Abstract
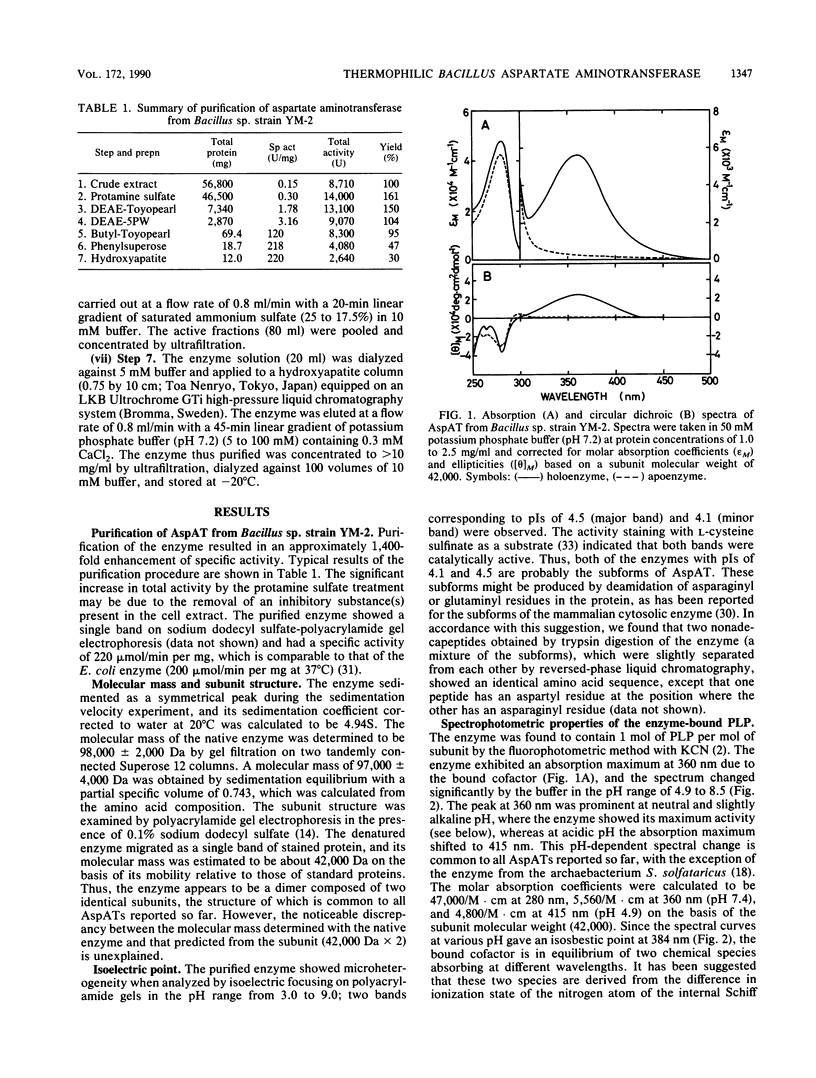
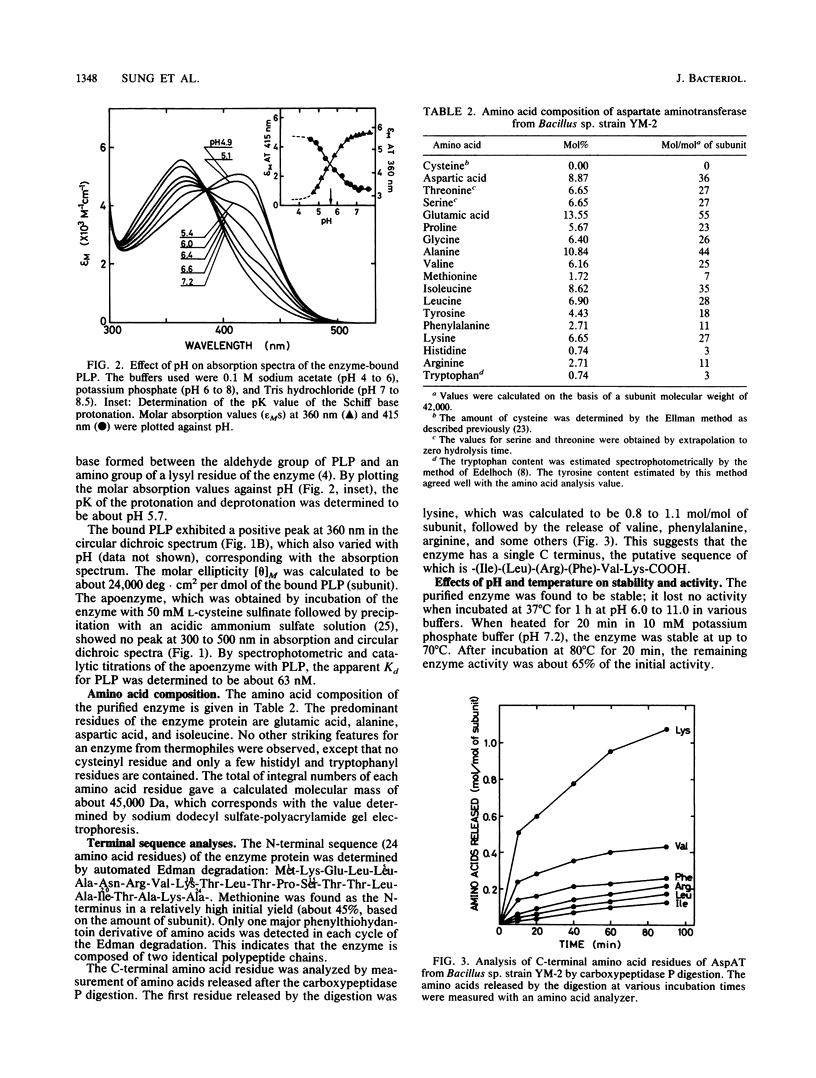
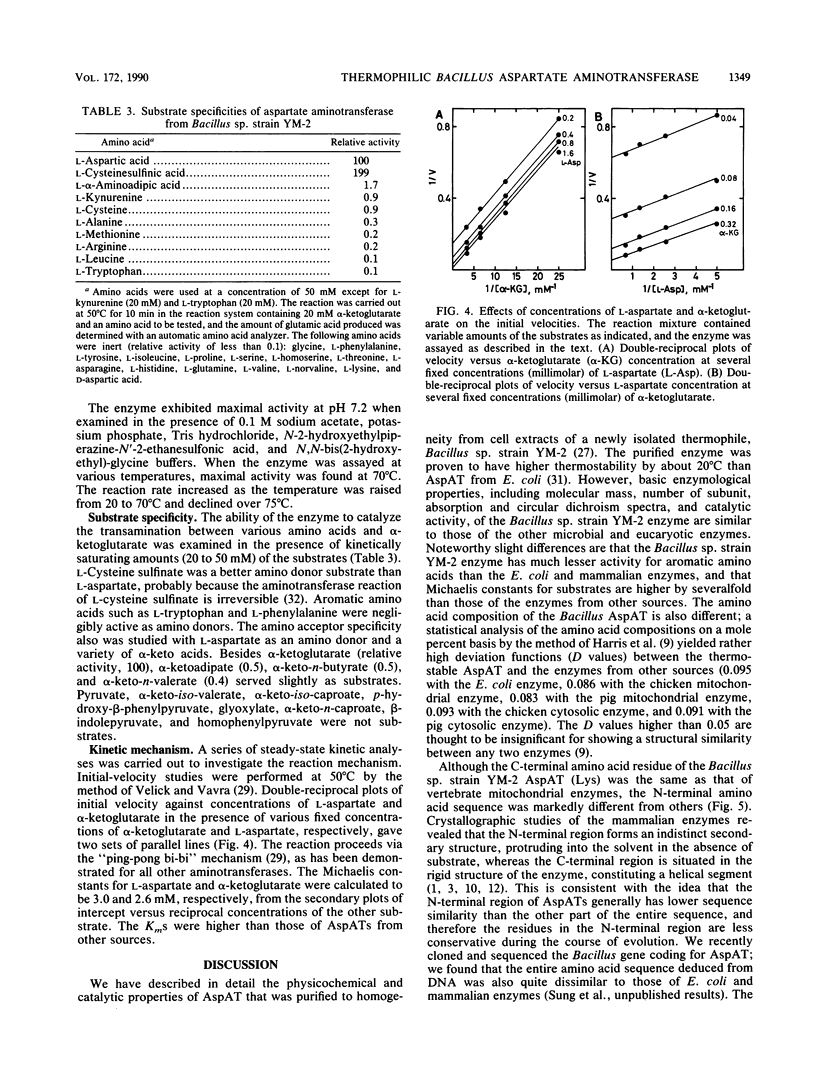
Aspartate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.1) was purified to homogeneity from cell extracts of a newly isolated thermophilic bacterium, Bacillus sp. strain YM-2. The enzyme consisted of two subunits identical in molecular weight (Mr, 42,000) and showed microheterogeneity, giving two bands with pIs of 4.1 and 4.5 upon isoelectric focusing. The enzyme contained 1 mol of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate per mol of subunit and exhibited maxima at about 360 and 415 nm in absorption and circular dichroism spectra. The intensities of the two bands were dependent on the buffer pH; at neutral or slightly alkaline pH, where the enzyme showed its maximum activity, the absorption peak at 360 nm was prominent. The enzyme was specific for L-aspartate and L-cysteine sulfinate as amino donors and alpha-ketoglutarate as an amino acceptor; the KmS were determined to be 3.0 mM for L-aspartate and 2.6 mM for alpha-ketoglutarate. The enzyme was most active at 70 degrees C and had a higher thermostability than the enzyme from Escherichia coli. The N-terminal amino acid sequence (24 residues) did not show any similarity with the sequences of mammalian and E. coli enzymes, but several residues were identical with those of the thermoacidophilic archaebacterial enzyme recently reported.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONAVITA V. The reaction of pyridoxal 5-phosphate with cyanide and its analytical use. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Jun;88:366–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesne S., Pelmont J. Glutamate-oxaloacétate transaminase d'Escherichia coli. I. Purification et spécificité. Biochimie. 1973;55(3):237–244. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSON C. P., CLELAND W. W. KINETIC STUDIES OF GLUTAMIC OXALOACETIC TRANSAMINASE ISOZYMES. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:338–345. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. E., Kobes R. D., Teller D. C., Rutter W. J. The molecular characteristics of yeast aldolase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2442–2454. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A. A note on the spectrometric assay of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase in human blood serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):131–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Wakabayashi S., Kagamiyama H. Structural studies on aspartate aminotransferase from Escherichia coli. Covalent structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8648–8657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Wakabayashi S., Yagi T., Kagamiyama H. The complete amino acid sequence of aspartate aminotransferase from Escherichia coli: sequence comparison with pig isoenzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):62–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino G., Nitti G., Arnone M. I., Sannia G., Gambacorta A., De Rosa M. Purification and characterization of aspartate aminotransferase from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12305–12309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrides C., Orr W. Multispecific aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferases in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4128–4133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. T., Morrison J. F. The purification and properties of the aspartate aminotransferase and aromatic-amino-acid aminotransferase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):391–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Ellman's reagent: 5,5'-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)--a reexamination. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90792-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCARDI V., SCOTTO P., IACCARINO M., SCARANO E. The binding of pyridoxal 5-phosphate to aspartate aminotransferase of pig heart. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:172–175. doi: 10.1042/bj0880172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Williamson J. R. Mitochondrial-cytosolic interactions in perfused rat heart. Role of coupled transamination in repletion of citric acid cycle intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2570–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VELICK S. F., VAVRA J. A kinetic and equilibrium analysis of the glutamic oxaloacetate transaminase mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2109–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., John R. A. Generation of aspartate aminotransferase multiple forms by deamidation. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):121–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1770121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kagamiyama H., Motosugi K., Nozaki M., Soda K. Crystallization and properties of aspartate aminotransferase from Escherichia coli B. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M. A sensitive method for the detection of aspartate: 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity of polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):146–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M. Aspartate: 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase from bakers' yeast: crystallization and characterization. J Biochem. 1982 Jul;92(1):35–43. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M. Cysteine sulfinate transamination activity of aspartate aminotransferases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M., Soda K. Glutamate-aspartate transaminase from microorganisms. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:83–89. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Toyosato M., Soda K. Crystalline aspartate aminotransferase from Pseudomonas striata. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 1;61(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Oobayashi A., Tanabe O., Sugawara S., Araki E. Production and some properties of a new type of acid carboxypeptidase of Penicillium molds. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):953–960. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.953-960.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


