Abstract
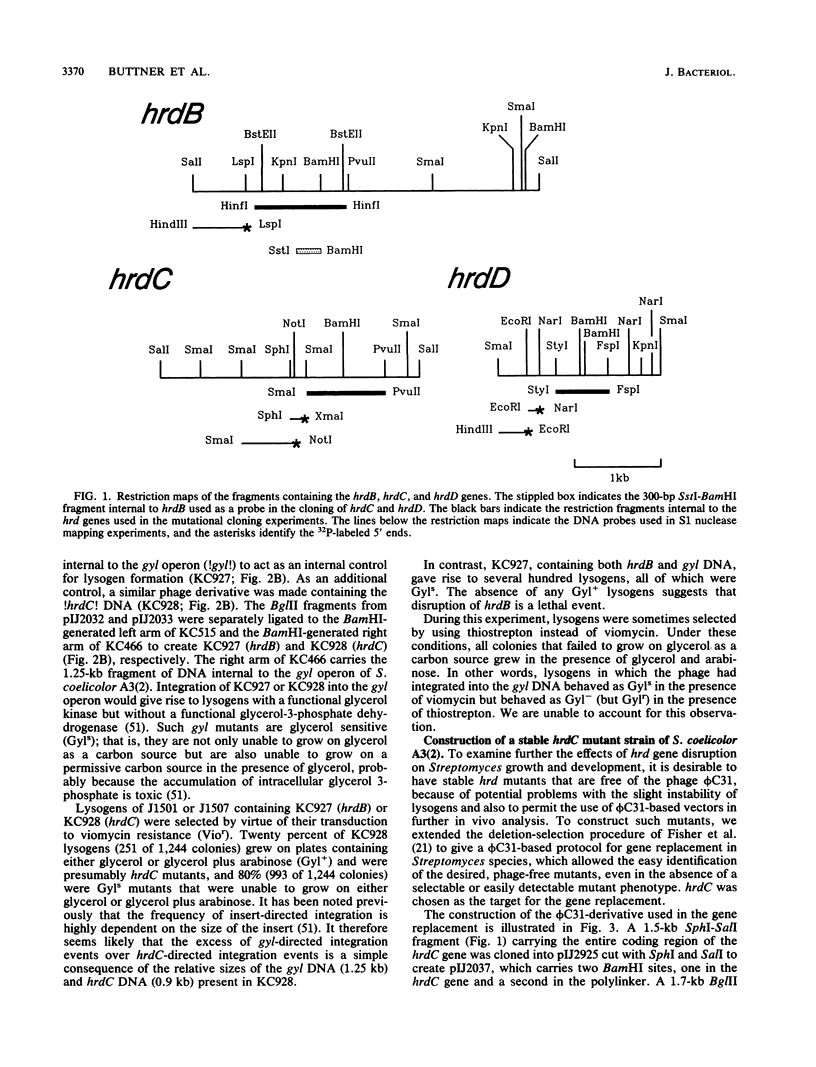
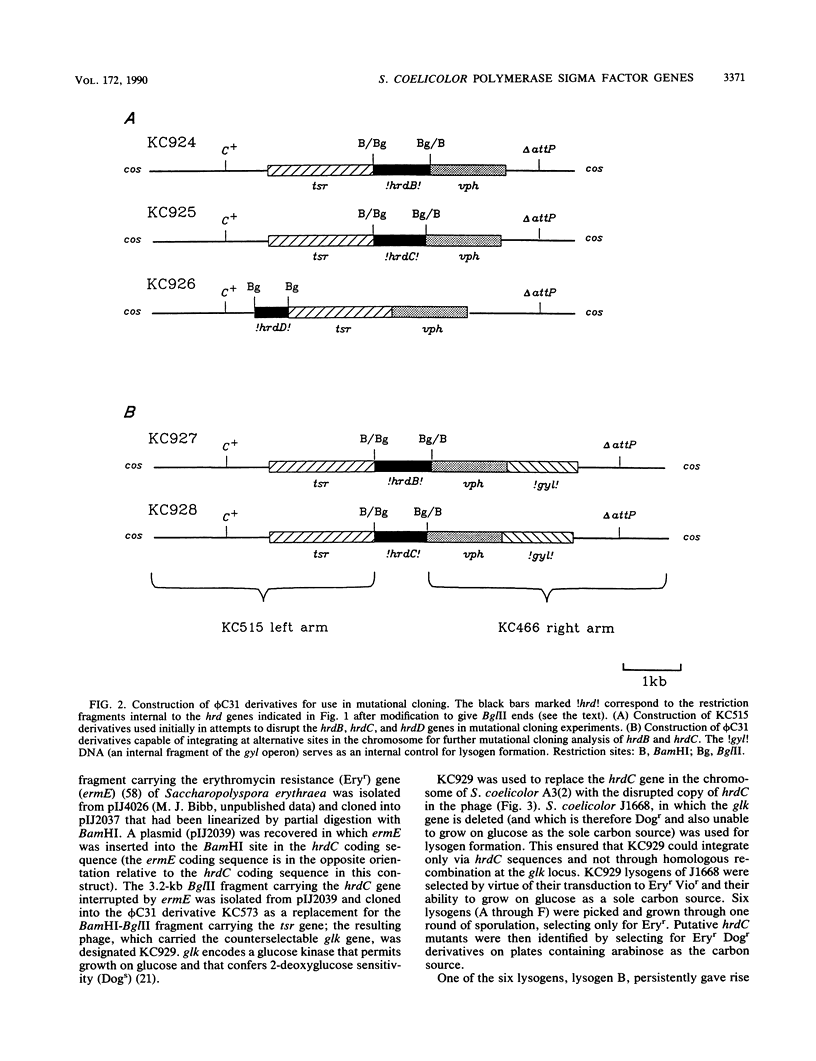
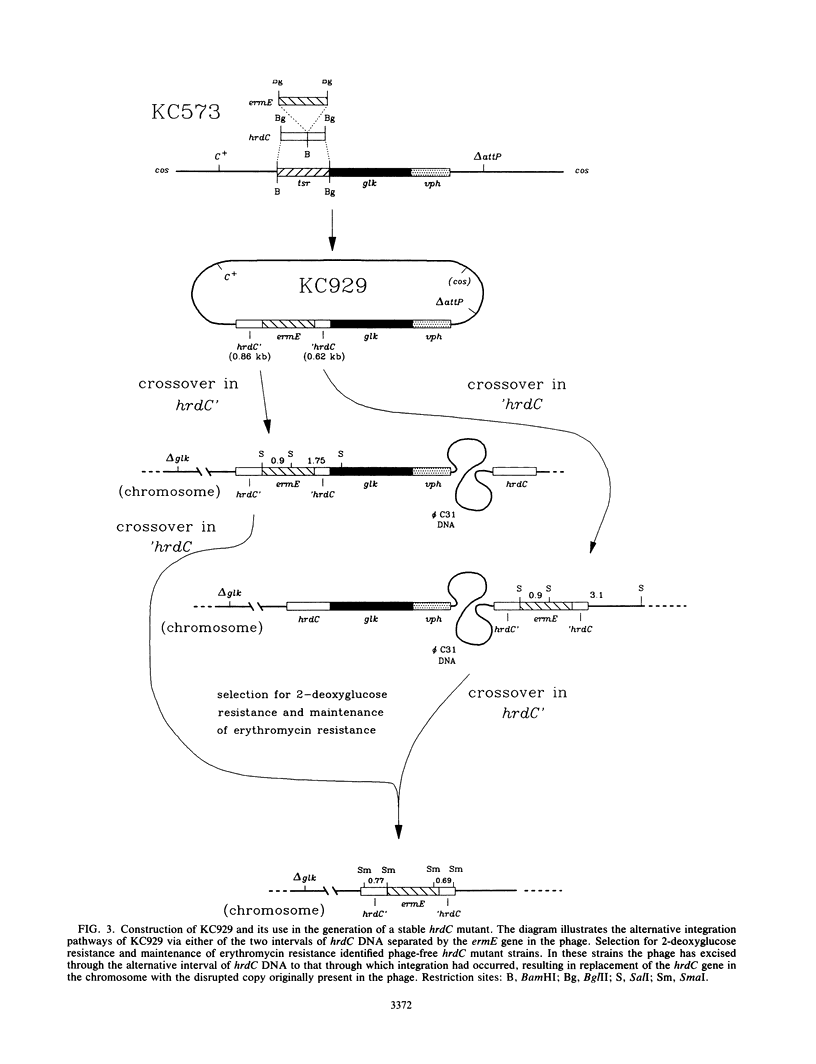
The rpoD gene of Myxococcus xanthus was used as a probe to isolate three Streptomyces coelicolor genes, hrdB, hrdC, and hrdD, which appear to encode RNA polymerase sigma factors extremely similar to the sigma 70 polypeptide of Escherichia coli. Gene disruption experiments suggested that hrdB is essential in S. coelicolor A3(2) but showed that hrdC and hrdD mutants are viable and are apparently unaffected in differentiation, gross morphology, and antibiotic production. S1 nuclease mapping showed that hrdB and hrdD, but not hrdC, were transcribed in liquid culture. The most upstream of two hrdD promoters is internal to an open reading frame (ORF X) on the opposite strand. The predicted product of this gene is homologous to the phosphinothricin acetyltransferases of Streptomyces hygroscopicus and Streptomyces viridochromogenes. The possible significance of the overlapping and divergent transcription of hrdD and ORF X is discussed. A general method for in vivo gene replacement was developed that allowed a positive selection for the desired mutants even in the absence of a mutant phenotype; it was used to isolate a stable hrdC mutant.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anzai H., Kumada Y., Hara O., Murakami T., Itoh R., Takano E., Imai S., Satoh A., Nagaoka K. Replacement of Streptomyces hygroscopicus genomic segments with in vitro altered DNA sequences. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988 Feb;41(2):226–233. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnosti D. N., Chamberlin M. J. Secondary sigma factor controls transcription of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Gene expression in Streptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors in Streptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(2):265–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00331128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Findlay P. R., Johnson M. W. The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett W. V., Henner J., Eckhardt T. The nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for XP55, a major secreted protein from Streptomyces lividans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3926–3926. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttner M. J. RNA polymerase heterogeneity in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1653–1659. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttner M. J., Smith A. M., Bibb M. J. At least three different RNA polymerase holoenzymes direct transcription of the agarase gene (dagA) of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90472-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F. A morphological and genetic mapping study of white colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Aug;72(1):9–28. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., King A. A., Suarez J. E. The expression of Streptomyces and Escherichia coli drug-resistance determinants cloned into the Streptomyces phage phi C31. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J. Mutational cloning in Streptomyces and the isolation of antibiotic production genes. