Abstract
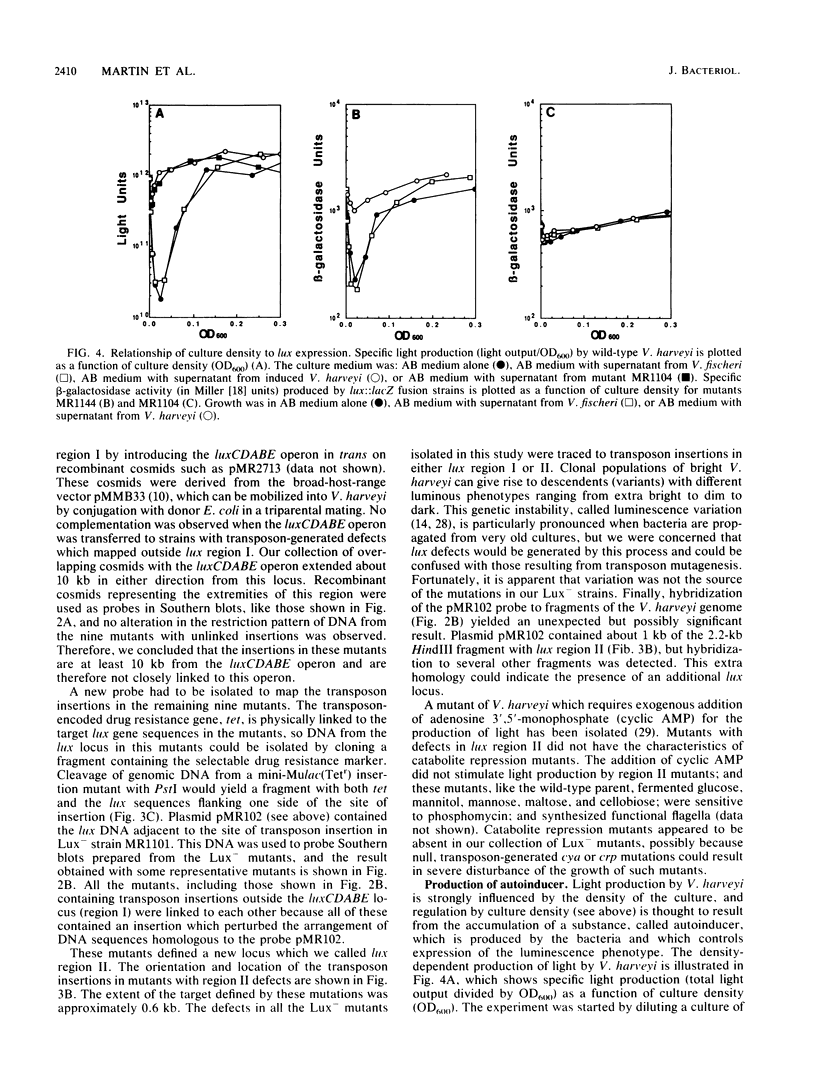
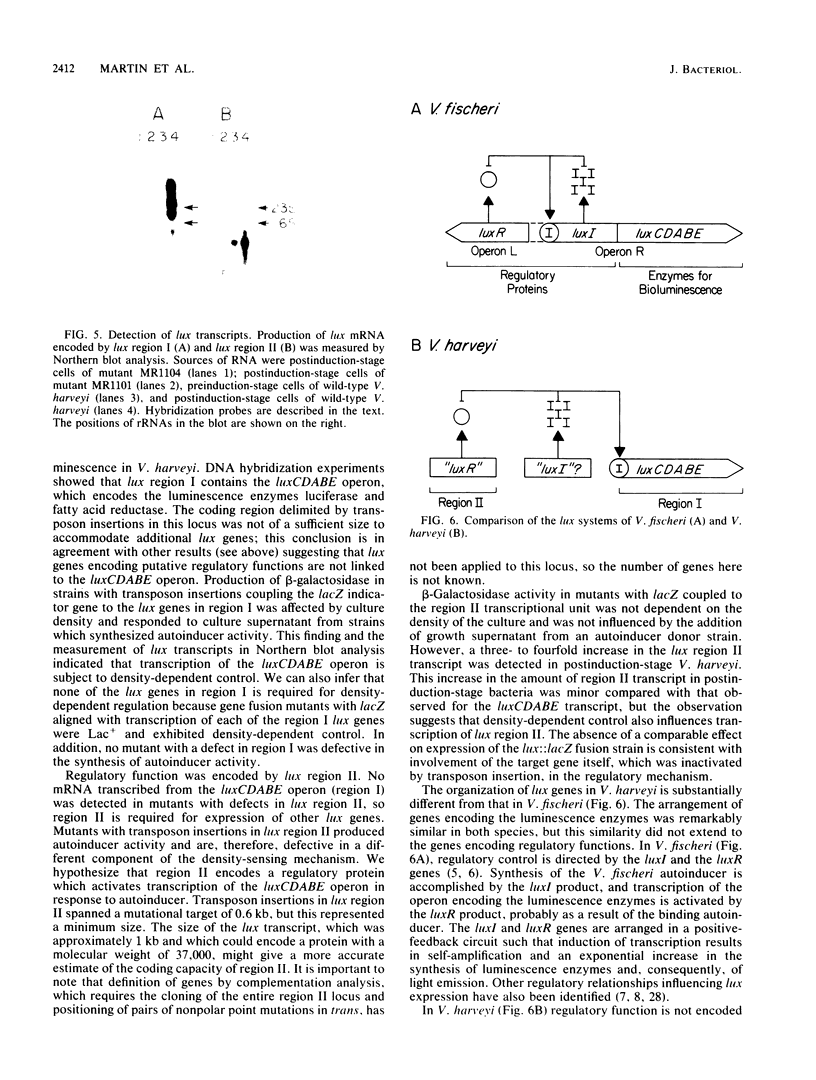
Mutagenesis with transposon mini-Mulac was used to identify loci containing genes for bioluminescence (lux) in the marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi. Transposon insertions which resulted in a Lux- phenotype were mapped to two unlinked regions of the genome. Region I contained the luxCDABE operon which was previously shown to encode the enzymes luciferase and fatty acid reductase, which are required for light production. The other locus, region II, which was identified for the first time in this study, appeared to have a regulatory function. In Northern blot analysis of mRNA from mutants with defects in this region, no transcription from the luxCDABE operon could be detected. Strains with transposon-generated lux::lacZ gene fusions were used to analyze control of the transcription of these regions. Expression of luminescence in the wild type was strongly influenced by the density of the culture, and in strains with the lacZ indicator gene coupled to the luxCDABE operon, beta-galactosidase synthesis was density dependent. So, transcription of this operon is responsive to a density-sensing mechanism. However, beta-galactosidase synthesis in strains with lacZ fused to the region II transcriptional unit did not respond to cell density. The organization and regulation of the lux genes of V. harveyi are discussed, particularly with regard to the contrasts observed with the lux system of the fish light-organ symbiont Vibrio fischeri.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Mileham A., Cohn D., Hilman M., Simon M., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and expression of the luciferase genes from Vibrio harveyi. Science. 1982 Nov 19;218(4574):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.10636771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Mileham A., Simon M., Silverman M. Transposon mutagenesis of marine Vibrio spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):890–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.890-896.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A., Burlingame A. L., Eberhard C., Kenyon G. L., Nealson K. H., Oppenheimer N. J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2444–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Nealson K., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory locus controlling expression of bacterial genes for bioluminescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10455–10467. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Bagdasarian M., Feiss D., Franklin F. C., Deshusses J. Stable cosmid vectors that enable the introduction of cloned fragments into a wide range of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempner E. S., Hanson F. E. Aspects of light production by Photobacterium fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):975–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.975-979.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C. M., Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Organization of the lux structural genes of Vibrio harveyi. Expression under the T7 bacteriophage promoter, mRNA analysis, and nucleotide sequence of the luxD gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13393–13399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C. M., Graham A. D., Boylan M., Evans J. F., Hasel K. W., Meighen E. A., Graham A. F. Polycistronic mRNAs code for polypeptides of the Vibrio harveyi luminescence system. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):995–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.995-1001.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C. M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Nucleotide sequence of the LuxC gene and the upstream DNA from the bioluminescent system of Vibrio harveyi. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1551–1562. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C., Byers D., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Expression of bioluminescence by Escherichia coli containing recombinant Vibrio harveyi DNA. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):247–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.247-253.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H. Autoinduction of bacterial luciferase. Occurrence, mechanism and significance. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00446657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden R. C., Adams D. A. Electrophoresis in agarose and acrylamide gels. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:61–87. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S., Yashphe J. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-requiring mutant of the luminous bacteria Beneckea harveyi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 9;404(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90339-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]