Abstract
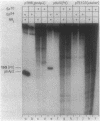
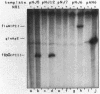
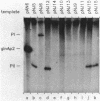
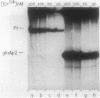
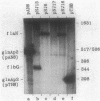
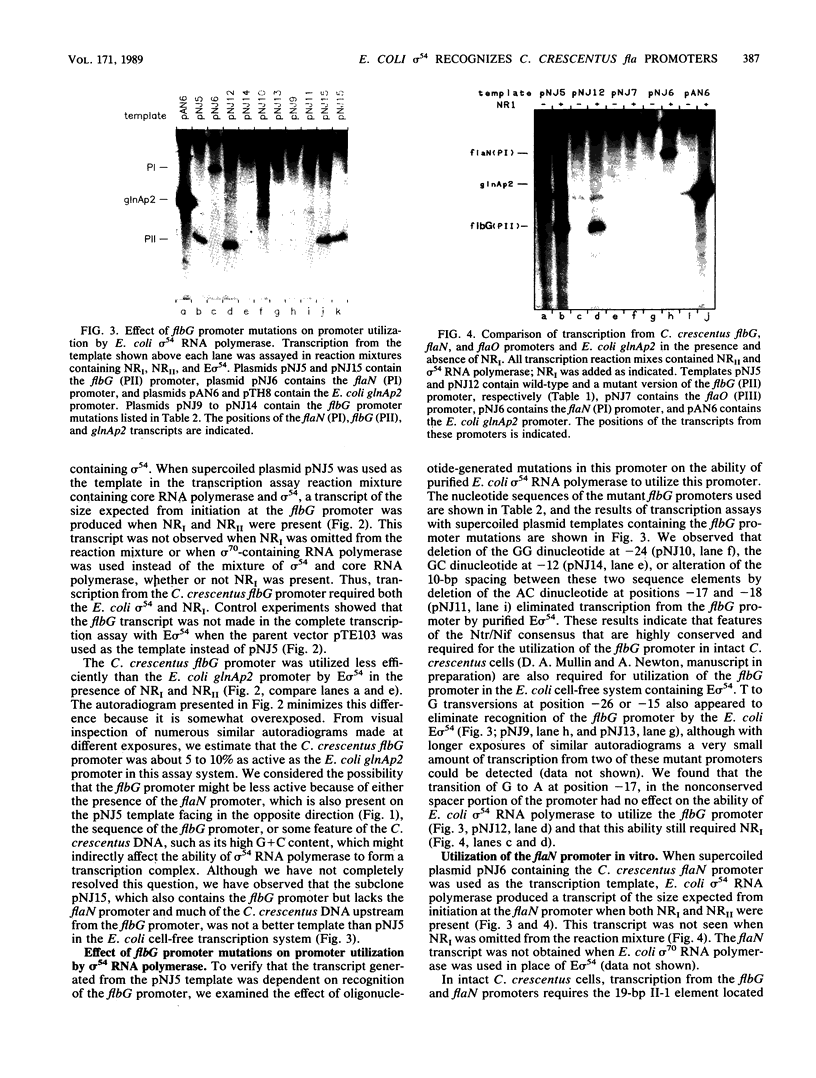
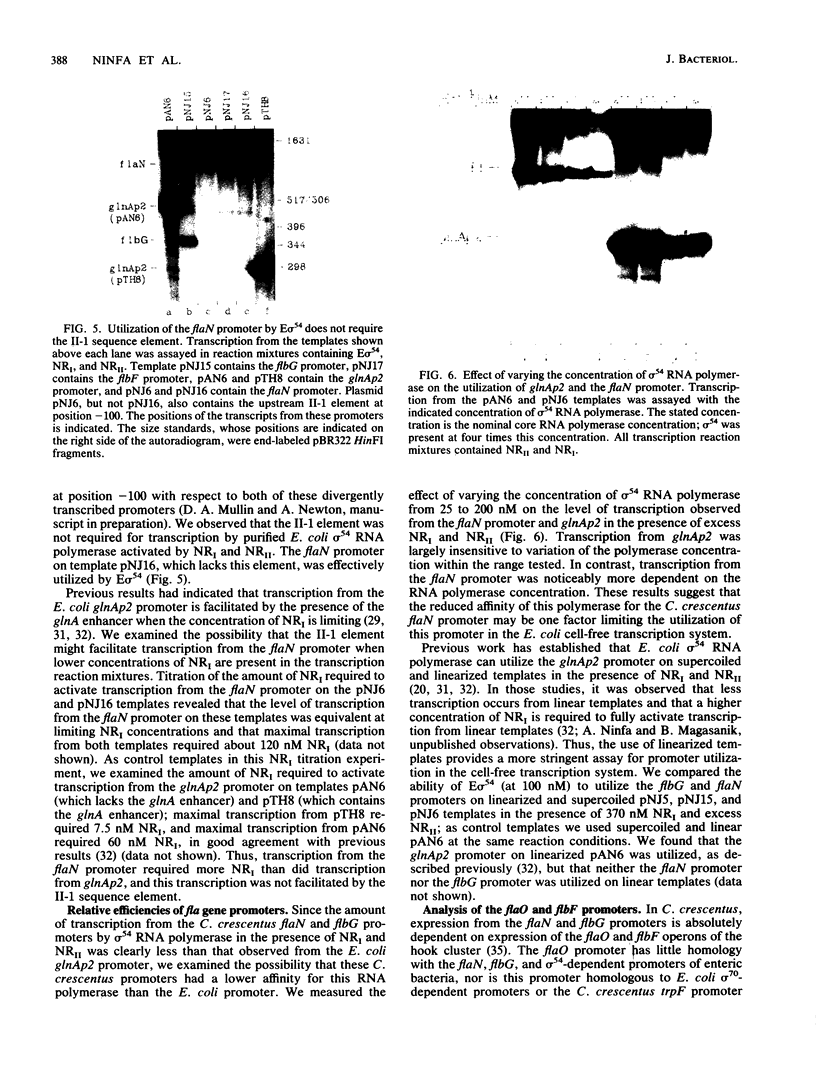
A set of the periodically regulated flagellar (fla) genes of Caulobacter crescentus contain conserved promoter sequence elements at -24 and -12 that are very similar to the sequence of the nitrogen assimilation (Ntr) and nitrogen fixation (Nif) promoters of enteric bacteria and Rhizobium spp. Transcription from Ntr and Nif promoters requires RNA polymerase containing sigma 54 instead of the usual sigma 70 and, in the case of the Ntr promoters, is activated by the transcription factors NRI and NRII. We have now demonstrated that the C. crescentus flbG and flaN promoters, which contain the Ntr/Nif type of consensus sequence, are utilized by purified Escherichia coli sigma 54 RNA polymerase (E sigma 54) in the presence of NRI and NRII but not by the purified sigma 70 RNA polymerase (E sigma 70) of E. coli. Oligonucleotide-generated flbG promoter deletions that removed the highly conserved GG dinucleotide at -24 or the GC dinucleotide at -12 or altered the spacing between the -24 and -12 sequence elements prevented utilization of the flbG promoter by the E. coli E sigma 54. Transversions of T to G at positions -26 and -15 also inactivated flbG promoter function in the E. coli cell-free transcription system, while a transition of G to A at position -16 in the nonconserved spacer region had no effect. The C. crescentus flaO and flbF promoters, which do not contain the Ntr/Nif-type promoter consensus sequence, were not utilized by either purified E sigma 54 or E sigma 70 from E. coli. Our results help to define the features of the Ntr/Nif-type consensus sequence required for promoter utilization by purified E. coli E sigma 54 and support the idea that C. crescentus may contain a specialized polymerase with similar promoter specificity required for expression of a set of fla genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin S., Henderson N., Dixon R. Requirements for transcriptional activation in vitro of the nitrogen-regulated glnA and nifLA promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae: dependence on activator concentration. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Mutations affecting regulation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH (nitrogenase reductase) promotor. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):143–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.143-147.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M. Deletion analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter: importance of spacing between conserved sequences around positions -12 and -24 for activation by the nifA and ntrC (glnG) products. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.545-551.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Khan H., Dixon R. Site-directed mutagenesis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifL and nifH promoters and in vivo analysis of promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7621–7638. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champer R., Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Cascade regulation of Caulobacter flagellar and chemotaxis genes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90716-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. S., Mullin D., Newton A. Identification, nucleotide sequence, and control of developmentally regulated promoters in the hook operon region of Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2860–2864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. The xylABC promoter from the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid is activated by nitrogen regulatory genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00330393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Clements J., Merrick M., Dixon R. Positive control and autogenous regulation of the nifLA promoter in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1983 Jan 27;301(5898):302–307. doi: 10.1038/301302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Amarasinghe A. B., Bender R. A. Ammonia assimilation and glutamate formation in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):225–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.225-230.