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F., Bruton C. J., Plaskitt K. A., Buttner M. J., Méndez C., Helmann J. D. The developmental fate of S. coelicolor hyphae depends upon a gene product homologous with the motility sigma factor of B. subtilis. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90876-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. H., Bruton C. J., Chater K. F. The glucose kinase gene of Streptomyces coelicolor and its use in selecting spontaneous deletions for desired regions of the genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jan;206(1):35–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00326533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Schmidt F. J., Adams C. W., Rosenberg M., Brawner M. E. Two promoters, one inducible and one constitutive, control transcription of the Streptomyces lividans galactose operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. DNA sequence analysis suggests that expression of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is controlled by an alternative sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6422–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Márquez L. M., Chamberlin M. J. Cloning, sequencing, and disruption of the Bacillus subtilis sigma 28 gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1568–1574. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1568-1574.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J. Plasmids, recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2257–2269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S. Cloning and DNA sequence of the gene coding for the major sigma factor from Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):80–85. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.80-85.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Ward J. M., Bibb M. J. Unusual transcriptional and translational features of the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene (aph) from Streptomyces fradiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):415–429. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmazyn-Campelli C., Bonamy C., Savelli B., Stragier P. Tandem genes encoding sigma-factors for consecutive steps of development in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):150–157. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K., Ali-Dunkrah U., Cullum J. Cloning of the galactokinase gene (galK) from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):721–725. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya N. D., Mkrtumian N. M., Gostimskaya N. L., Danilenko V. N. Characterization of temperate actinophage phi C31 isolated from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):258–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.258-262.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez C., Chater K. F. Cloning of whiG, a gene critical for sporulation of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5715–5720. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5715-5720.