Abstract
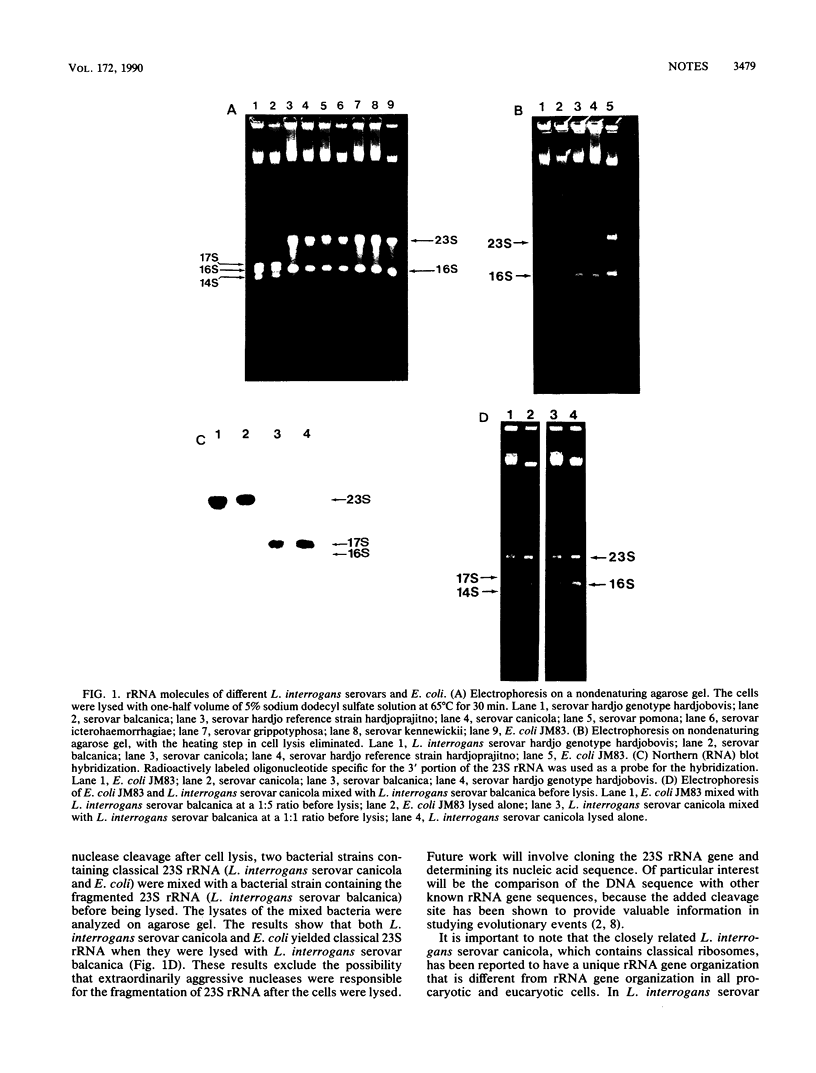
All known ribosomes of procaryotic organisms are made up of three rRNA components that are 23, 16, and 5S in size. We now report that in some Leptospira interrogans strains, the classical 23S rRNA is further processed to generate 14 and 17S rRNAs. This processing step was previously known to occur only in some eucaryotes and in a small group of procaryotes. The implications of this finding are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell D. A., Kubo K., Clark C. G., Boothroyd J. C. Precise identification of cleavage sites involved in the unusual processing of trypanosome ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Gerbi S. A. Ribosomal RNA evolution by fragmentation of the 23S progenitor: maturation pathway parallels evolutionary emergence. J Mol Evol. 1982;18(5):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF01733899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Tague B. W., Ware V. C., Gerbi S. A. Xenopus laevis 28S ribosomal RNA: a secondary structure model and its evolutionary and functional implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6197–6220. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Pace N. R. Transcriptional organization of the ribosomal RNA cistrons in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1786–1790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Horie I., Mifuchi I. Nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2123–2123. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Mifuchi I. Unique organization of Leptospira interrogans rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5763–5767. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5763-5767.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H. Evolution of ribosomal RNA. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1977;58(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(77)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq B. Sequence homologies between eukaryotic 5.8S rRNA and the 5' end of prokaryotic 23S rRNa: evidences for a common evolutionary origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2913–2932. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Latil-Damotte M., Jourdan R. Coding and spacer sequences in the 5.8S-2S region of Sciara coprophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3565–3573. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B. DNA probe for detection of the Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo genotype hardjo-bovis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2236–2238. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2236-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Thiermann A. B., Foley J. Genetic and antigenic differences of serologically indistinguishable leptospires of serovar hardjo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2094–2097. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2094-2097.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Ribosomal RNA phylogeny and the primary lines of evolutionary descent. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):325–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Jordan B. R., Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N. Sequence and secondary structure of Drosophila melanogaster 5.8S and 2S rRNAs and of the processing site between them. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2213–2238. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. H., Crichton P. B., Old D. C., Higgins C. F. Ribosomal-RNA patterns of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and related Enterobacteriaceae. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(3):223–228. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-3-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. F., Collings J. C., Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. Multiple spacer sequences in the nuclear large subunit ribosomal RNA gene of Crithidia fasciculata. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1063–1071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware V. C., Renkawitz R., Gerbi S. A. rRNA processing: removal of only nineteen bases at the gap between 28S alpha and 28S beta rRNAs in Sciara coprophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3581–3597. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G. Components of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:155–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]