Abstract
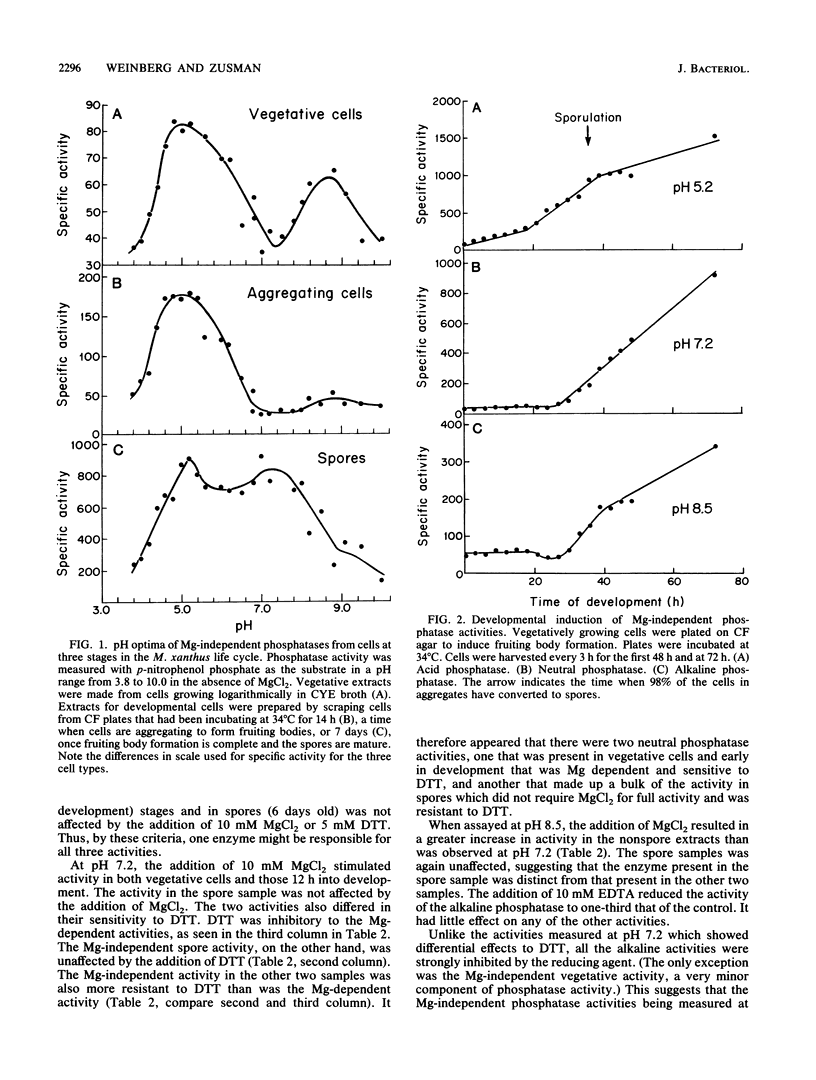
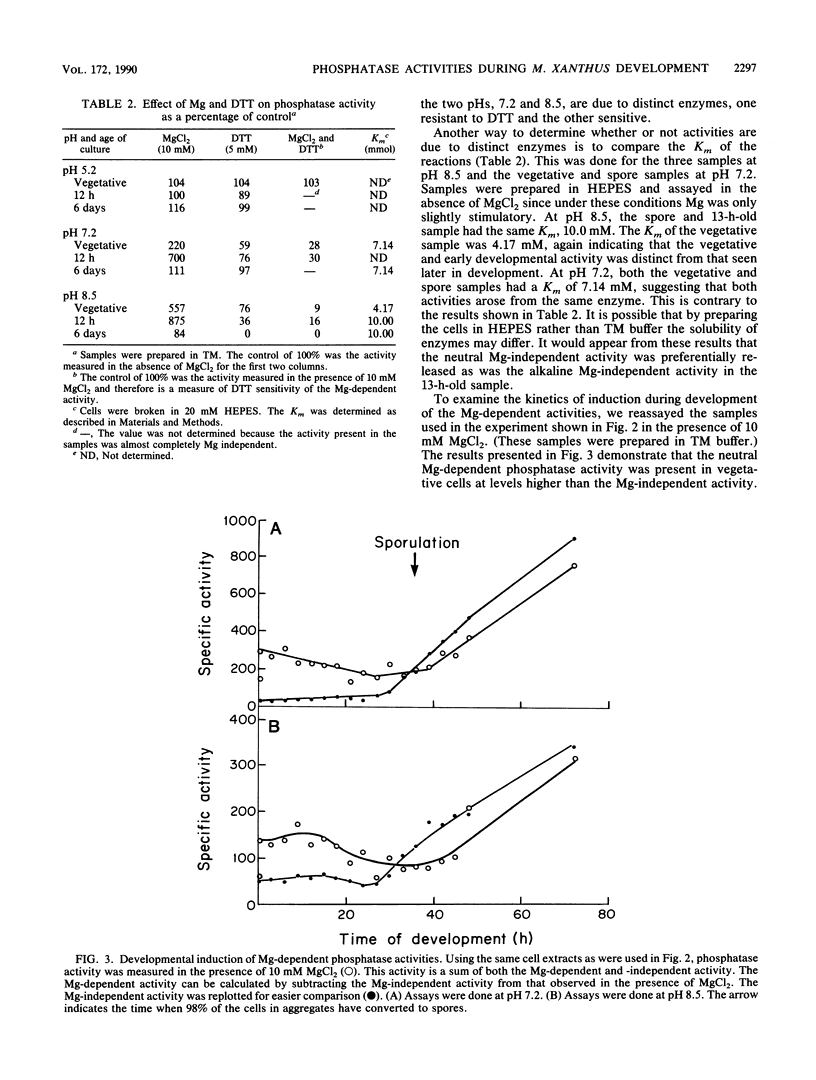
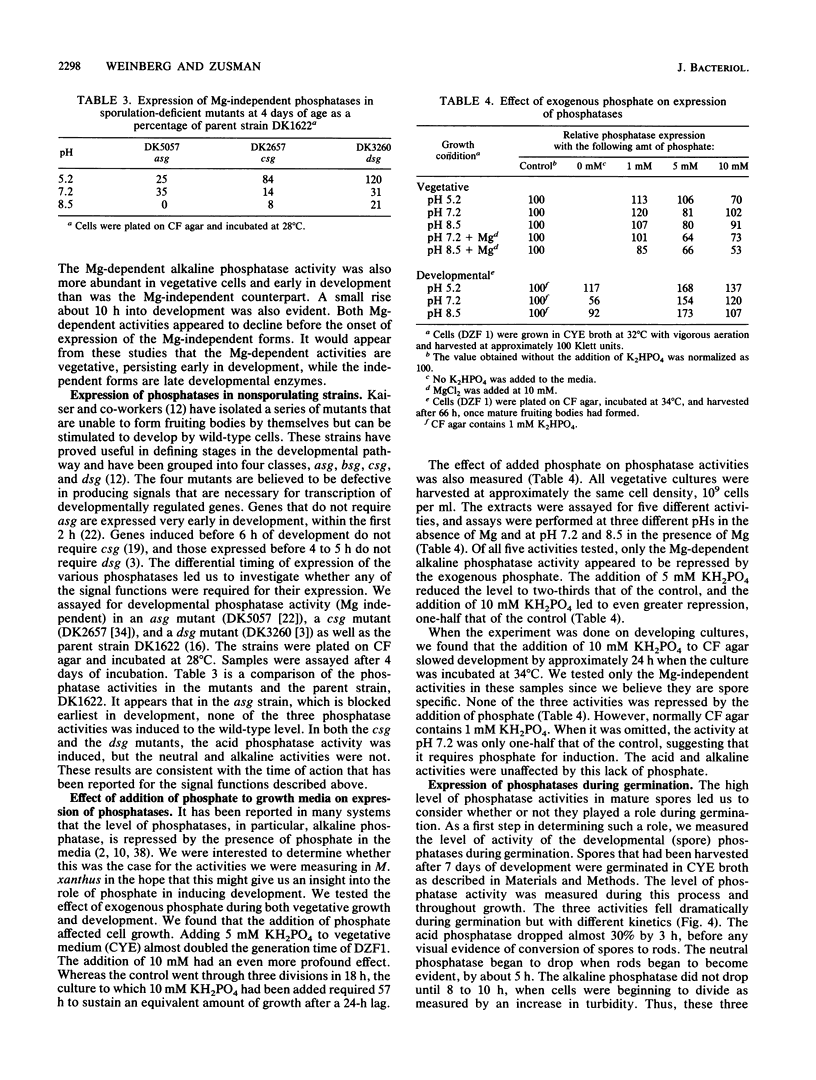
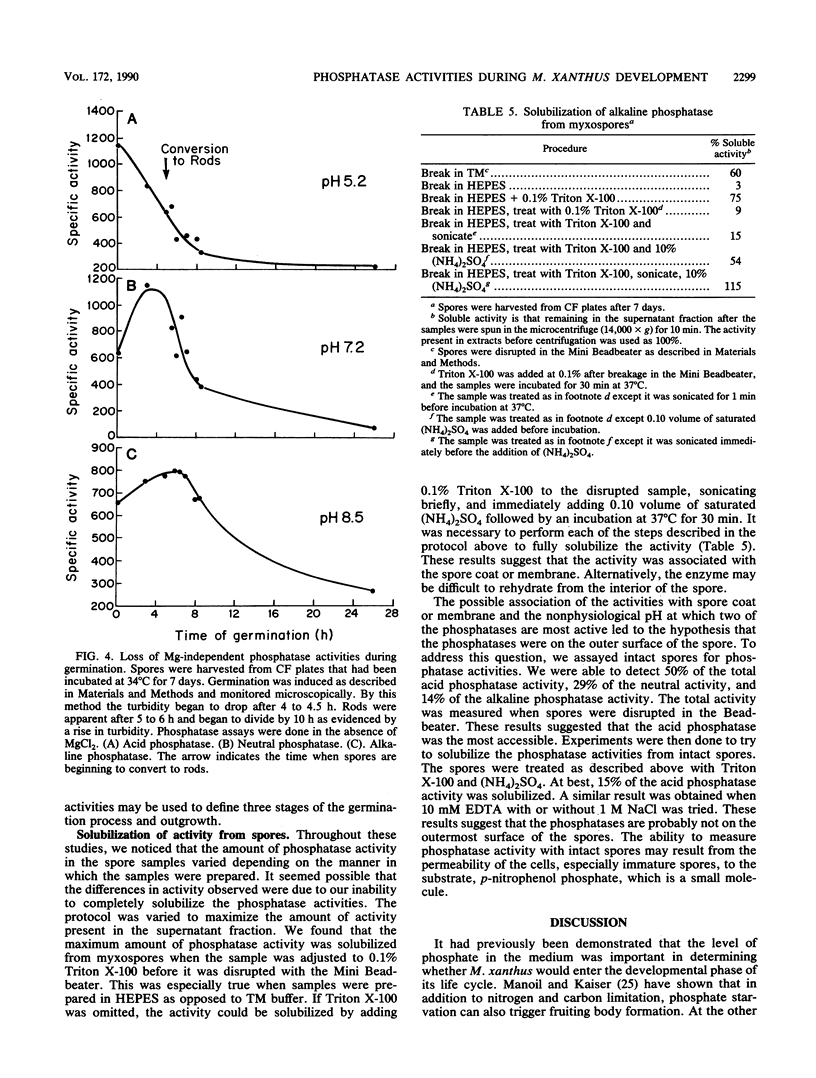
One of the signals that has been reported to be important in stimulating fruiting body formation of Myxococcus xanthus is starvation for phosphate. We therefore chose to study phosphatase activity during M. xanthus development. Many phosphatases can cleave the substrate p-nitrophenol phosphate. Using this substrate in buffers at various pHs, we obtained a profile of phosphatase activities during development and germination of M. xanthus. These experiments indicated that there are five patterns of phosphatase activity in M. xanthus: two vegetative and three developmental. The two uniquely vegetative activities have pH optima at 7.2 and 8.5. Both require magnesium and both are inhibited by the reducing agent dithiothreitol. The developmental (spores) patterns of activity have pH optima of 5.2, 7.2, and 8.5. All three activities are Mg independent. Only the alkaline phosphatase activity is inhibited by dithiothreitol. The acid phosphatase activity is induced very early in development, within the first 2 to 4 h. Both the neutral and alkaline phosphatase Mg-independent activities are induced much later, about the time that myxospores become evident (24 to 30 h). The three activities are greatly diminished upon germination; however, the kinetics of loss differ for all three. The acid phosphatase activity declines very rapidly, the neutral activity begins to decline only after spores begin to convert to rods, and the alkaline phosphatase activity remains high until the time the cells begin to divide. All three developmental activities were measured in the developmental signalling mutants carrying asg, csg, and dsg. The pattern of expression obtained in the mutants was consistent with that of other developmentally regulated genes which exhibit similar patterns of expression during development. The ease with which phosphatases can be assayed should make the activities described in this report useful biochemical markers of stages of both fruiting body formation and germination.