Abstract
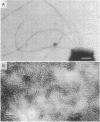
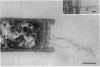
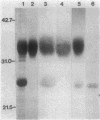
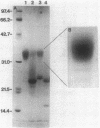
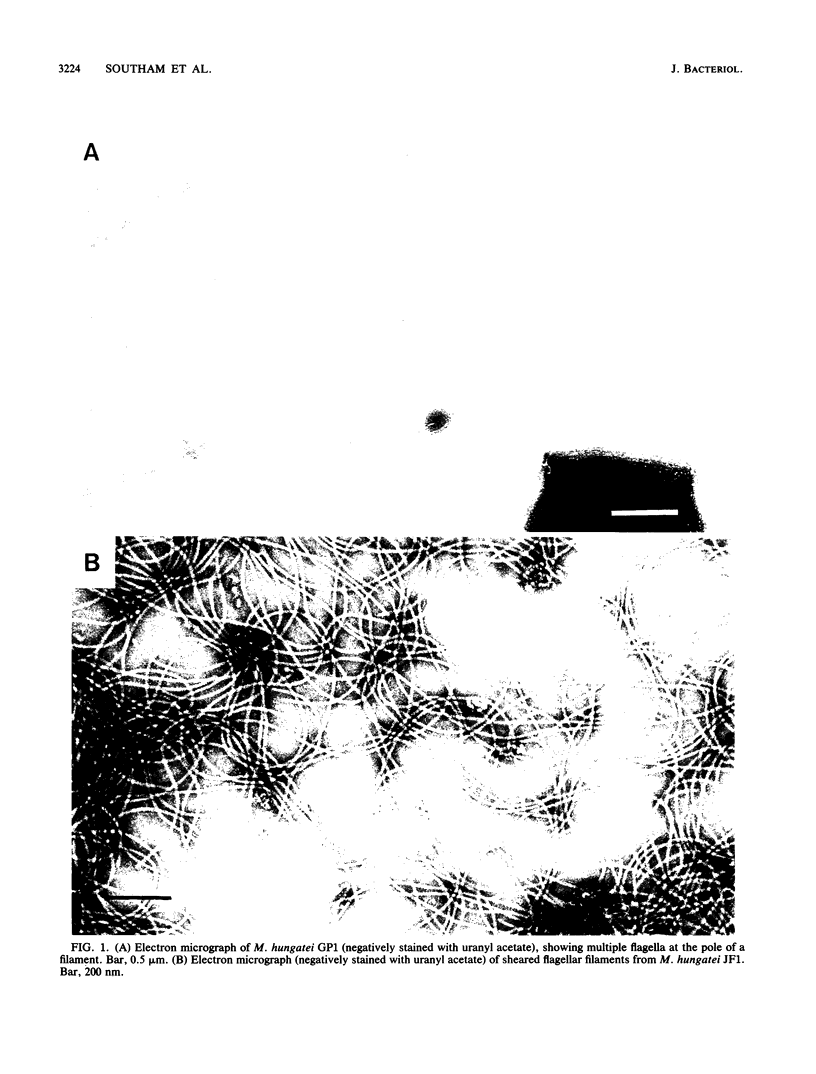
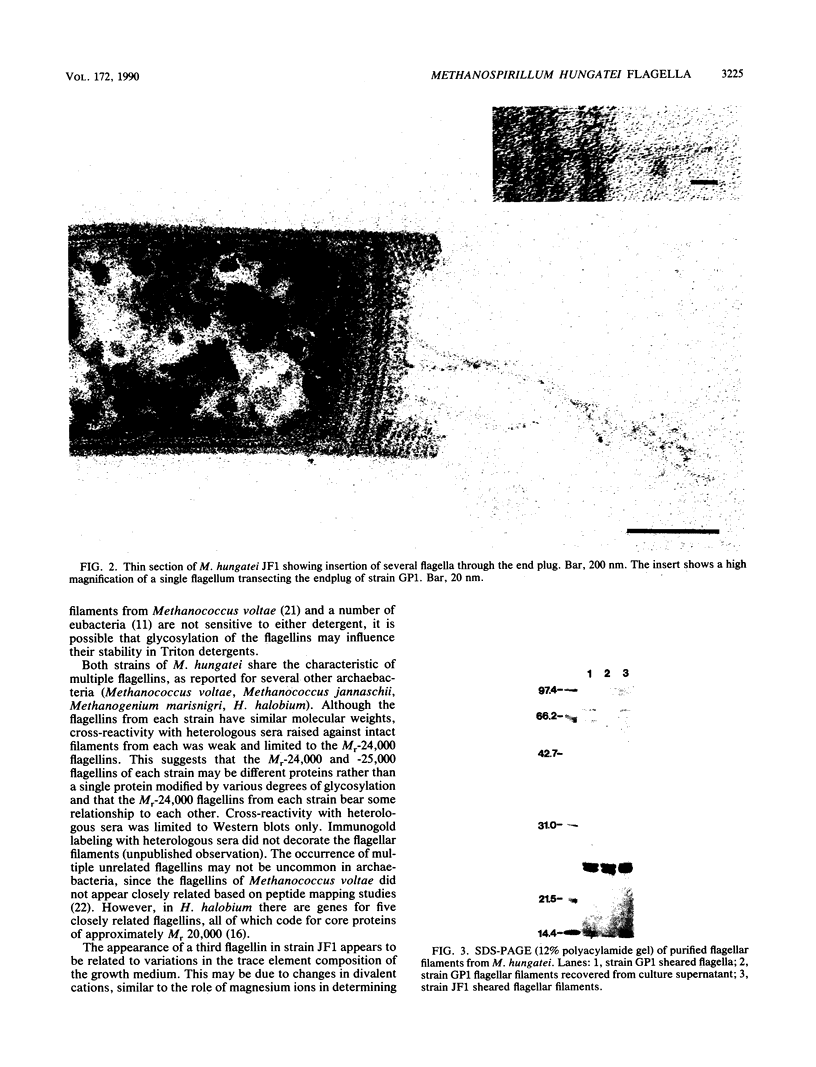
In high (45 mM)-phosphate medium, Methanospirillum hungatei strains GP1 and JF1 grew as very long, nonmotile chains of cells that did not possess flagella. However, growth in lower (3 or 30 mM)-phosphate medium resulted in the production of mostly single cells and short chains that were motile by means of two polar tufts of flagella, which transected the multilayered terminal plug of the cell. Electron microscopy of negatively stained whole mounts revealed a flagellar filament diameter of approximately 10 nm. Flagellar filaments were isolated from either culture fluid or concentrated cell suspensions that were subjected to shearing. Flagellar filaments were sensitive to treatment with both Triton X-100 and Triton X-114 at concentrations as low as 0.1% (vol/vol). The filaments of both strains were composed of two flagellins of Mr 24,000 and 25,000. However, variations in trace element composition of the medium resulted in the production of a third flagellin in strain JF1. This additional flagellin appeared as a ladderlike smear on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacylamide gels with a center of intensity of Mr 35,000 and cross-reacted with antisera produced from filaments containing only the Mr-24,000 and -25,000 flagellins. On sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, all flagellins stained by the thymol-sulfuric acid and Alcian blue methods, suggesting that they were glycosylated. This was further supported by chemical deglycosylation of the strain JF1 flagellins, which resulted in a reduction in their apparent molecular weight on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacylamide gels. Heterologous reactions to sera raised against the flagella from each strain were limited to the Mr-24,000 flagellins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Purification, reconstitution and polymorphic transition of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90677-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahamsha B., Greenberg E. P. Biochemical and cytological analysis of the complex periplasmic flagella from Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4023–4032. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4023-4032.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahamsha B., Greenberg E. P. Cloning and sequence analysis of flaA, a gene encoding a Spirochaeta aurantia flagellar filament surface antigen. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1692–1697. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1692-1697.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton J. W., Murray R. G. Cell envelope associations of Aquaspirillum serpens flagella. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1037–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1037-1049.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton J. W., Murray R. G. Membrane-associated components of the bacterial flagellar apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):290–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruden D., Sparling R., Markovetz A. J. Isolation and Ultrastructure of the Flagella of Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus and Methanospirillum hungatei. