Abstract
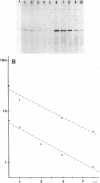
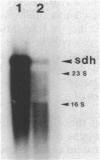
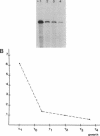
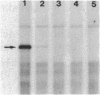
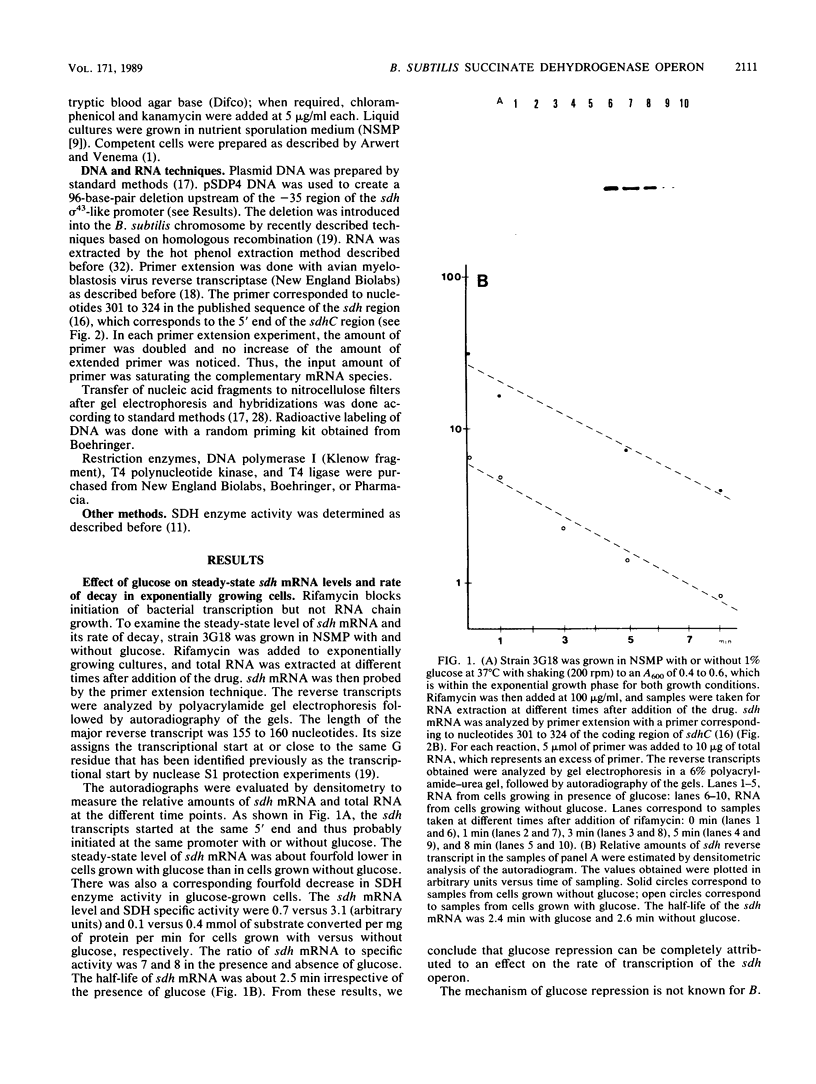
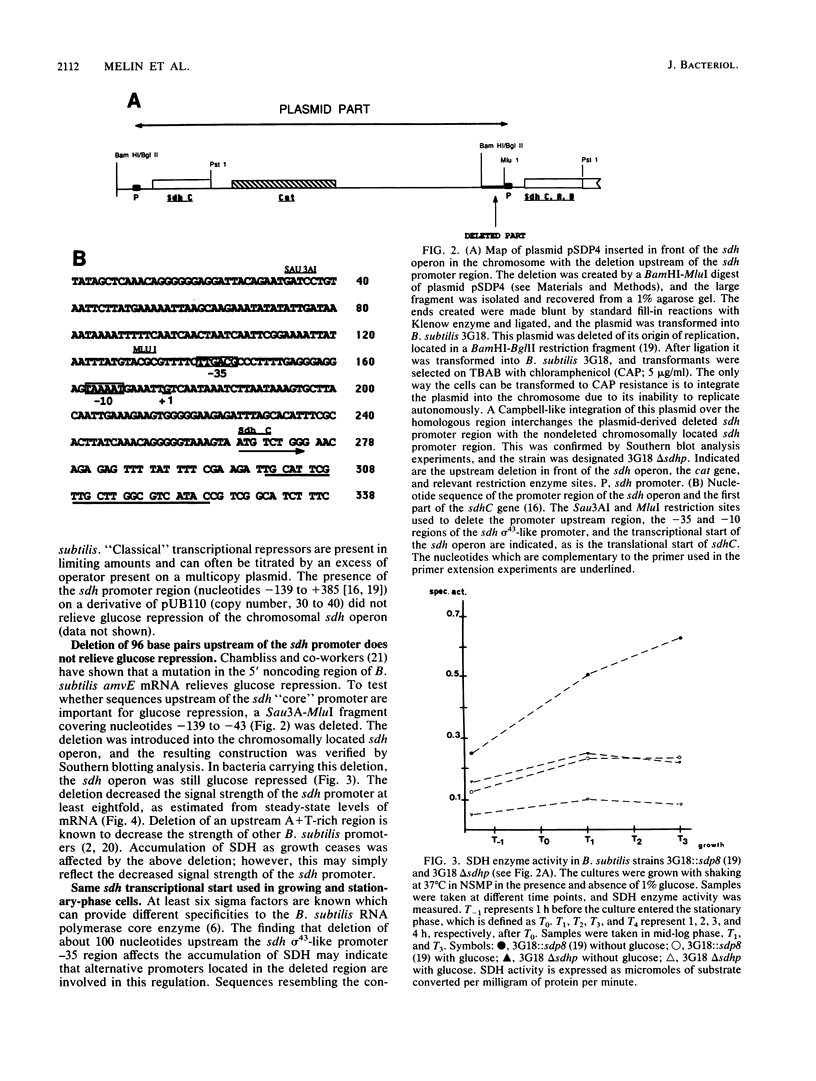
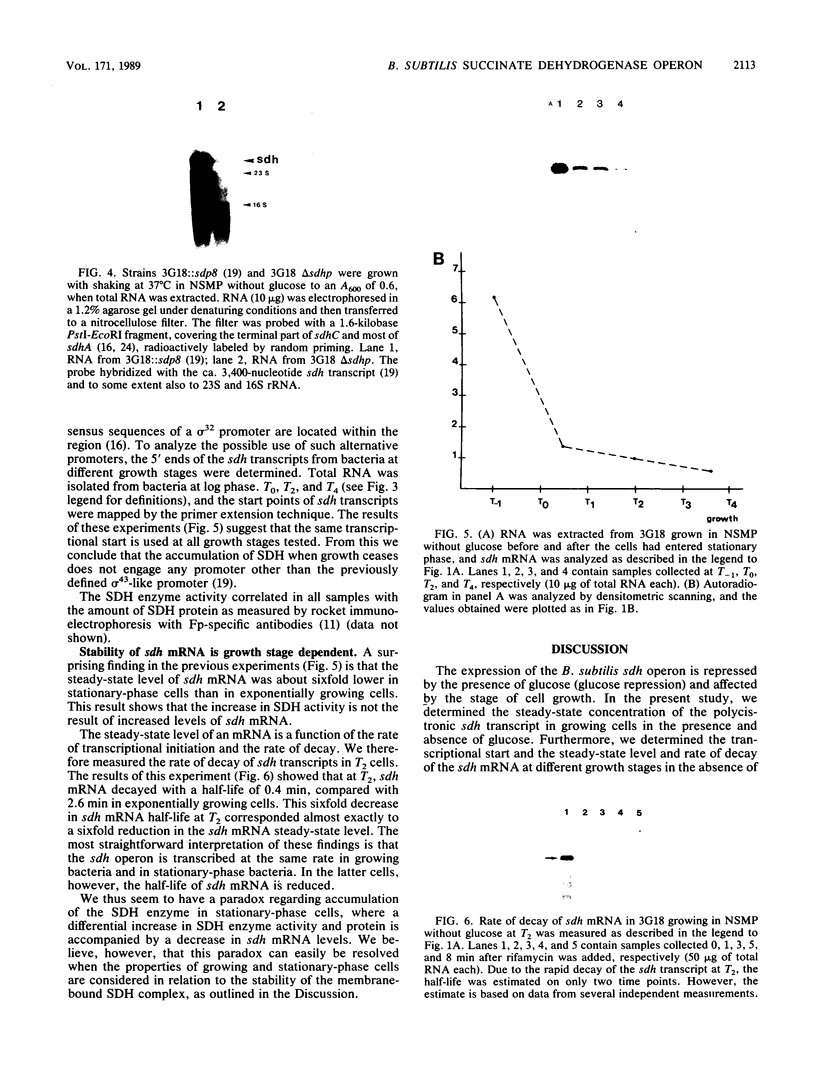
The amount of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) in Bacillus subtilis varies with growth conditions. In this work we studied the steady-state level and the rate of decay of B. subtilis sdh mRNA under different growth conditions. In exponentially growing cells, the steady-state level of sdh mRNA was severalfold lower when glucose was present compared with growth without glucose, whereas the rate of decay of sdh mRNA was the same with and without glucose. Thus, glucose repression seems to act by decreasing sdh mRNA synthesis. When the bacteria entered the stationary phase, the steady-state level of sdh mRNA dropped about sixfold. At the same time, sdh mRNA half-life decreased from 2.6 to 0.4 min. This result indicates that transcription of the sdh operon is initiated at the same rate in exponentially growing and in stationary-phase cells. The start point of the sdh transcripts, as measured by primer extension, was the same under all conditions studied, suggesting that the sdh operon is solely controlled by the previously identified sigma 43-like promoter. The increase of SDH activity in stationary phase may be explained by reduced dilution of the SDH proteins as a result of the retarded growth rate. We suggest that enhanced degradation of the sdh transcript is a means by which the bacteria adjust expression to the demands of stationary phase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arwert F., Venema G. Transformation in Bacillus subtilis. Fate of newly introduced transforming DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;123(2):185–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00267334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner C. D., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Deletion analysis of a complex promoter for a developmentally regulated gene from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Hederstedt L. Bacillus subtilis citM, the structural gene for dihydrolipoamide transsuccinylase: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;61(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman D. W., Rosenkrantz M. S., Sonenshein A. L. Relationship between aconitase gene expression and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3068–3075. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3068-3075.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Wang L. F. Multiple procaryotic ribonucleic acid polymerase sigma factors. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Sep;50(3):227–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.227-243.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feavers I. M., Price V., Moir A. The regulation of the fumarase (citG) gene of Bacillus subtilis 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Mar;211(3):465–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00425702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari E., Henner D. J., Perego M., Hoch J. A. Transcription of Bacillus subtilis subtilisin and expression of subtilisin in sporulation mutants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):289–295. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.289-295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortnagel P., Freese E. Analysis of sporulation mutants. II. Mutants blocked in the citric acid cycle. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1431–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1431-1438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Fujita T. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis gluconate operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1237–1252. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hederstedt L. Molecular properties, genetics, and biosynthesis of Bacillus subtilis succinate dehydrogenase complex. Methods Enzymol. 1986;126:399–414. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)26040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hederstedt L., Rutberg L. Succinate dehydrogenase--a comparative review. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):542–555. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.542-555.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. M., Uratani-Wong B., Freese E. Catabolite repression of enzyme synthesis does not prevent sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1447–1449. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1447-1449.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K., Philips M. K., Guest J. R., Rutberg L. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for cytochrome b558 of the Bacillus subtilis succinate dehydrogenase complex. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1067–1071. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1067-1071.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melefors O., von Gabain A. Site-specific endonucleolytic cleavages and the regulation of stability of E. coli ompA mRNA. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin L., Magnusson K., Rutberg L. Identification of the promoter of the Bacillus subtilis sdh operon. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3232–3236. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3232-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., Losick R. