Biochem J. 1954 May;57(1):10–16. doi: 10.1042/bj0570010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers G., Böck A. Novel transcriptional control of the pyruvate formate-lyase gene: upstream regulatory sequences and multiple promoters regulate anaerobic expression. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2485–2498. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2485-2498.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers G., Wagner A. F., Böck A. Transcription initiation at multiple promoters of the pfl gene by E sigma 70-dependent transcription in vitro and heterologous expression in Pseudomonas putida in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4930–4937. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4930-4937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlindwein C., Giordano G., Santini C. L., Mandrand M. A. Identification and expression of the Escherichia coli fdhD and fdhE genes, which are involved in the formation of respiratory formate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6112–6121. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6112-6121.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Misra T. K. Plasmid-mediated heavy metal resistances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:717–743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Selenium biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:111–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Heider J., Böck A. Features of the formate dehydrogenase mRNA necessary for decoding of the UGA codon as selenocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]