Abstract
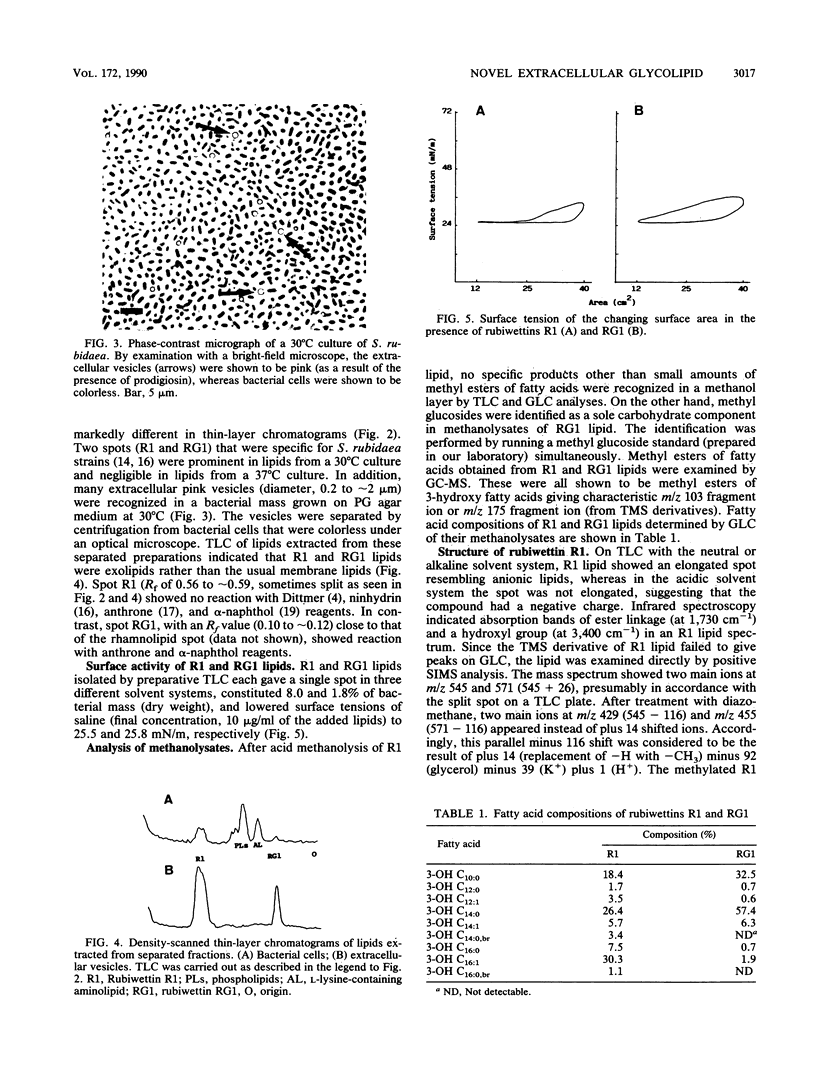
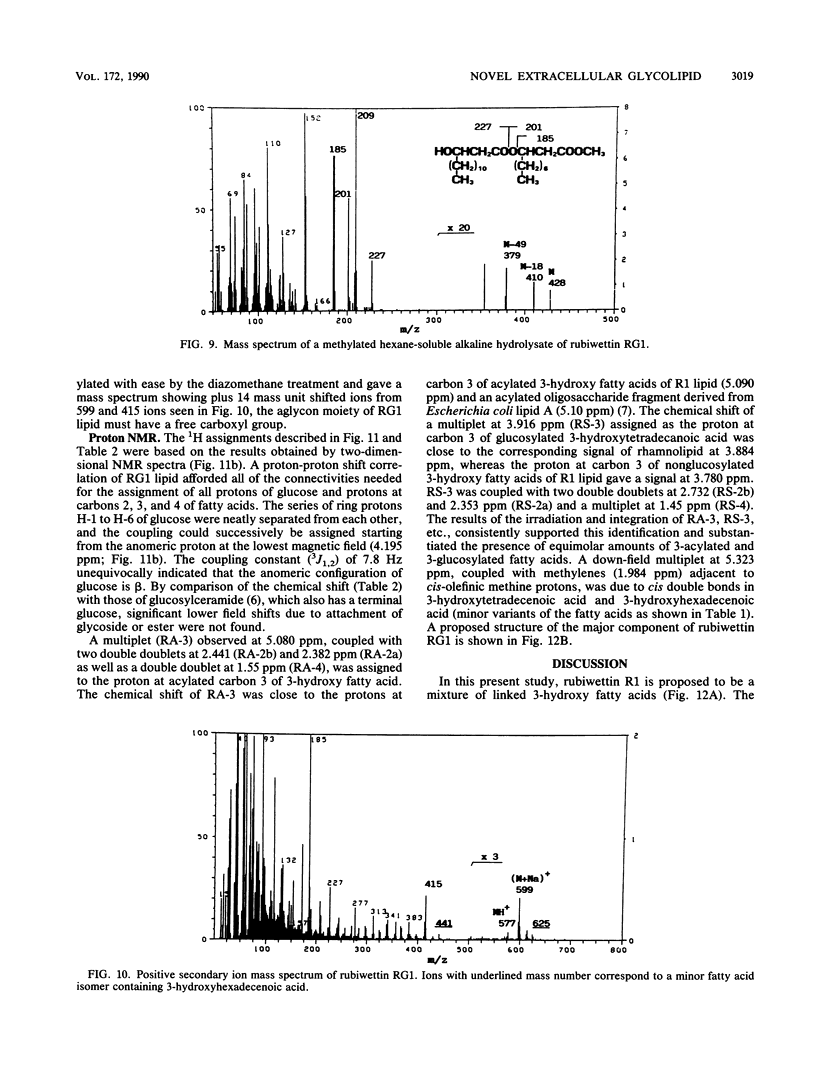
A Serratia rubidaea isolate with wetting activity when grown at 30 but not 37 degrees C was examined for the production of specific lipids. Two novel lipids (rubiwettins R1 and RG1) were isolated and shown to be able to lower the surface tension of saline to 26 mN/m. These lipids were located in extracellular vesicles found in a 30 degrees C culture of S. rubidaea. Chemical structures of these biosurfactants were determined by degradation product analyses, infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Rubiwettin R1 was proposed to be a mixture of 3-(3'-hydroxytetradecanoyloxy)decanoate, 3-(3'-hydroxyhexadecenoyloxy)decanoate, and minor molecular isomers. The structure of rubiwettin RG1 was proposed to be beta-D-glucopyranosyl 3-(3'-hydroxytetradecanoyloxy)decanoate. The importance of such surface-active exolipids in bacterial occupancy on surfaces was suggested.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Ness R., Avrahamy N., Matsuyama T., Rosenberg M. Increased cell surface hydrophobicity of a Serratia marcescens NS 38 mutant lacking wetting activity. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4361–4364. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4361-4364.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. R., Hayashi J. A. Structure of a rhamnolipid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Aug;111(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida N., Toida T., Kushi Y., Handa S., Fredman P., Svennerholm L., Ishizuka I. A sulfated glucosylceramide from rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5974–5980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda K., Naito S., Imaizumi S., Yano I., Mizuno S., Tomiyasu I., Baba T., Kusunose E., Kusunose M. Determination of molecular species composition of C80 or longer-chain alpha-mycolic acids in Mycobacterium spp. by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and mass chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1060–1070. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1060-1070.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Sogawa M., Nakagawa Y. Fractal spreading growth of Serratia marcescens which produces surface active exolipids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Oct 15;52(3):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Sogawa M., Yano I. Direct Colony Thin-Layer Chromatography and Rapid Characterization of Serratia marcescens Mutants Defective in Production of Wetting Agents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1186–1188. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1186-1188.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADIN N. S., LAVIN F. B., BROWN J. R. Determination of cerebrosides. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siakotos A. N. Analytical separation of nonlipid water soluble substances and gangliosides from other lipids by dextran gel column chromatography. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Nov;42(11):913–919. doi: 10.1007/BF02632444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