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus subtilis promoter recognized by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase containing sigma 37. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5979–5990. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Park Y. K., Henkin T. M., Won M., Weickert M. J., Gaskell J. A., Chambliss G. H. Catabolite repression-resistant mutations of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase promoter affect transcription levels and are in an operator-like sequence. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohné M. Regulation of the dicarboxylic acid part of the citric acid cycle in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):224–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.224-234.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. K., Hederstedt L., Hasnain S., Rutberg L., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence encoding the flavoprotein and iron-sulfur protein subunits of the Bacillus subtilis PY79 succinate dehydrogenase complex. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):864–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.864-873.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. W., Doi R. H. Genetic mapping of rpoD implicates the major sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase in sporulation initiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(1):88–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00397991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrantz M. S., Dingman D. W., Sonenshein A. L. Bacillus subtilis citB gene is regulated synergistically by glucose and glutamine. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):155–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.155-164.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferrari E. Replacement of the Bacillus subtilis subtilisin structural gene with an In vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.411-418.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Takahashi I. A catabolite-resistance mutation is localized in the rpo operon of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Apr;30(4):423–429. doi: 10.1139/m84-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi I. Catabolite repression-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1283–1287. doi: 10.1139/m79-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. F., Doi R. H. Promoter switching during development and the termination site of the sigma 43 operon of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):114–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00331498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]