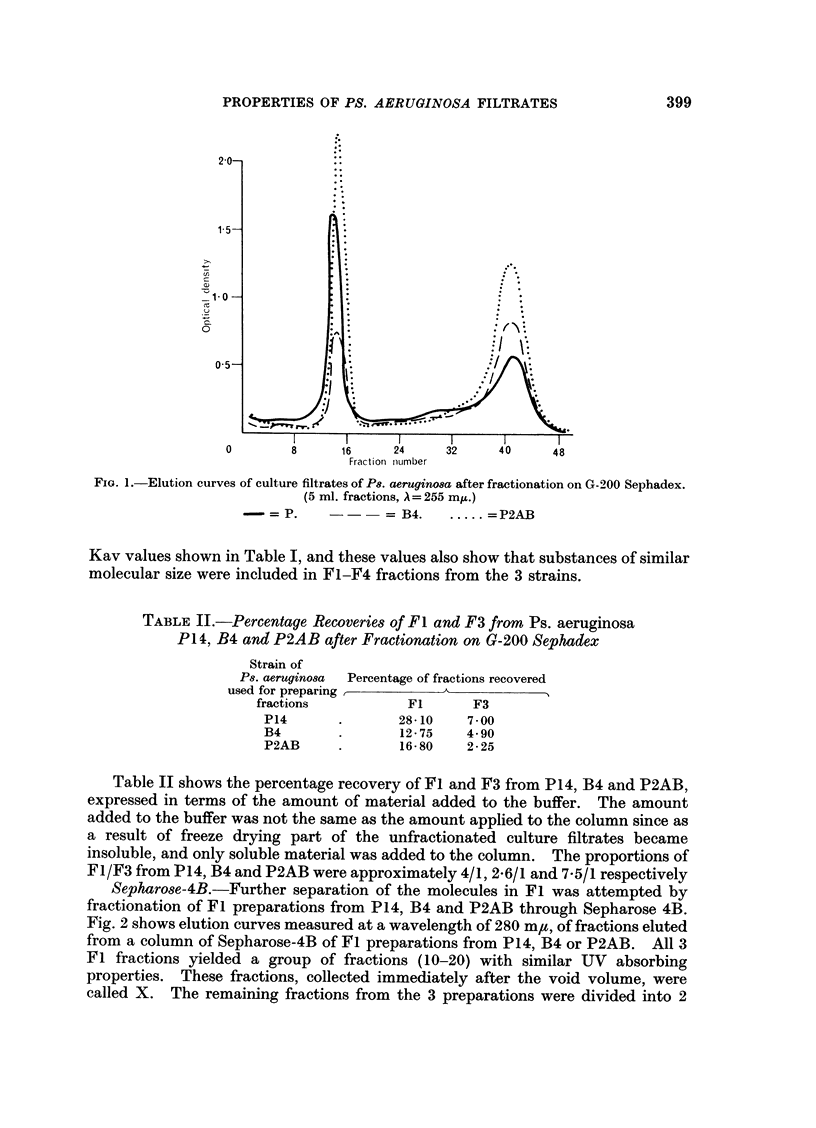
Full text
PDF



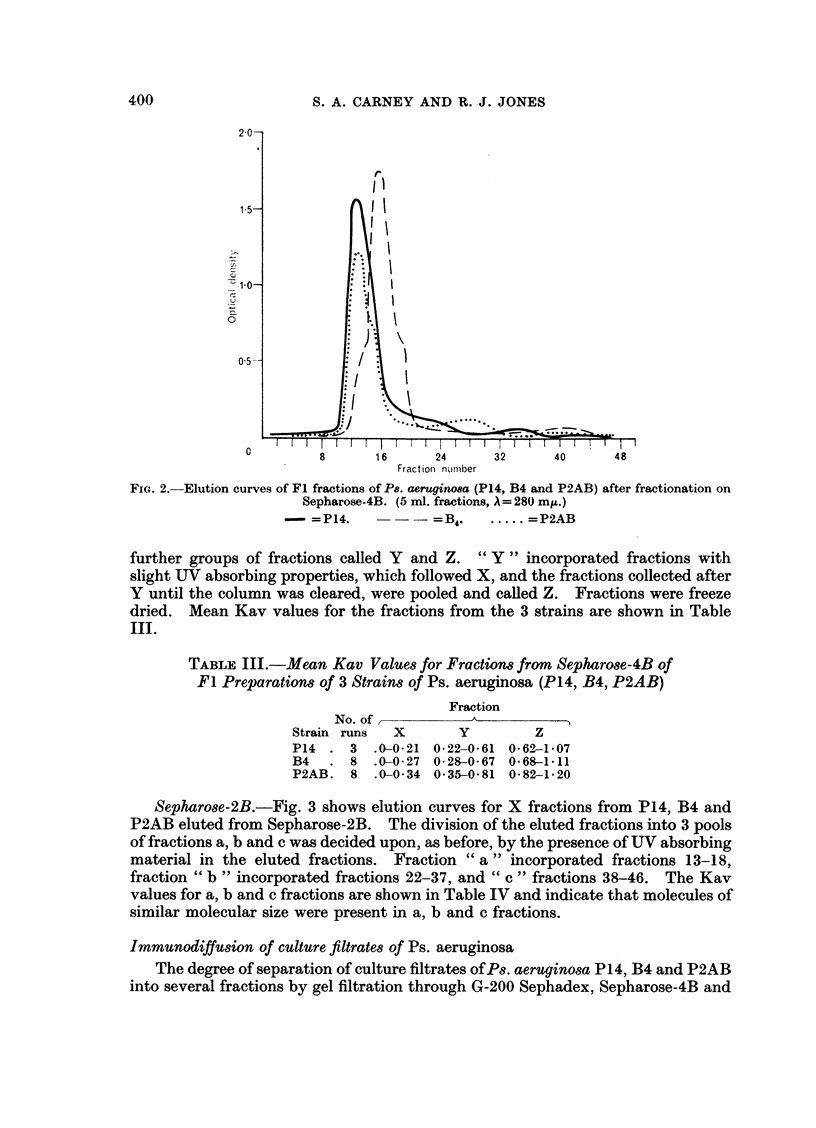
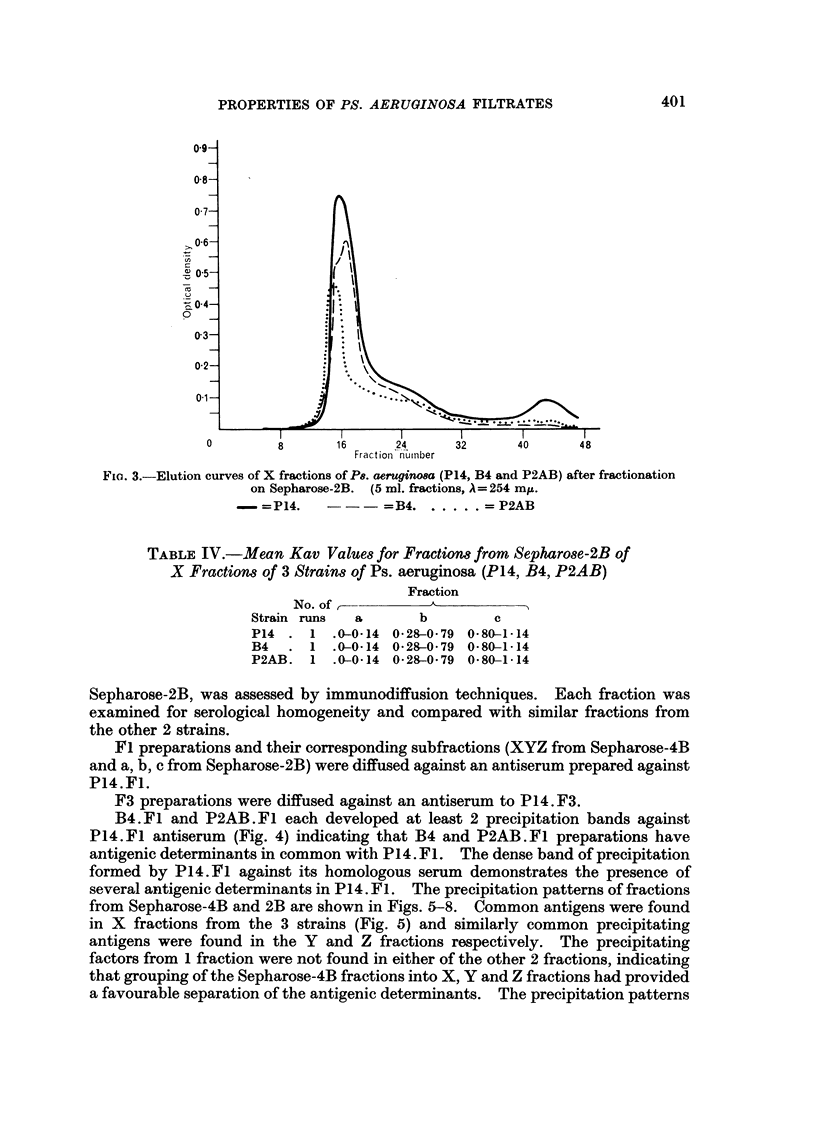

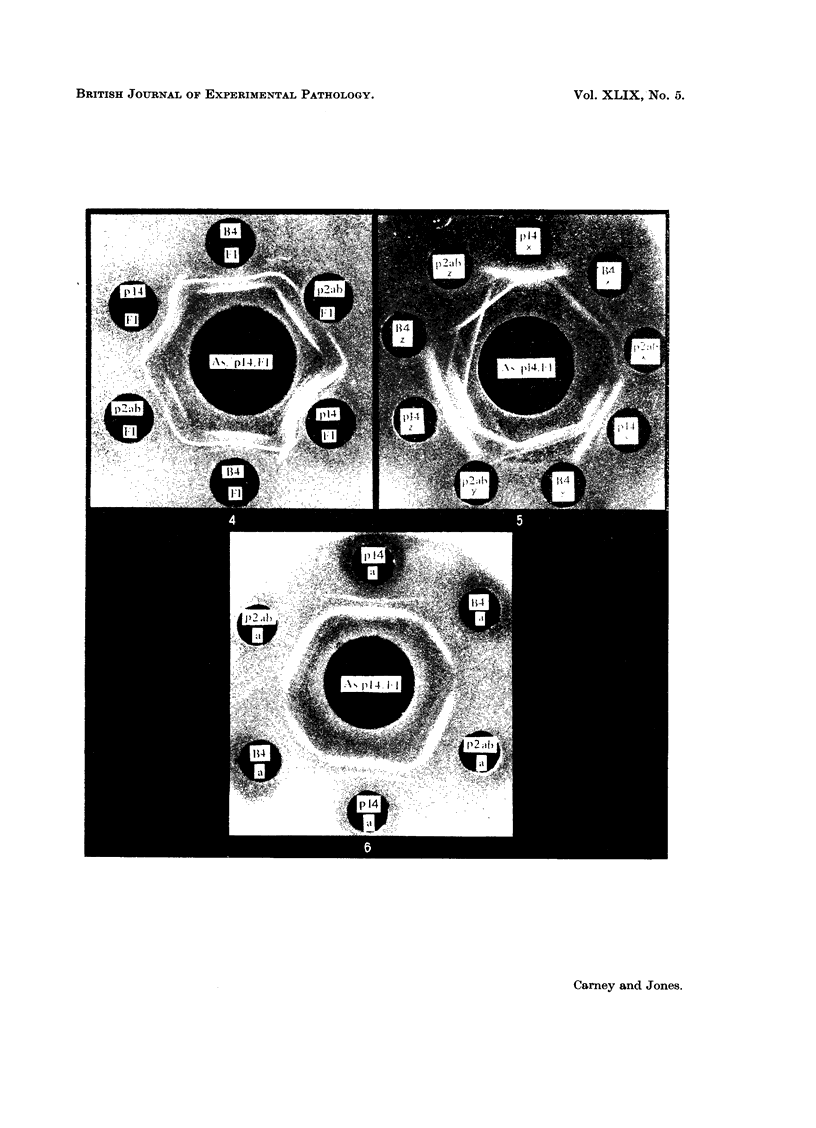
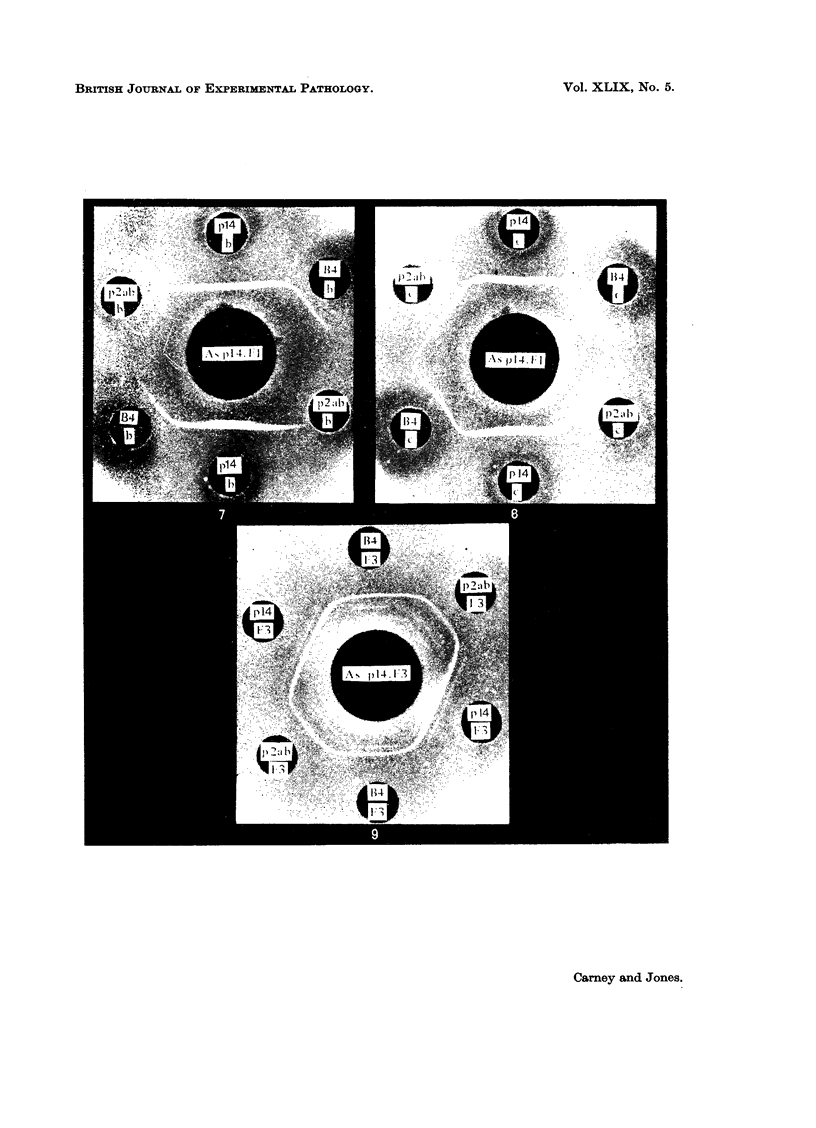






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown V. I., Lowbury E. J. Use of an improved cetrimide agar medium and other culture methods for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Nov;18(6):752–756. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.6.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke K., Gray G. W., Reaveley D. A. The extraction of cell walls of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with aqueous phenol. The insoluble residue and material from the aqueous layers. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):759–765. doi: 10.1042/bj1050759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABS I. Untersuchungen über die O-Antigene von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1957;144(3):218–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. J., LOWBURY E. J. STAPHYLOCOCCAL ANTIBODIES IN BURNED PATIENTS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Dec;44:576–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. G., Morris J. M., Berk R. S. The extracellular protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibiting elastase activity. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jun;13(6):711–719. doi: 10.1139/m67-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V., ABE Y., BATES J. L. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Mar-Apr;108:218–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lányi B. Serological properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Group-specific somatic antigens. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1966;13(4):295–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mull J. D., Callahan W. S. The role of the elastase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in experimental infection. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Dec;4(6):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDGE J. M. Dark-field illumination for photographing precipitin bands in gel. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Nov;13:530–531. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.6.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERDER E., EVANS J. A proposed antigenic schema for the identification of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1961 Sep-Oct;109:183–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]