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1414–1419. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1414-1419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Purification of intact flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.376-383.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris F. G., Beveridge T. J., Marceau-Day M. L., Larson A. D. Structure and cell envelope associations of flagellar basal complexes of Vibrio cholerae and Campylobacter fetus. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):322–333. doi: 10.1139/m84-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerl L., Deutzmann R., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are encoded by a multigene family. Identification of all five gene products. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerl L., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are encoded by a multigene family. Characterization of five flagellin genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13246–13251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Fujita H., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Excretion of unassembled flagellin by Salmonella typhimurium mutants deficient in hook-associated proteins. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1056–1059. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1056-1059.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. F., Colvin J. R., Sprott G. D. Spontaneous protoplast formation in Methanobacterium bryantii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):346–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.346-353.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. F., Koval S. F. Ultrastructure and biochemistry of Methanococcus voltae. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1989;17(1):53–87. doi: 10.3109/10408418909105722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The flagellar filament protein. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):452–458. doi: 10.1139/m88-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmokoff M. L., Jarrell K. F., Koval S. F. Isolation of flagella from the archaebacterium Methanococcus voltae by phase separation with Triton X-114. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1752–1758. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1752-1758.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmokoff M. L., Karnauchow T. M., Jarrell K. F. Conserved N-terminal sequences in the flagellins of archaebacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91744-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaka H., Armfield A. Y., Lombard G. L., Dowell V. R., Jr Practical procedure for demonstrating bacterial flagella. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):948–952. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.948-952.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koval S. F., Jarrell K. F. Ultrastructure and biochemistry of the cell wall of Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1298–1306. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1298-1306.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha S. C., Kates M., Sprott G. D., Smith I. C. Novel complex polar lipids from the methanogenic archaebacterium Methanospirillum hungatei. Science. 