Abstract
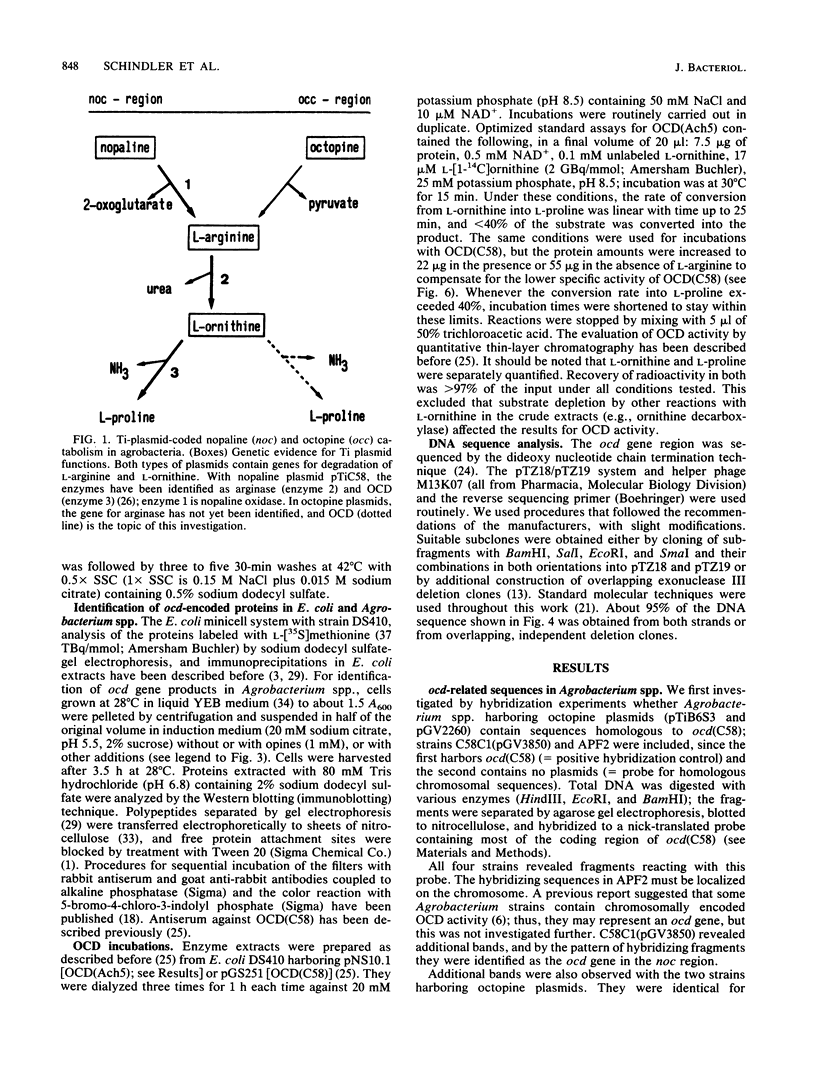
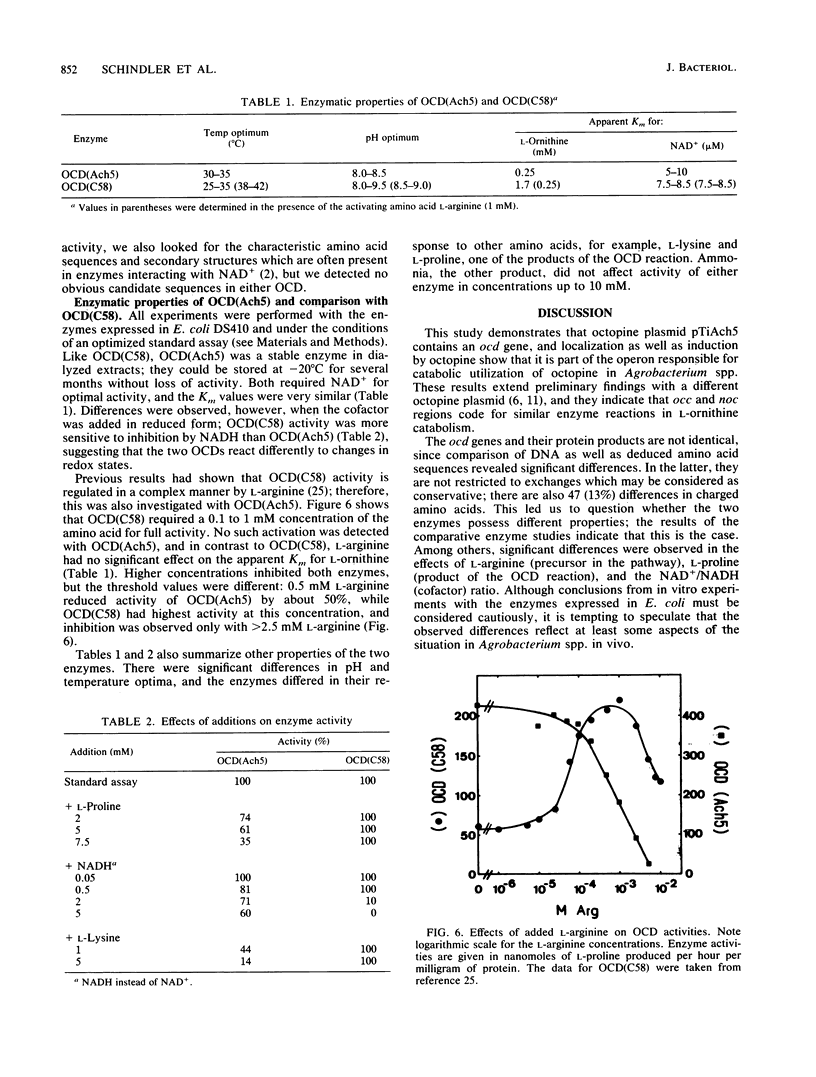
Octopine and nopaline are two arginine-derived opines synthesized in plant cells transformed with octopine or nopaline plasmids. Utilization in Agrobacterium tumefaciens is mediated by Ti plasmid regions called occ or noc (octopine or nopaline catabolism), and recent experiments showed that noc in pTiC58 codes for a pathway from nopaline to L-proline. The last enzyme is ornithine cyclodeaminase (OCD), an unusual protein converting L-ornithine directly into L-proline. We investigated whether octopine plasmid pTiAch5 also harbors a gene for OCD. The results revealed an ocd gene which is induced by octopine and maps in the occ region. DNA sequence analysis and comparison with the gene from pTiC58 showed that the two genes are related (69% homology in DNA and deduced amino acid sequence), and antiserum against OCD(C58) also reacted with OCD(Ach5). The enzyme activity was characterized, and a comparison with OCD(C58) showed that the properties are similar, but not identical. Differences were detected in the regulation of enzyme activity by L-arginine and L-proline and in the response to varying ratios of NAD+/NADH. It is proposed that this reflects different mechanisms for integration of opine catabolism into general metabolism.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann I., Marner F. J., Schröder G., Waffenschmidt S., Schröder J. Tumour genes in plants: T-DNA encoded cytokinin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):853–859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Greve H., Decraemer H., Seurinck J., Van Montagu M., Schell J. The functional organization of the octopine Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiB6s3. Plasmid. 1981 Sep;6(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos G., De Beuckeleer M., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the octopine tumor-inducing plasmid pTiAch5 of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1981 Sep;6(2):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deblaere R., Bytebier B., De Greve H., Deboeck F., Schell J., Van Montagu M., Leemans J. Efficient octopine Ti plasmid-derived vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer to plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4777–4788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessaux Y., Petit A., Tempé J., Demarez M., Legrain C., Wiame J. M. Arginine catabolism in Agrobacterium strains: role of the Ti plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.44-50.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., De Greve H., Decraemer H., Schell J., Van Montagu M. Rapid mapping of transposon insertion and deletion mutations in the large Ti-plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1837–1849. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. G., Kerr A., Tempé J., Petit A. Arginine catabolism: a new function of both octopine and nopaline Ti-plasmids of Agrobacterium. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jun 20;173(3):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00268636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler G., Depicker A., Maenhaut R., Villarroel R., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Physical mapping of DNA base sequence homologies between an octopine and a nopaline Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):183–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrand S. K., Dessaux Y. Proline biosynthesis encoded by the noc and occ loci of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):732–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.732-734.