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Interactions of alkaline phosphatase and the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.325-336.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Kaiser D. dsg, a gene required for cell-cell interaction early in Myxococcus development. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3719–3726. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3719-3726.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. NUTRITIONAL REGU.ATION OF MORPHOGENESIS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:67–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.67-72.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Kaiser D. Cell interactions in myxobacterial growth and development. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):18–24. doi: 10.1126/science.3929384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filer D., Kindler S. H., Rosenberg E. Myxospore coat synthesis in Myxococcus xanthus: enzymes associated with uridine 5'-diphosphate-N-acetylgalactosamine formation during myxospore development. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):745–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.745-750.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Wouters J. T., Lampen J. O. Distribution of the sites of alkaline phosphatase(s) activity in vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):928–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.928-937.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Wright A. Fusions of secreted proteins to alkaline phosphatase: an approach for studying protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5107–5111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S. T., Kawamura H. Persistence of circadian rhythmicity in a mammalian hypothalamic "island" containing the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen K. P., Nelson D. R. Acceleration of starvation- and glycerol-induced myxospore formation by prior heat shock in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5200–5207. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5200-5207.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K., Pratt C., Torriani A. Genetic analysis of regulatory mutants of alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. Genetics. 1975 Nov;81(3):459–468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/81.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Construction of Tn5 lac, a transposon that fuses lacZ expression to exogenous promoters, and its introduction into Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5816–5820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kaiser D. Expression of many developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus depends on a sequence of cell interactions. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroos L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. A global analysis of developmentally regulated genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):252–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Jr Developmental regulation of alkaline phosphatase in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):417–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.417-422.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Kaiser D. Guanosine pentaphosphate and guanosine tetraphosphate accumulation and induction of Myxococcus xanthus fruiting body development. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):305–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.305-315.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Patterns of cellular interactions during fruiting-body formation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6013–6024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6013-6024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradel E., Boquet P. L. Acid phosphatases of Escherichia coli: molecular cloning and analysis of agp, the structural gene for a periplasmic acid glucose phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4916–4923. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4916-4923.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey W. S., Dworkin M. Microcyst germination in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2249–2257. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2249-2257.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. N., Torriani A. Utilization by Escherichia coli of a high-molecular-weight, linear polyphosphate: roles of phosphatases and pore proteins. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5216–5223. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5216-5223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Asher S. J. Use of recombination techniques to examine the structure of the csg locus of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00338394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Control of morphogenesis in myxobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(3):195–227. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaks B., Zuckerberg A., Rosenberg E. Purification and partial characterization of an antibiotic produced by Myxococcus xanthus. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Feb;20(2):155–161. doi: 10.1139/m74-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelz H., Ortigoza R. O. Cytochemistry of phosphatases in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1357–1365. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1357-1365.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Zusman D. R. Evidence that the Myxococcus xanthus frz genes are developmentally regulated. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6174–6186. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6174-6186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


