Abstract
The DNA fragment encoding the integrase and excisionase genes involved in site-specific recombination of staphylococcal bacteriophage phi 11 was cloned and sequenced. The int and xis genes and the recombination site, attP, were highly clustered in a 1.7-kilobase DNA fragment with the gene order attP-int-xis. The int and xis genes were transcribed divergently, with the int gene transcribed toward the attp site and the xis gene transcribed away from the attP site. The deduced Int is a basic protein of 348 residues with an estimated molecular weight of 41,357. In contrast, the deduced Xis is an acidic protein containing 66 amino acids with an estimated molecular weight of 7,621. The site-specific recombination system of phi 11 was compared with that of a closely related bacteriophage, L54a.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. T., Brown N. C., Burlingham B. T. Morphology and physical properties of Staphylococcus bacteriophage P11-M15. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.664-671.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi B. Physical mapping of the BglI, BglII, PstI and EcoRI restriction fragments of staphylococcal phage phi 11 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):391–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00425853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Belin D., Nagamine Y. A pSC101-derived plasmid which shows no sequence homology to other commonly used cloning vectors. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W. DNA sequence of the int-xis-Pi region of the bacteriophage lambda; overlap of the int and xis genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1765–1782. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., Iandolo J. J. Rapid isolation of DNA from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.283-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Foeller C., Bidwell K., Landy A. Site-specific recombination functions of bacteriophage lambda: DNA sequence of regulatory regions and overlapping structural genes for Int and Xis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2482–2486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoheisel J., Pohl F. M. Simplified preparation of unidirectional deletion clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3605–3605. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Löfdahl S., Betley M. J., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. The toxic shock syndrome exotoxin structural gene is not detectably transmitted by a prophage. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):709–712. doi: 10.1038/305709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer P. J., Egan J. B. Genetic map of the Staphylococcal bacteriophage phi11. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):642–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.642-651.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Buranen S. L. Extent of the DNA sequence required in integration of staphylococcal bacteriophage L54a. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1652–1657. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1652-1657.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Integration of staphylococcal phage L54a occurs by site-specific recombination: structural analysis of the attachment sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5474–5478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococcal lipase is caused by insertion of the bacteriophage L54a genome into the lipase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):385–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.385-391.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
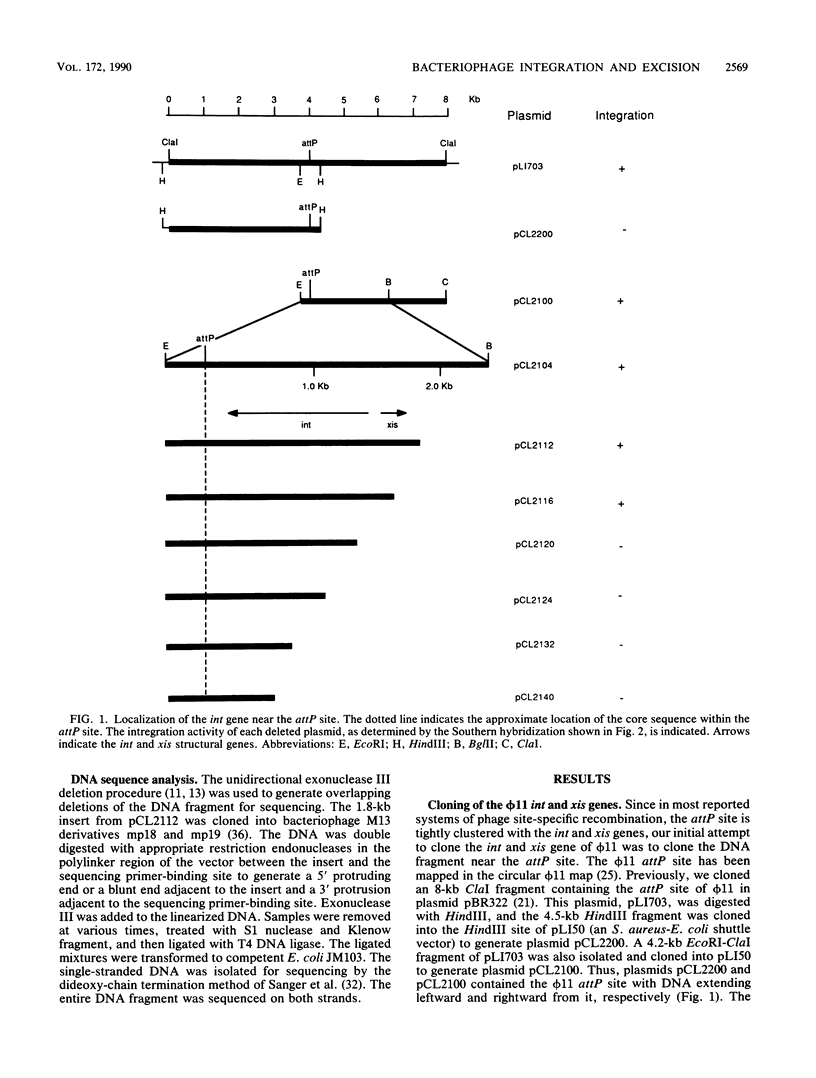
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Structural analysis of staphylococcal bacteriophage phi 11 attachment sites. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2409–2411. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2409-2411.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Nunes-Düby S. E., Oser A. B., Lesser C. F., Youderian P., Susskind M. M., Landy A. Structural and regulatory divergence among site-specific recombination genes of lambdoid phage. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 20;189(4):603–616. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
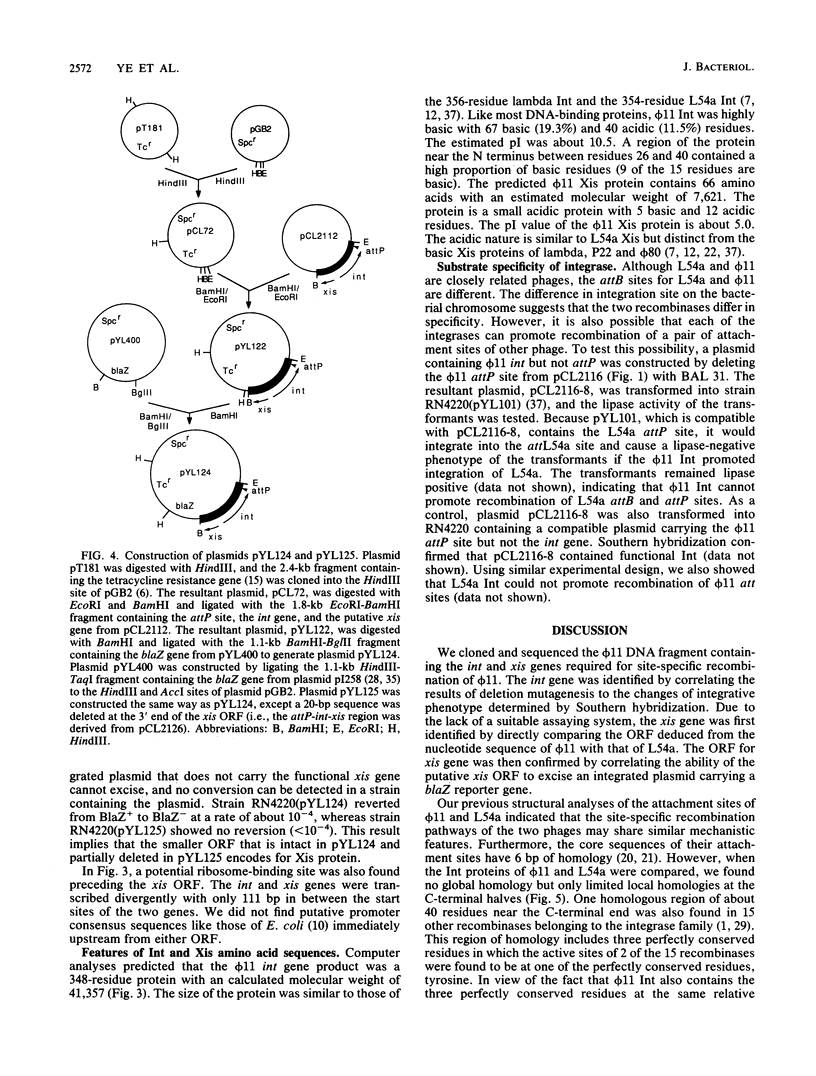
- Löfdahl S., Sjöström J. E., Philipson L. Cloning of restriction fragments of DNA from staphylococcal bacteriophage phi 11. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.795-801.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl S., Zabielski J., Philipson L. Structure and restriction enzyme maps of the circularly permuted DNA of staphylococcal bacteriophage phi 11. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):784–794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.784-794.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Murphy E., Gryczan T. J., Baron E., Edelman I. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus: restriction-deletion maps. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):109–129. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Thompson N. E., Haubrich D., Novick R. P. Chromosomal map locations of integrated plasmids and related elements in Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
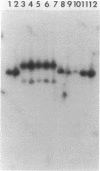
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. Z., Novick R. P. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the beta-lactamase gene from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258 in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1763–1766. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1763-1766.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. H., Lee C. Y. Nucleotide sequence and genetic characterization of staphylococcal bacteriophage L54a int and xis genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4146–4153. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4146-4153.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]