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Croft R. H., Gerardot C. J. Genetic mapping of genes required for motility in Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1984 Nov;108(3):523–532. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. The nucleotide sequence of the Mr = 28,500 flagellin gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7395–7401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahnenberger K. M., Shapiro L. Identification of a gene cluster involved in flagellar basal body biogenesis in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 5;194(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90718-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Ebina Y., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Nucleotide sequence surrounding transcription initiation site of xylABC operon on TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1688–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y. Fusions of flagellar operons to lactose genes on a mu lac bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):16–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.16-26.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich S. A., Newton A. Promoter mapping and cell cycle regulation of flagellin gene transcription in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1142–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin D., Minnich S., Chen L. S., Newton A. A set of positively regulated flagellar gene promoters in Caulobacter crescentus with sequence homology to the nif gene promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):939–943. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Initiation of transcription at the bacterial glnAp2 promoter by purified E. coli components is facilitated by enhancers. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Ueno-Nishio S., Hunt T. P., Robustell B., Magasanik B. Purification of nitrogen regulator II, the product of the glnL (ntrB) gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1002–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1002-1004.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Chen L. S., Swanson E., Newton A. Transcriptional regulation of a periodically controlled flagellar gene operon in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Swanson E., Ely B., Newton A. Physical mapping and complementation analysis of transposon Tn5 mutations in Caulobacter crescentus: organization of transcriptional units in the hook gene cluster. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):897–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.897-904.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Xiong Y., Gu Q., Shen S. C. Mutational analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter: sequences essential for positive control by nifA and ntrC (glnG) products. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):868–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.868-874.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Expression of glnA in Escherichia coli is regulated at tandem promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1979–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. M., Winkler M. E. Structure of the Caulobacter crescentus trpFBA operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):757–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.757-768.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. C., Xue Z. T., Kong Q. I., Wu Q. L. An open reading frame upstream from the nifH gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4241–4250. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro transcription of the nitrogen fixation regulatory operon nifLA of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2876-2880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]