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirel D. B., Chamberlin M. J. The Bacillus subtilis flagellin gene (hag) is transcribed by the sigma 28 form of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3095–3101. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3095-3101.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piret J. M., Chater K. F. Phage-mediated cloning of bldA, a region involved in Streptomyces coelicolor morphological development, and its analysis by genetic complementation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.965-972.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodicio M. R., Bruton C. J., Chater K. F. New derivatives of the Streptomyces temperate phage phi C31 useful for the cloning and functional analysis of Streptomyces DNA. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno E. T., Bruton C. J., Chater K. F. The glycerol utilization operon of Streptomyces coelicolor: genetic mapping of gyl mutations and the analysis of cloned gylDNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):119–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00327424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Kunkel B., Kroos L., Losick R. Chromosomal rearrangement generating a composite gene for a developmental transcription factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):507–512. doi: 10.1126/science.2536191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Shiina T., Takahashi H. Multiple principal sigma factor homologs in eubacteria: identification of the "rpoD box". Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1040–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.3194753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Kieser T., Ward J. M., Hopwood D. A. Physical analysis of antibiotic-resistance genes from Streptomyces and their use in vector construction. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. J., Movva N. R., Tizard R., Crameri R., Davies J. E., Lauwereys M., Botterman J. Characterization of the herbicide-resistance gene bar from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02538.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vögtli M., Hütter R. Characterisation of the hydroxystreptomycin phosphotransferase gene (sph) of Streptomyces glaucescens: nucleotide sequence and promoter analysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):195–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00330442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westpheling J., Brawner M. Two transcribing activities are involved in expression of the Streptomyces galactose operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1355–1361. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1355-1361.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westpheling J., Ranes M., Losick R. RNA polymerase heterogeneity in Streptomyces coelicolor. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):22–27. doi: 10.1038/313022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlleben W., Arnold W., Broer I., Hillemann D., Strauch E., Pühler A. Nucleotide sequence of the phosphinothricin N-acetyltransferase gene from Streptomyces viridochromogenes Tü494 and its expression in Nicotiana tabacum. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




