Abstract
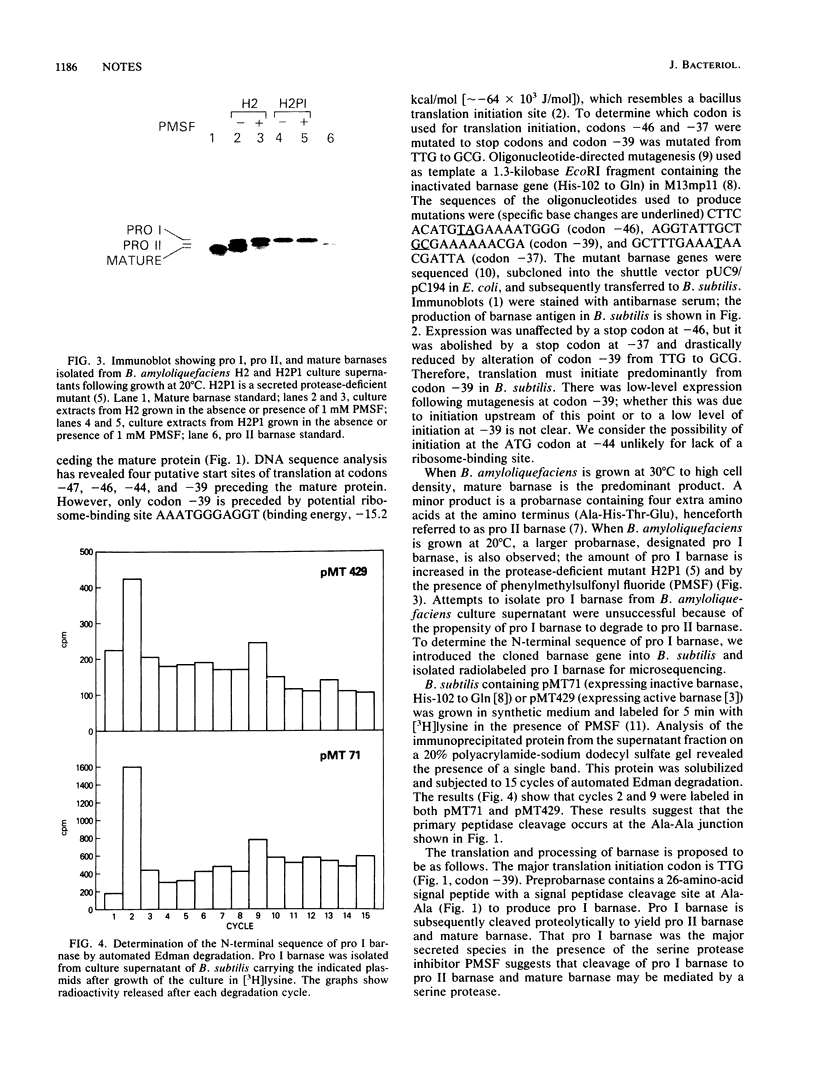
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracellular RNase has been previously cloned and expressed in Bacillus subtilis. Site-specific mutagenesis experiments have identified codon -39 as the start site of translation. We have determined the primary signal peptide cleavage site of preprobarnase and propose a pathway for the conversion of probarnase to mature barnase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley R. W., Barker E. A. Amino-acid sequence of extracellular ribonuclease (barnase) of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):15–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio235015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley R. W. Barnase and barstar. Expression of its cloned inhibitor permits expression of a cloned ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):913–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90568-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley R. W., Paddon C. J. Use of plasmid pTV1 in transposon mutagenesis and gene cloning in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Plasmid. 1986 Jul;16(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley R. W., Rogerson D. L., Jr, Smeaton J. R. Production and purification of the extracellular ribonuclease of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (barnase) and its intracellular inhibitor (barstar). II. Barstar. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(3):243–250. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddon C. J., Hartley R. W. Cloning, sequencing and transcription of an inactivated copy of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracellular ribonuclease (barnase). Gene. 1985;40(2-3):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddon C. J., Hartley R. W. Expression of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracellular ribonuclease (barnase) in Escherichia coli following an inactivating mutation. Gene. 1987;53(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pielak G. J., Mauk A. G., Smith M. Site-directed mutagenesis of cytochrome c shows that an invariant Phe is not essential for function. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):152–154. doi: 10.1038/313152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Thompson L. D. Fusion of pro region of subtilisin to staphylococcal protein A and its secretion by Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1986;49(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]