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutants affected in crown gall tumorigenesis and octopine catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):732–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.732-743.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsters M., Silva B., Van Vliet F., Genetello C., De Block M., Dhaese P., Depicker A., Inzé D., Engler G., Villarroel R. The functional organization of the nopaline A. tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. Plasmid. 1980 Mar;3(2):212–230. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. F., Simon R., Pühler A. The development of plasmid-free strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by using incompatibility with a Rhizobium meliloti plasmid to eliminate pAtC58. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Soldati L., Stalon V., Falmagne P., Terawaki Y., Leisinger T., Haas D. Anabolic ornithine carbamoyltransferase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional control of the argF structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2725–2734. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2725-2734.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Dimond R. L. Visualization of antigenic proteins on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muth W. L., Costilow R. N. Ornithine cyclase (deaminating). II. Properties of the homogeneous enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7457–7462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Inouye M. Construction of versatile expression cloning vehicles using the lipoprotein gene of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):771–775. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sans N., Schindler U., Schröder J. Ornithine cyclodeaminase from Ti plasmid C58: DNA sequence, enzyme properties and regulation of activity by arginine. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):123–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sans N., Schröder G., Schröder J. The Noc region of Ti plasmid C58 codes for arginase and ornithine cyclodeaminase. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardl C. L., Kado C. I. A functional map of the nopaline catabolism genes on the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00330882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardl C. L., Kado C. I. Ti plasmid and chromosomal ornithine catabolism genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):196–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.196-202.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., An G., Flores C., Nester E. W. A Tn3 lacZ transposon for the random generation of beta-galactosidase gene fusions: application to the analysis of gene expression in Agrobacterium. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):891–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalon V., Vander Wauven C., Momin P., Legrain C. Catabolism of arginine, citrulline and ornithine by Pseudomonas and related bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Sep;133(9):2487–2495. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-9-2487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P., Joos H., Genetello C., Leemans J., Montagu M. V., Schell J. Ti plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



