Abstract
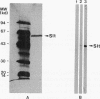
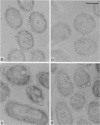
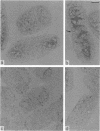
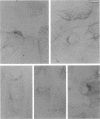
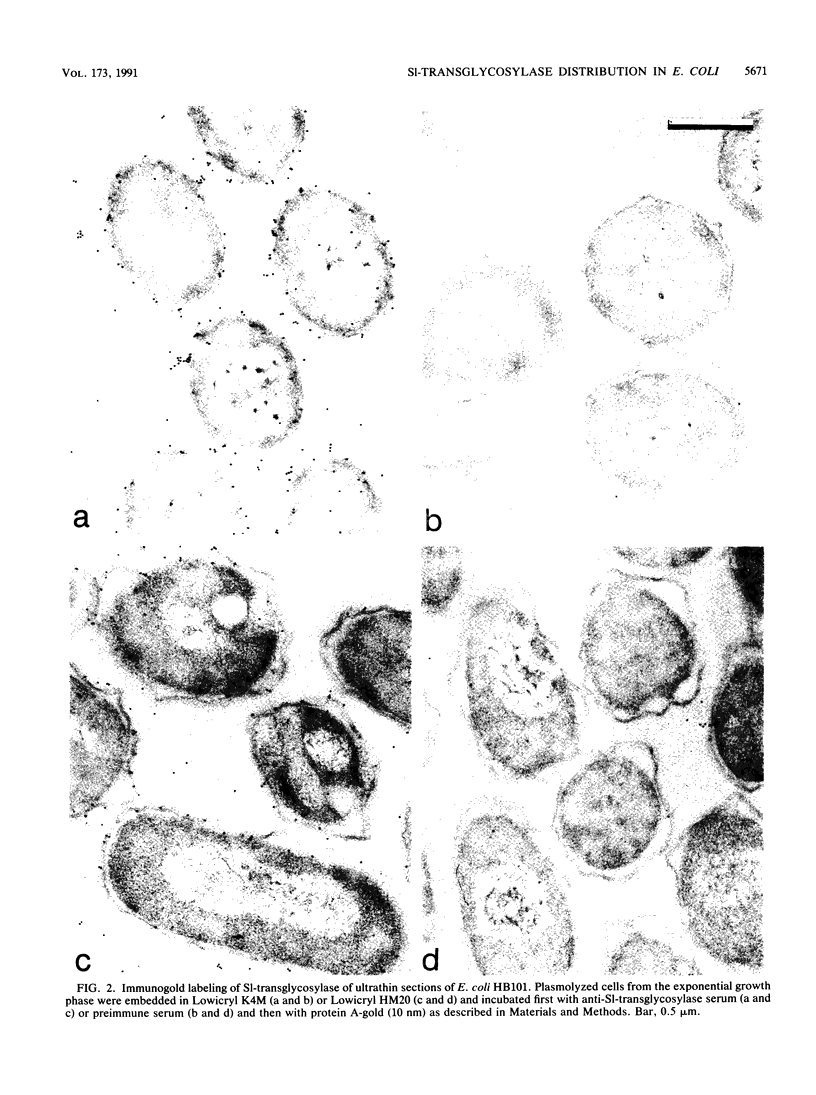
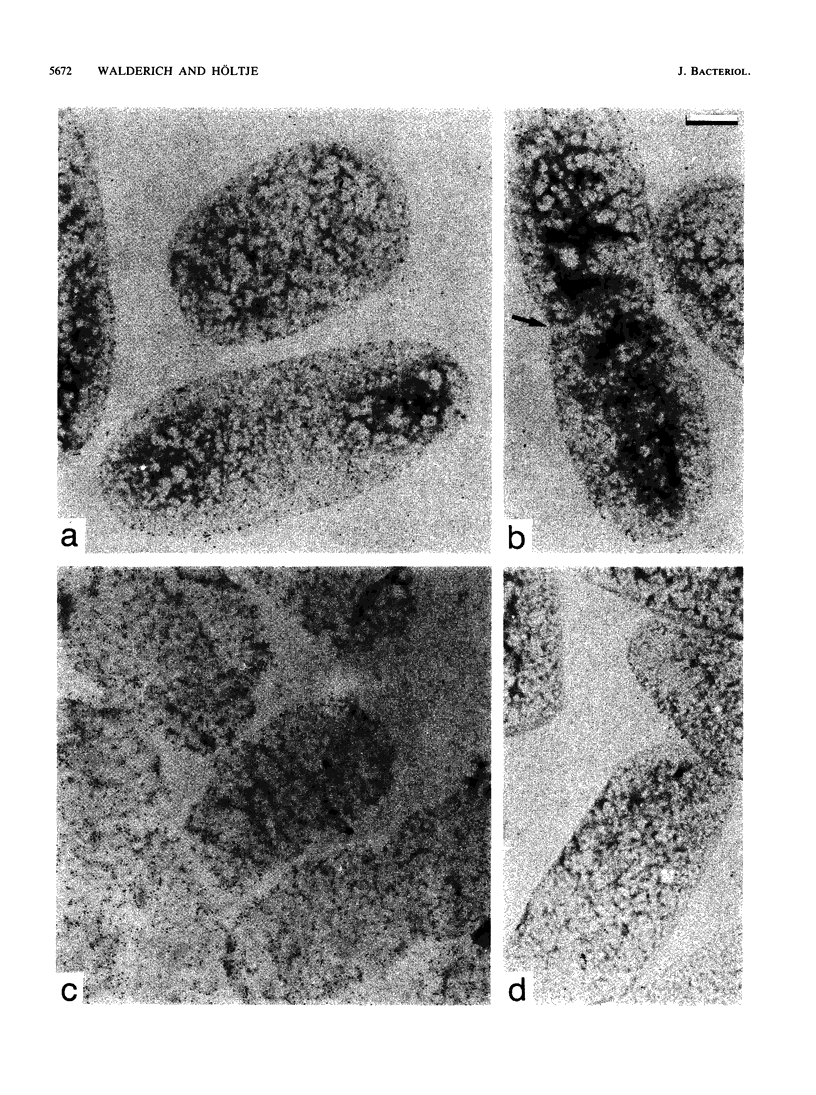
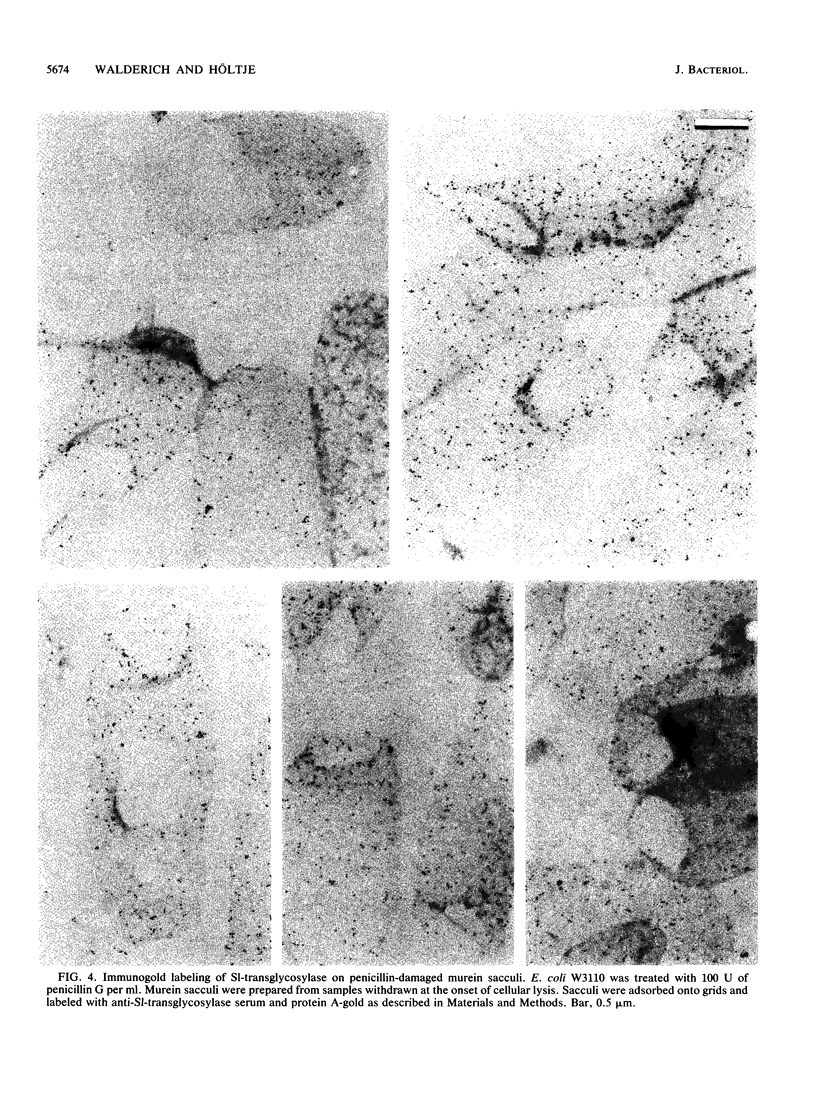
The localization of the major autolytic enzyme, the soluble lytic transglycosylase, in the different cell compartments of Escherichia coli was investigated by immunoelectron microscopy. Ultrathin sections were labeled with a specific antiserum against purified soluble lytic transglycosylase, and the antibody-enzyme complexes were visualized with colloidal protein A-gold. A preferential localization of the lytic transglycosylase in the envelope was observed, with only 20 to 30% of the enzyme left in the cytoplasm. Most of the enzyme associated with the cell wall was tightly bound to the murein sacculus. Sacculi prepared by boiling of cells in 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate could be immunolabeled with the specific antiserum, indicating a surprisingly strong interaction of the lytic transglycosylase with murein. The enzyme-substrate complex could be reconstituted in vitro by incubating pronase-treated, protein-free murein sacculi with purified lytic transglycosylase at 0 degrees C. Titration of sacculi with increasing amounts of enzyme indicated a limiting number of binding sites for about 1,000 molecules of enzyme per sacculus. Ruptured murein sacculi obtained after penicillin treatment revealed that the enzyme is exclusively bound to the outer surface of the sacculus. This finding is discussed in the light of recent evidence suggesting that the murein of E. coli might be a structure of more than one layer expanding by inside-to-outside growth of patches of murein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnickel G., Labischinski H., Bradaczek H., Giesbrecht P. Conformational energy calculation on the peptide part of murein. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar 15;95(1):157–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. F., Dolinger D. L., Schramm V. L., Shockman G. D. The mechanism of soluble peptidoglycan hydrolysis by an autolytic muramidase. A processive exodisaccharidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11818–11827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Keck W., de Pedro M. A., Schwarz U. Exoenzymatic activity of transglycosylase isolated from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):355–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betzner A. S., Ferreira L. C., Höltje J. V., Keck W. Control of the activity of the soluble lytic transglycosylase by the stringent response in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 15;55(1-2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90187-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betzner A. S., Keck W. Molecular cloning, overexpression and mapping of the slt gene encoding the soluble lytic transglycosylase of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Nov;219(3):489–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00259625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Interaction of penicillin with the bacterial cell: penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin-sensitive enzymes. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):291–335. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.291-335.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Gnirke H., Henning U., Rehn K. Model for the structure of the shape-maintaining layer of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1264-1270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. The concept of the penicillin target from 1965 until today. The thirteenth marjory stephenson memorial lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jul;101(1):13–33. doi: 10.1099/00221287-101-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauner B., Höltje J. V., Schwarz U. The composition of the murein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10088–10095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W. Recycling of murein by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):305–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.305-310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Schwarz U. Release of cell wall peptides into culture medium by exponentially growing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):391–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.391-397.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harz H., Burgdorf K., Höltje J. V. Isolation and separation of the glycan strands from murein of Escherichia coli by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1990 Oct;190(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Rogers H. J. Intracellular location of the autolytic N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase in Bacillus subtilis 168 and in an autolysis-deficient mutant by immunoelectron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):961–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.961-967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Glauner B. Structure and metabolism of the murein sacculus. Res Microbiol. 1990 Jan;141(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Mirelman D., Sharon N., Schwarz U. Novel type of murein transglycosylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1067-1076.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tuomanen E. I. The murein hydrolases of Escherichia coli: properties, functions and impact on the course of infections in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):441–454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck W., Wientjes F. B., Schwarz U. Comparison of two hydrolytic murein transglycosylases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):493–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Additional arguments for the key role of "smart" autolysins in the enlargement of the wall of gram-negative bacteria. Res Microbiol. 1990 Jun;141(5):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90017-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. The surface stress theory of microbial morphogenesis. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:301–366. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlrausch U., Höltje J. V. Analysis of murein and murein precursors during antibiotic-induced lysis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3425–3431. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3425-3431.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusser W., Schwarz U. Escherichia coli murein transglycosylase. Purification by affinity chromatography and interaction with polynucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):277–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labischinski H., Goodell E. W., Goodell A., Hochberg M. L. Direct proof of a "more-than-single-layered" peptidoglycan architecture of Escherichia coli W7: a neutron small-angle scattering study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):751–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.751-756.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc M., Joseleau-Petit D., Rothfield L. I. Interactions of membrane lipoproteins with the murein sacculus of Escherichia coli as shown by chemical crosslinking studies of intact cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 1;51(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mett H., Keck W., Funk A., Schwarz U. Two different species of murein transglycosylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.45-52.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neukirchen R. O., Schlosshauer B., Baars S., Jäckle H., Schwarz U. Two-dimensional protein analysis at high resolution on a microscale. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15229–15234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Forsberg C. W. Role of autolysins in the killing of bacteria by some bactericidal antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1235-1243.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeis T., Kohlrausch U., Burgdorf K., Höltje J. V. Murein chemistry of cell division in Escherichia coli. Res Microbiol. 1991 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Asmus A., Frank H. Autolytic enzymes and cell division of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. IV. Unbalanced cell-wall synthesis: autolysis and cell-wall thickening. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):345–358. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.345-358.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag I., Schwarz H., Hirota Y., Henning U. Cell envelope and shape of Escherichia coli: multiple mutants missing the outer membrane lipoprotein and other major outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):280–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.280-285.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Leunissen J., van Damme-Jongsten M., Overduin P. Failure of E. coli K-12 to transport PhoE-LacZ hybrid proteins out of the cytoplasm. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderich B., Höltje J. V. Specific localization of the lysis protein of bacteriophage MS2 in membrane adhesion sites of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3331–3336. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3331-3336.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]