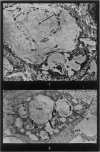
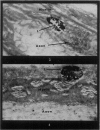
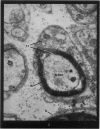
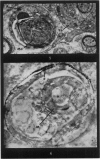
Full text
PDF


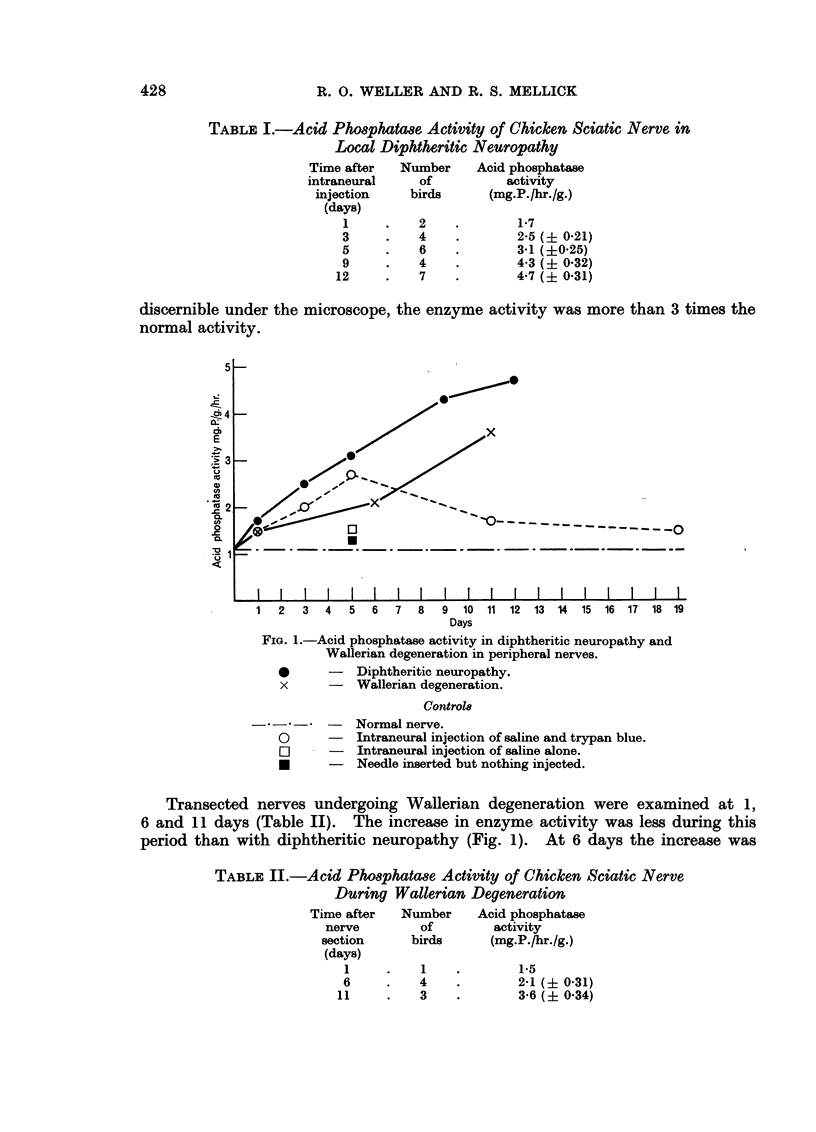


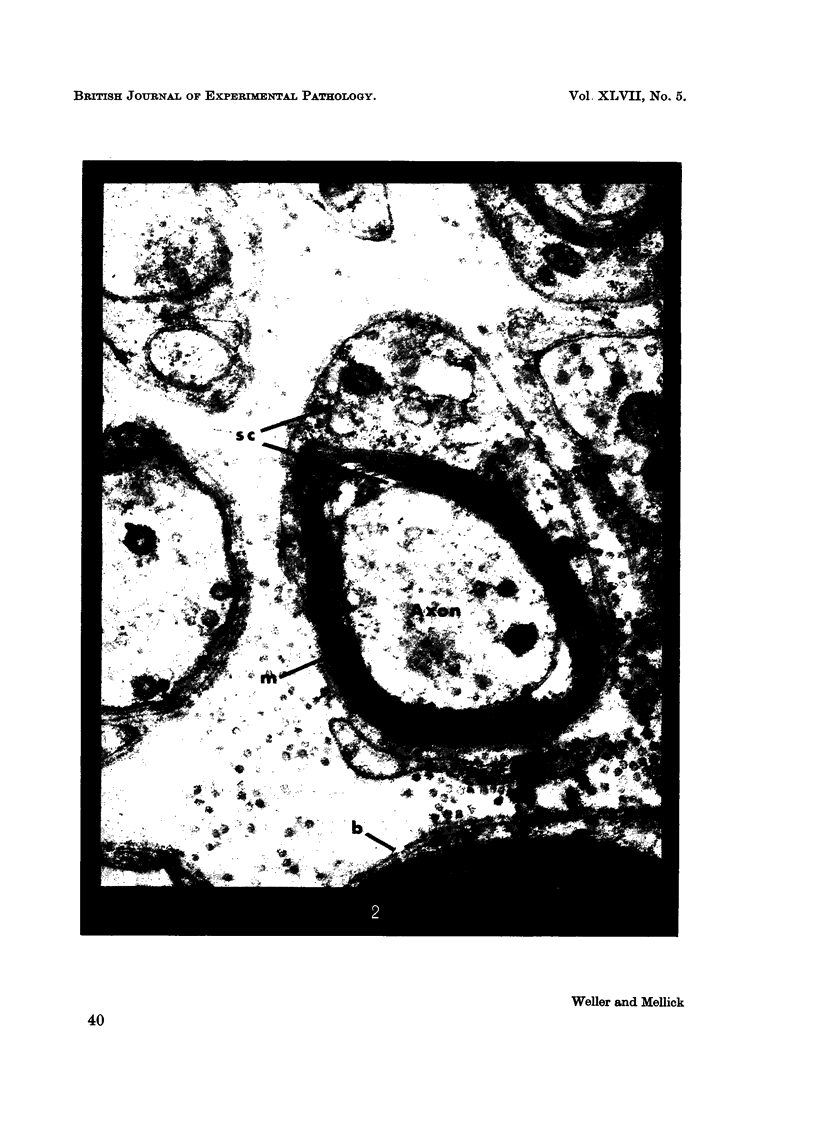
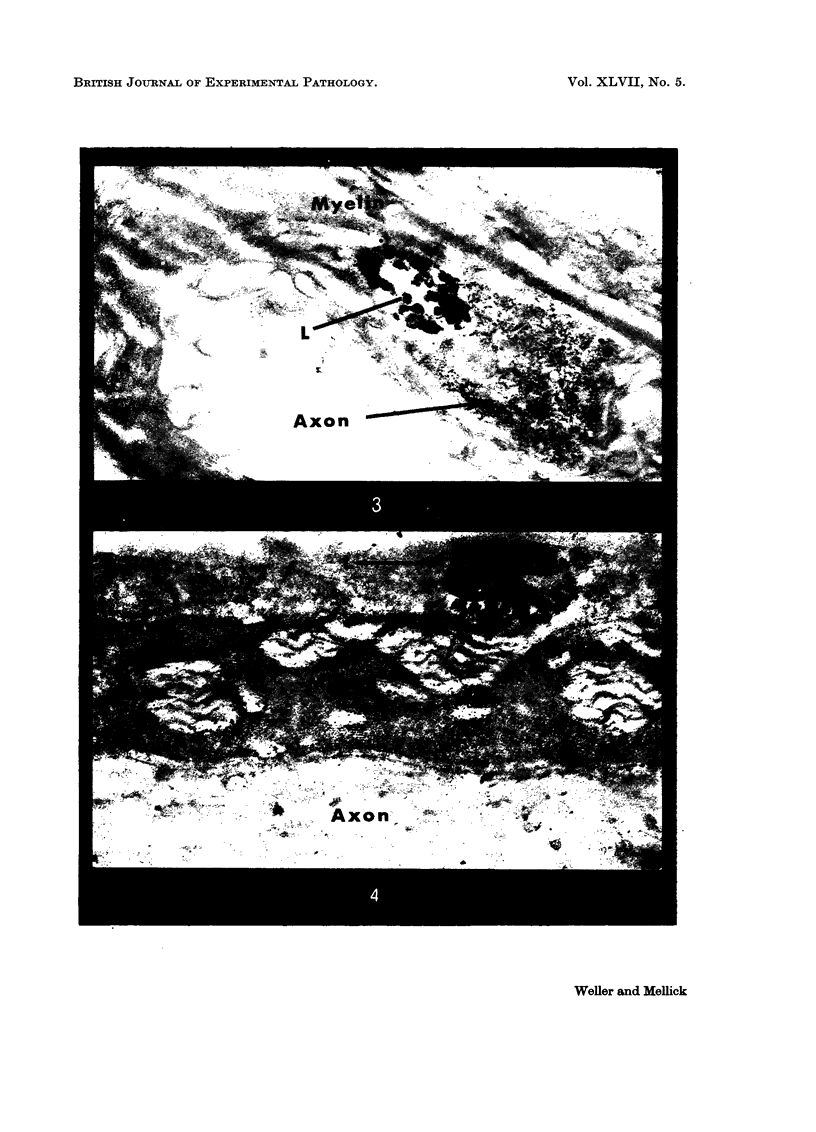
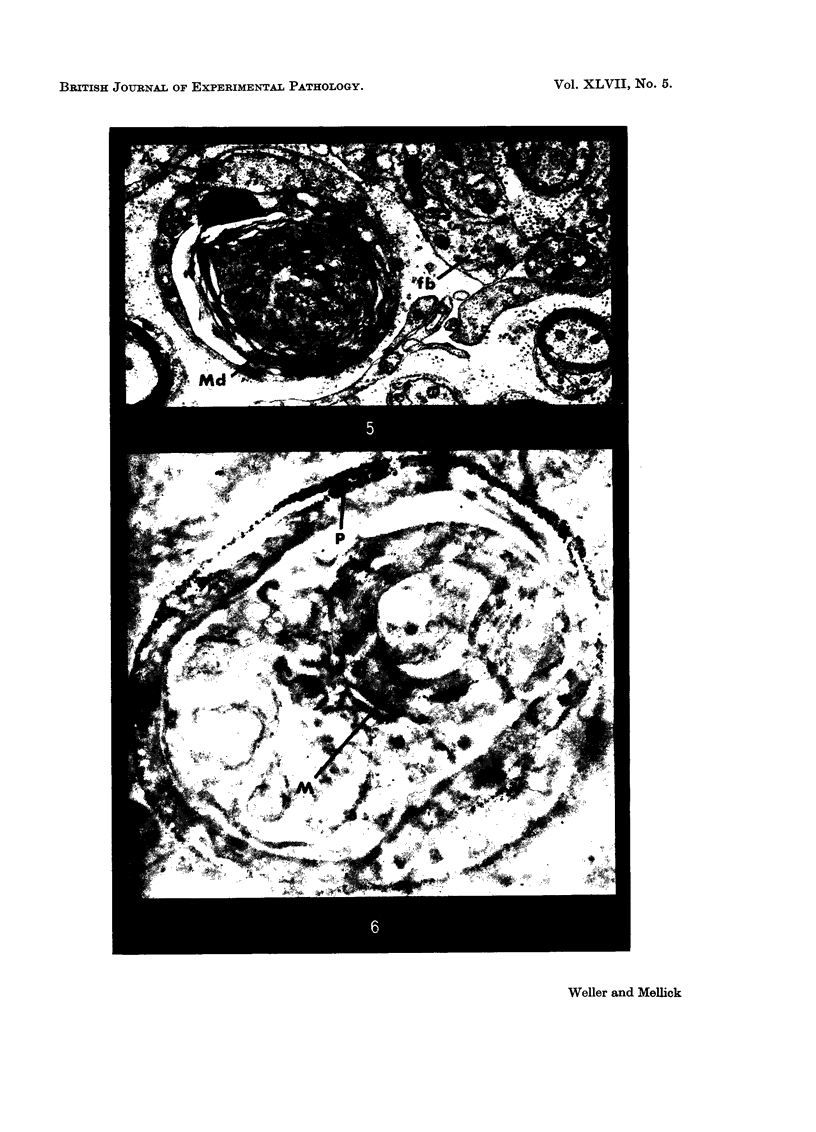
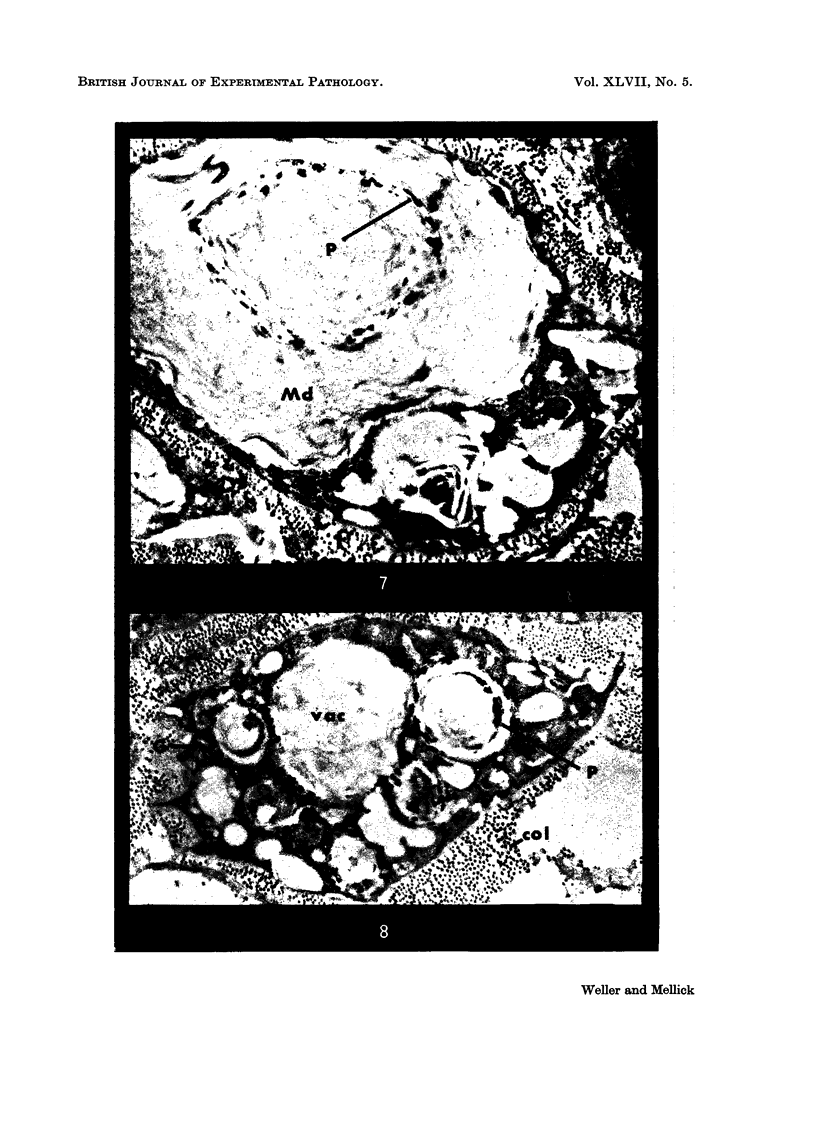




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS C. W., TUQAN N. A. Histochemistry of myelin. II. Proteins, lipid-protein dissociation and proteinase activity in Wallerian degeneration. J Neurochem. 1961 Mar;6:334–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abercrombie M., Johnson M. L. Quantitative histology of Wallerian degeneration: I. Nuclear population in rabbit sciatic nerve. J Anat. 1946 Jan;80(Pt 1):37–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., WEBSTER G. R. On the changes in ali-esterase and pseudocholinesterase activity of chicken sciatic nerve during Wallerian degeneration and their correlation with cellular proliferation. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1955 Jan;40(1):12–23. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1955.sp001093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTH L. Regeneration in the mammalian peripheral nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1956 Oct;36(4):441–478. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1956.36.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLINGER D. M., ROSSITER R. J., UPMALIS H. Chemical studies of peripheral nerve during wallerian degeneration. IV. Phosphatases. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):652–659. doi: 10.1042/bj0520652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. C., McNABB A. R., ROSSITER R. J. Chemistry of wallerian degeneration; a review of recent studies. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1950 Jul;64(1):105–121. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1950.02310250111010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. M., Cavanagh J. B., Mellick R. S. Intraneural injection of diphtheria toxin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Oct;47(5):507–517. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J., Armstrong A. R. A CONVENIENT METHOD FOR DETERMINING SERUM AND BILE PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY. Can Med Assoc J. 1934 Oct;31(4):376–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONALD W. I. THE EFFECTS OF EXPERIMENTAL DEMYELINATION ON CONDUCTION IN PERIPHERAL NERVE: A HISTOLOGICAL AND ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY. I. CLINICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS. Brain. 1963 Sep;86:481–500. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANIEL E. J. PEASE DC: DEGENERATIVE CHANGES IN RAT DORSAL ROOTS DURING WALLERIAN DEGENERATION. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Dec;52:511–532. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1952 Mar;95(3):285–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON H., ZETTERQVIST H., BRANDES D. Histochemical reactions for electron microscopy: acid phosphatase. Exp Cell Res. 1955 Dec;9(3):592–596. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(55)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K. CHANGES IN THE ENDONEURIAL SHEATHS OF PERIPHERAL MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES DURING WALLERIAN DEGENERATION. J Anat. 1964 Apr;98:175–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., LASCELLES R. G. SCHWANN-CELL ABNORMALITIES IN DIABETIC NEUROPATHY. Lancet. 1965 Jun 26;1(7400):1355–1357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., ADAMS R. D., MANSMANN H. C., Jr Experimental study of diphtheritic polyneuritis in the rabbit and guinea pig. I. Immunologic and histopathologic observations. J Exp Med. 1957 Jun 1;105(6):591–614. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.6.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]