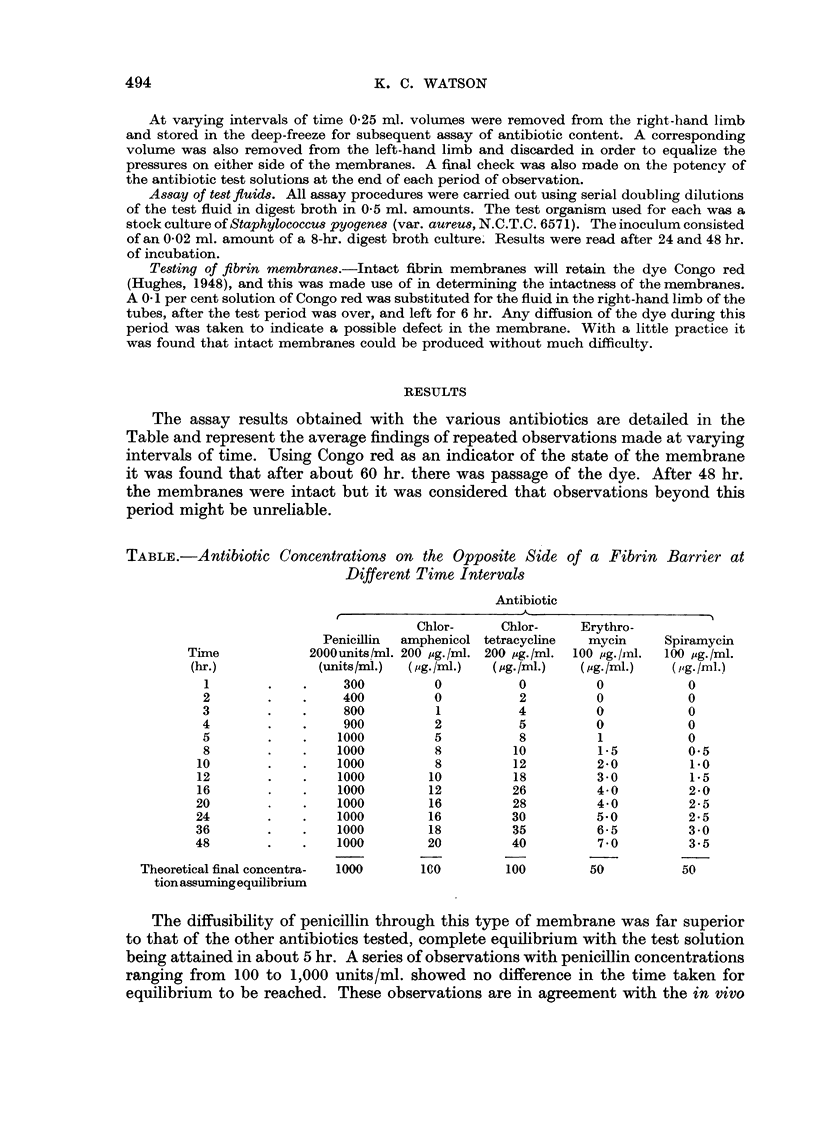
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- WEINSTEIN L., DAIKOS G. K., PERRIN T. S. Studies on the relationship of tissue fluid and blood levels of penicillin. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Nov;38(5):712–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERNER C. A., KNIGHT V., McDERMOTT W. Studies of microbial populations artificially localized in vivo. I. Multiplication of bacteria and distribution of drugs in agar loci. J Clin Invest. 1954 May;33(5):742–752. doi: 10.1172/JCI102943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