1981 Mar 13;211(4487):1163–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.7466385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam M. Y., McGroarty E. J., Kropinski A. M., MacDonald L. A., Pedersen S. S., Høiby N., Lam J. S. Occurrence of a common lipopolysaccharide antigen in standard and clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):962–967. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.962-967.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Treponema phagedenis has at least two proteins residing together on its periplasmic flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.105-112.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., DeRosier D. J. Bacterial flagellar structure and function. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):442–451. doi: 10.1139/m88-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Lowe G., Berg H. C. The proton flux through the bacterial flagellar motor. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):643–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel G. B., Roth L. A., van den Berg L., Clark D. S. Characterization of a strain of Methanospirillum hungatti. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1404–1410. doi: 10.1139/m76-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen D. Glycoprotein detection in polyacrylamide gel with thymol and sulfuric acid. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):474–476. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. J., Hills G. J., Henwood J. A., Harris J. E., Archer D. B. Three-dimensional architecture of the cell sheath and septa of Methanospirillum hungatei. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):750–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.750-757.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. Membrane-linked energy transductions. Bioenergetic functions of sodium: H+ is not unique as a coupling ion. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., McKellar R. C. Composition and properties of the cell wall of Methanospirillum hungatii. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):115–120. doi: 10.1139/m80-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Beveridge T. J., Sprott G. D. Crystalline order to high resolution in the sheath of Methanospirillum hungatei: a cross-beta structure. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M. Halobacterial glycoprotein biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 27;906(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Rittenberg S. C. Waveform analysis and structure of flagella and basal complexes from Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1038–1046. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1038-1046.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardi A. H., Michos G. A. Alcian blue staining of glycoproteins in acrylamide disc electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F., Paul G., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are sulfated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15180–15185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Bowen V. G. Fine structure of Methanospirillum hungatii. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):373–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.373-380.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]